Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2017; 23(27): 4856-4866
Published online Jul 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4856
Published online Jul 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4856
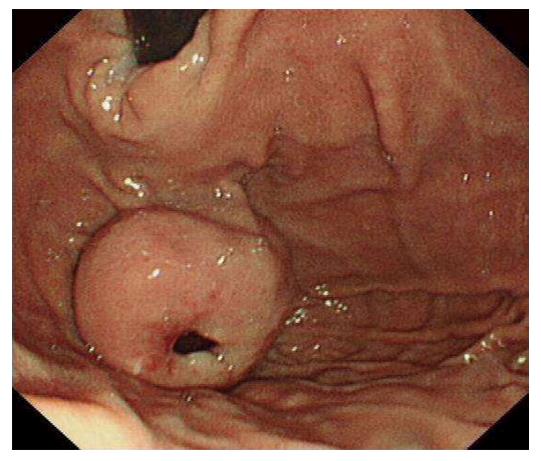
Figure 1 Gastroscopy view of a gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
A 4 cm × 4 cm in diameter gastric fundal submucosal tumor with a central ulceration associated with a recent bleed is shown.
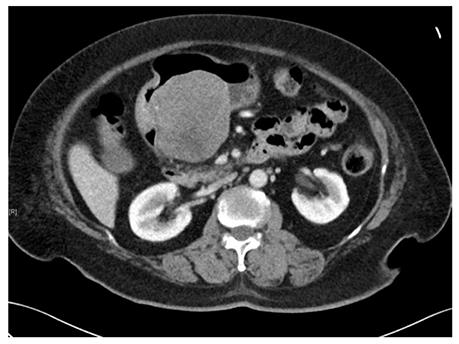
Figure 2 Computed tomography scan image of a gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
A submucosal tumor measuring 7.7 cm × 7.6 cm × 7.2 cm in dimension was located on the posterior wall of gastric antrum. An ill-defined hypodensity within the mass could represent an area of necrosis.
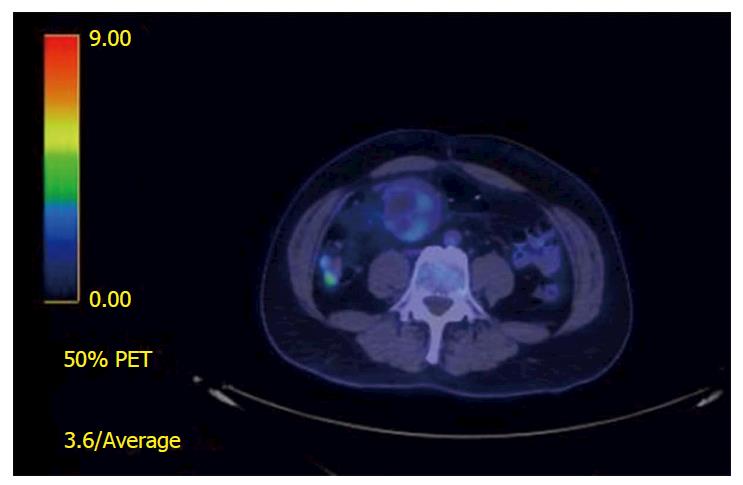
Figure 3 18Fluoro-deoxyglucose-positron emission tomography scan views of a small bowel gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
There is a mildly fluoro-deoxyglucose avid mass adjacent to the jejunal anastomosis with SUVmax 3.4 suggestive of a local recurrence.
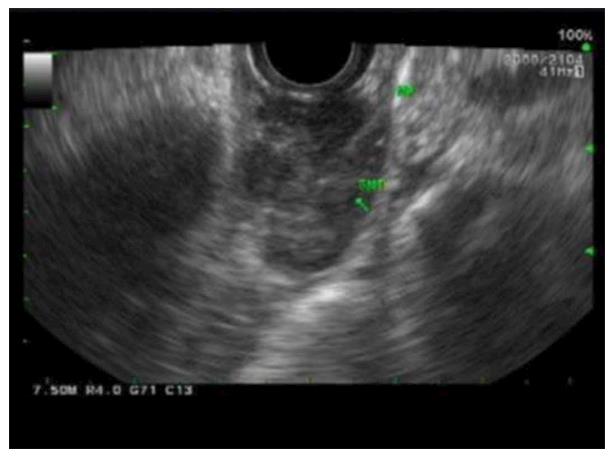
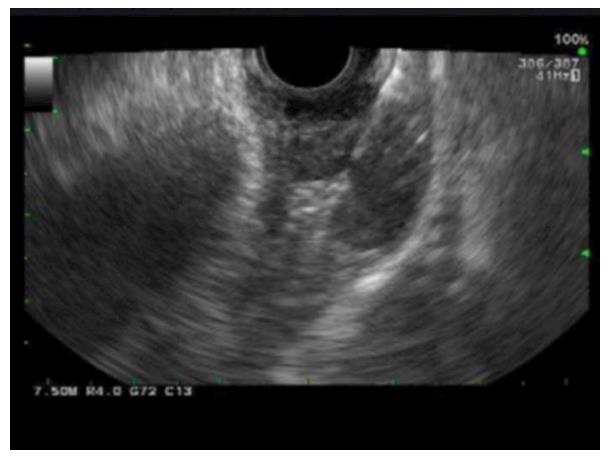
Figure 4 Endoscopic ultrasonography images of esophageal gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
A distal esophageal submucosal lesion measuring 2.6 cm × 1.3 cm in diameter was noted to be well circumscribed, heterogeneous with hypoechoic echotexture without disruption of wall architecture and with no perilesional lymph node.
Figure 5 Endoscopic ultrasound scan and fine needle aspiration image of an esophageal gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
The procedure was performed using a 22F procore needle with on-site cytotech.
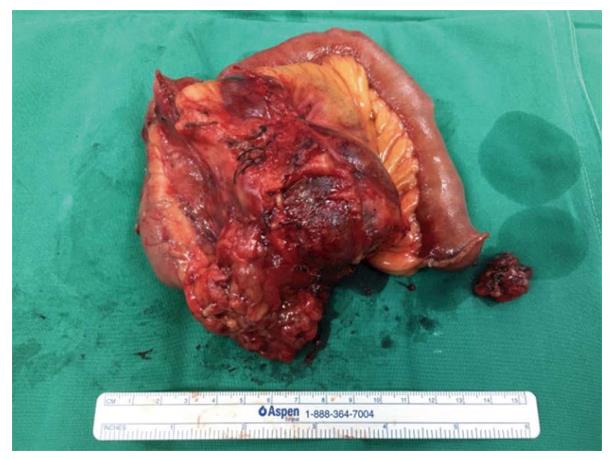
Figure 6 Macroscopic image of a recurrent small bowel gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
A picture of a large enbloc resection specimen of a small bowel mesentery and jejunum was taken along a separate smaller metastatic mesenteric nodule.
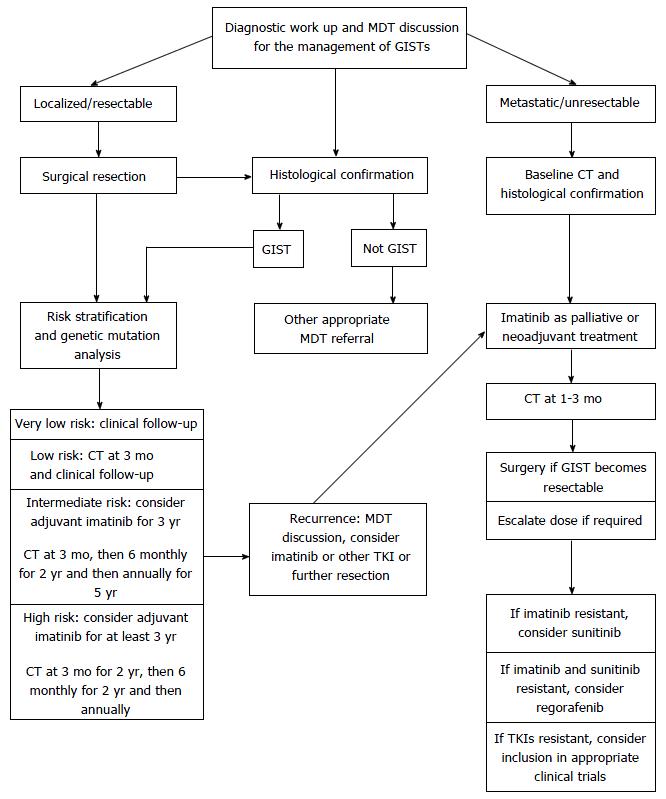
Figure 7 Algorithm for the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
GIST: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor; CT: Computed tomography; TKI: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
- Citation: Lim KT, Tan KY. Current research and treatment for gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(27): 4856-4866
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i27/4856.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i27.4856