Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2017; 23(27): 4879-4891
Published online Jul 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4879
Published online Jul 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4879
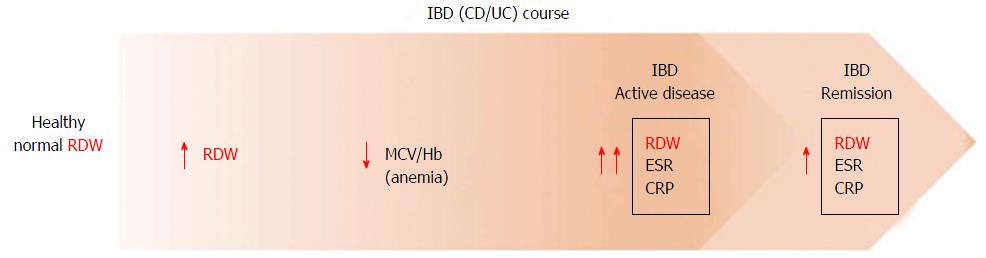
Figure 1 Changes in red blood cell distribution width levels during clinical course of inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease/ulcerative colitis).
RDW: Red blood cell distribution width; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; Hb: Hemoglobin; MCV: Mean corpuscular volume; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
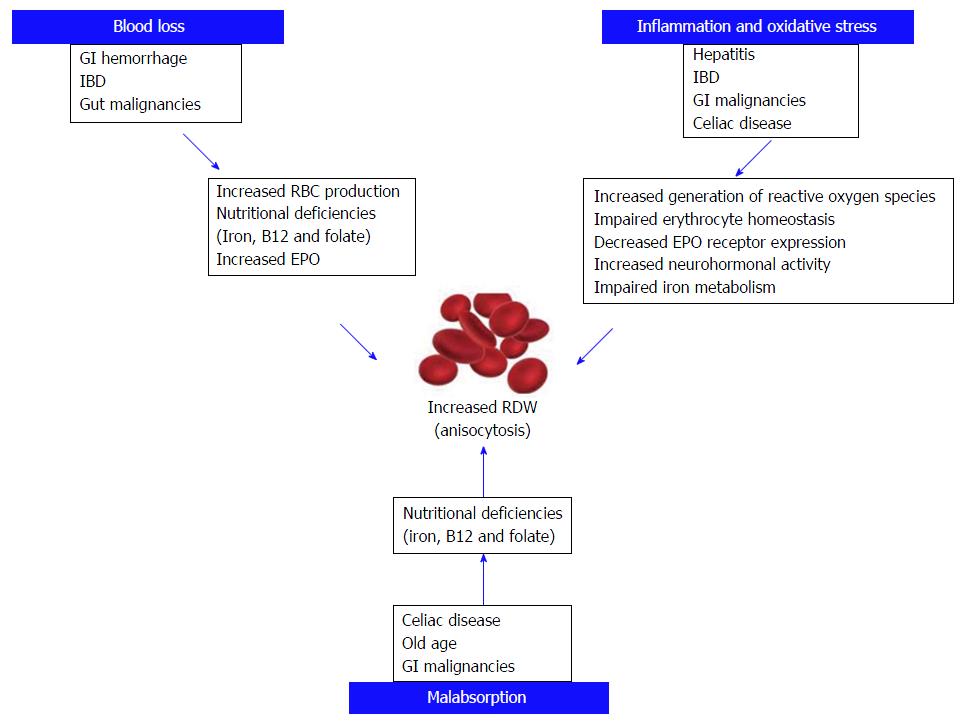
Figure 2 Possible mechanisms of increased red blood cell distribution width in gastrointestinal disorders.
GI: Gastrointestinal; RBC: Red blood cell; EPO: Erythropoietin; RDW: Red blood cell distribution width; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Citation: Goyal H, Lippi G, Gjymishka A, John B, Chhabra R, May E. Prognostic significance of red blood cell distribution width in gastrointestinal disorders. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(27): 4879-4891
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i27/4879.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4879