Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2017; 23(26): 4831-4838
Published online Jul 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i26.4831
Published online Jul 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i26.4831
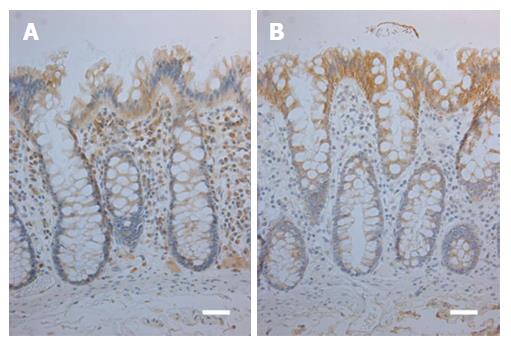
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical stainings for toll-like receptor 2 (A) and toll-like receptor 4 (B) in normal colorectal mucosa.
Weak TLR2 expression is present in the deeper parts of the crypt epithelium and moderate expression in uppermost part of the crypts and the surface (A). TLR4 expression shows a similar gradient, however, with a moderate expression in the lower parts of the crypts and strong in the surface (B). Reference lines, 50 μm. TLR: Toll-like receptor.
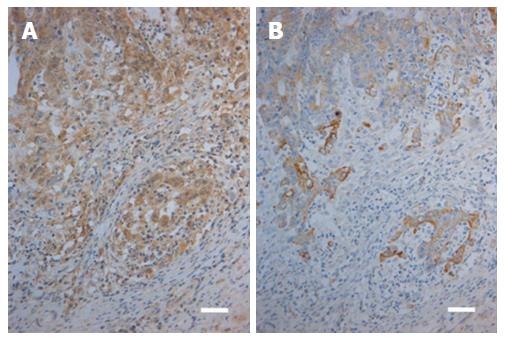
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical stainings for toll-like receptor 2 (A) and toll-like receptor 4 (B) in a case of colorectal carcinoma.
Moderate to strong TLR2 expression in the carcinoma cells is present in both the invasive front (lower part of the Figure) and in the tumor bulk (upper part of the Figure; A). In contrast, corresponding view showing TLR4 staining indicates that expression is moderate to weak in the front (lower part) and weak to negative in the bulk (upper part; B). Reference lines, 50 μm. TLR: Toll-like receptor.
- Citation: Paarnio K, Väyrynen S, Klintrup K, Ohtonen P, Mäkinen MJ, Mäkelä J, Karttunen TJ. Divergent expression of bacterial wall sensing Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(26): 4831-4838
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i26/4831.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i26.4831