Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2017; 23(2): 242-255
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.242
Published online Jan 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.242
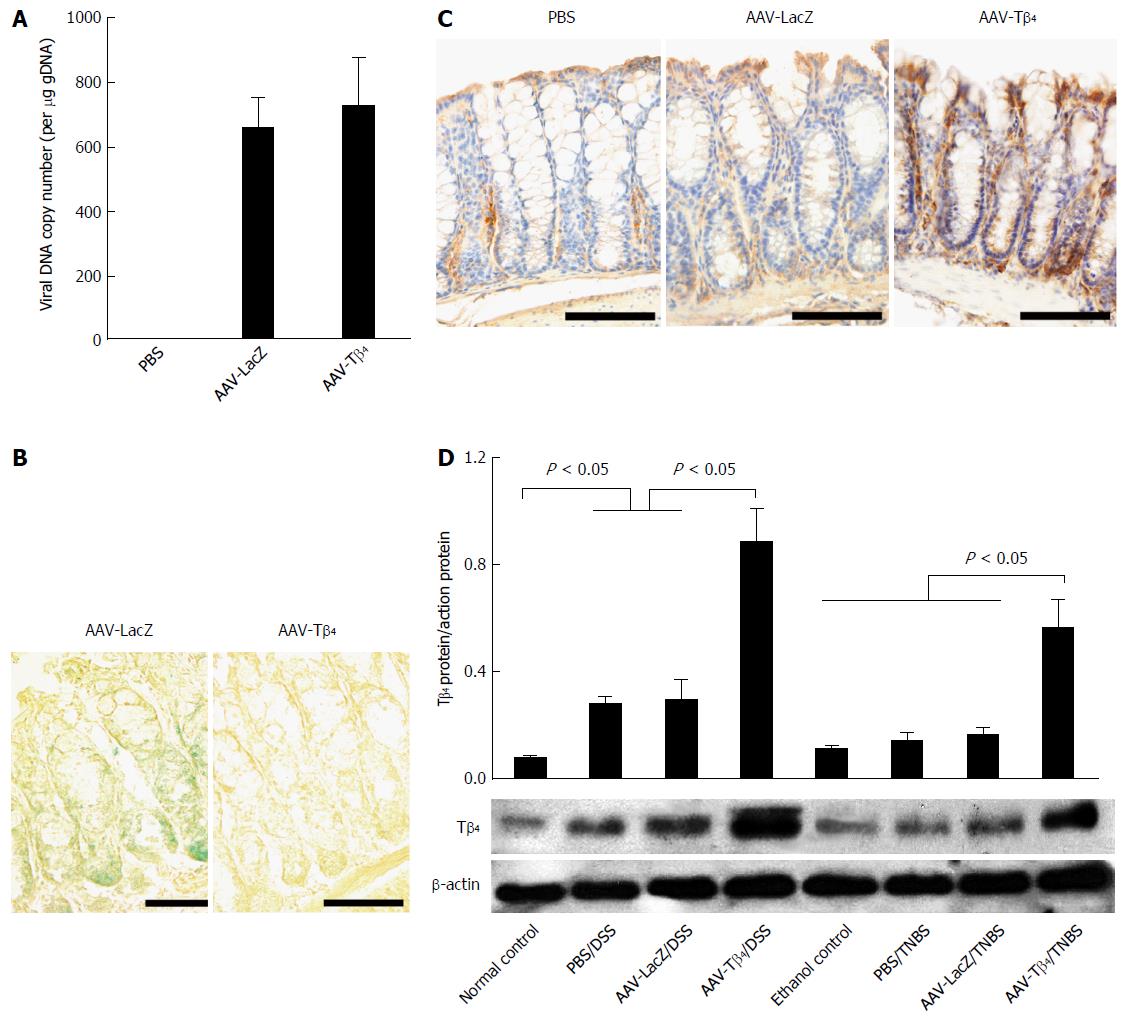
Figure 1 Intracolonic administration of adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 mediated secretory expression of thymosin β4 in mouse colons.
Two weeks after intracolonic (ic) adeno-associated virus (AAV)-LacZ, AAV-thymosin β4 (Tβ4) or PBS, the mice were euthanized to harvest their colons. A: Real-time PCR showed the presence of viral DNA in the colonic tissues of the AAV-treated mice; B: X-gal staining verified AAV-mediated expression of LacZ in the colonic tissues. C: Immunohistochemistry revealed that ic AAV-Tβ4 resulted in markedly increased expression of Tβ4 in the mouse colon; D: In the mice with experimental colitis, Western blot showed that dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) treatment remarkably upregulated the colonic Tβ4 expression while TNBS enemas only slightly increased colonic Tβ4. Intracolonic AAV-Tβ4 led to substantially increased expression of Tβ4 in the colonic tissues in both DSS- and TNBS-treated mice. Error bars indicate SD. Scale bars = 50 μm.
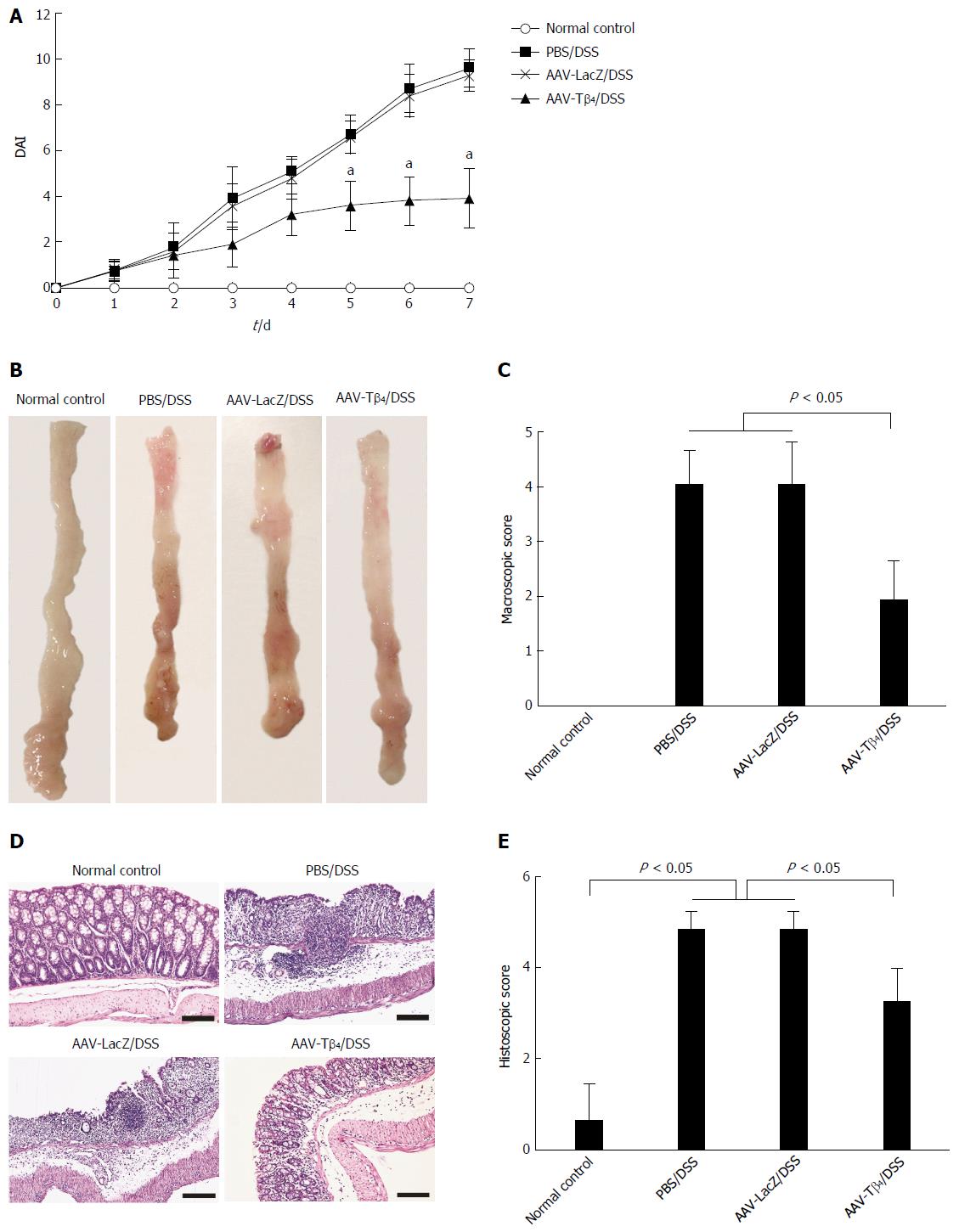
Figure 2 Adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 ameliorated dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice.
A: Dynamic changes in DAI [the asterisk indicates aP < 0.05 vs PBS/dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) or adeno-associated virus (AAV)-LacZ/DSS group]; B and C: AAV-thymosin β4 (Tβ4) improved DSS-induced colonic lesions including mucosal edema, hyperemia, and ulceration, resulting in a significantly decreased macroscopic score; D and E: Histological examination (HE staining, magnification × 200) revealed the mice in AAV-Tβ4/DSS group exhibited alleviated colonic lesions such as destruction of mucosal crypts, loss of epithelial cells, deep ulcerations, and inflammatory cell infiltration, leading to a significantly decreased histological score compared with the mice in the other two DSS groups. Error bars indicate the SD. Scale bars = 50 μm. DAI: Disease activity index.
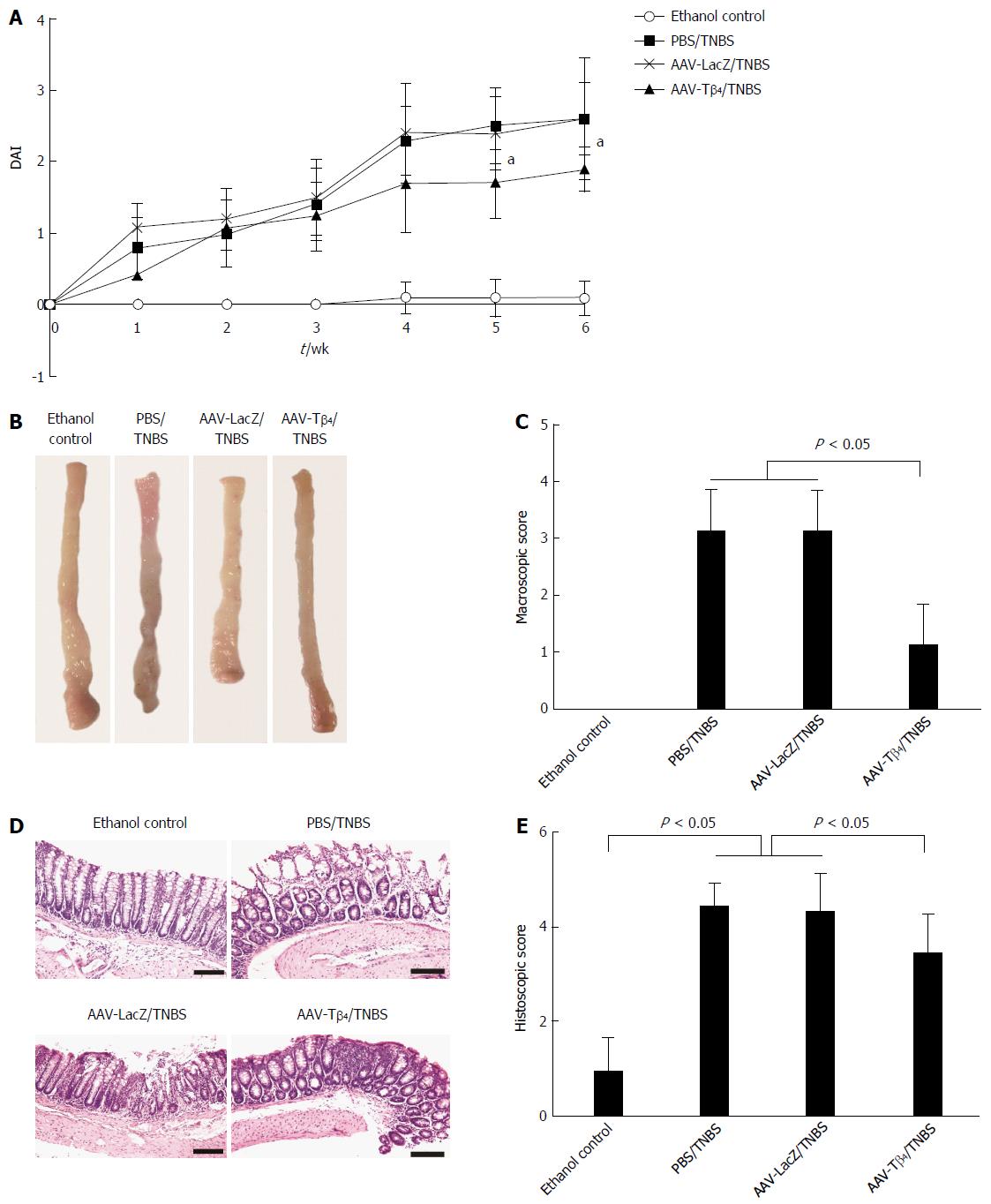
Figure 3 Adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 improved 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice.
A: Dynamic changes in DAI [the asterisk indicates aP < 0.05 vs PBS/2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) or adeno-associated virus (AAV)-LacZ/TNBS group]; B: TNBS treatment resulted in hyperemia, edema and ulceration, which were attenuated by Tβ4; C: Macroscopic score of AAV-Tβ4/TNBS group was significantly lower than those of the other two TNBS groups; D and E: Histological observation of colonic tissue (HE staining, magnification × 200) showed that AAV-Tβ4 relieved TNBS-induced colonic mucosal lesions and reduced the histological score. Error bars indicate the SD. Scale bars = 50 μm. DAI: Disease activity index.
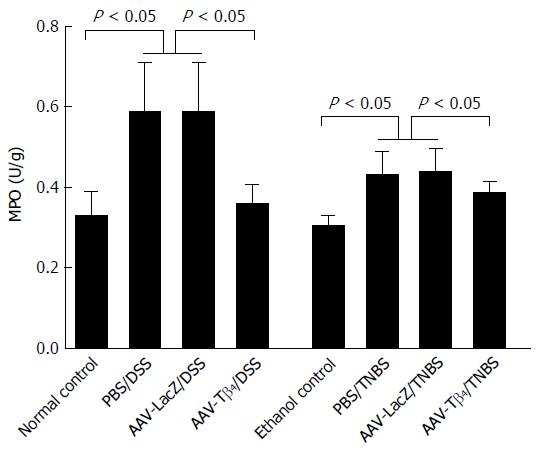
Figure 4 Adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 suppressed dextran sulfate sodium - and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced inflammation in colonic tissue, as indicated by myeloperoxidase activity assessment.
Error bars indicate the SD. AAV: Adeno-associated virus; Tβ4: Thymosin β4; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; TNBS: 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.
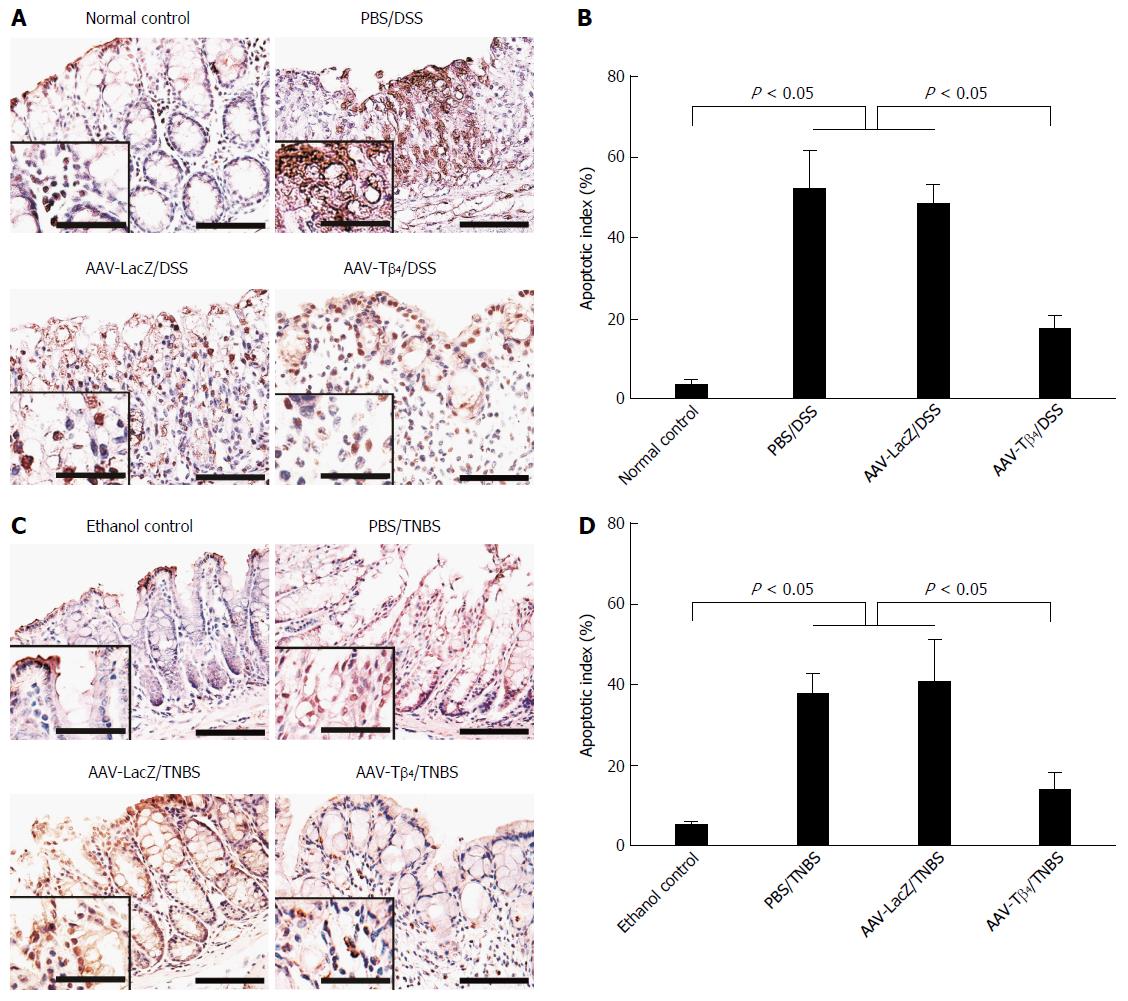
Figure 5 Adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 alleviated dextran sulfate sodium- and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced epithelial cell apoptosis in the colonic mucosa.
TUNEL staining showed that intracolonic adeno-associated virus (AAV)-thymosin β4 (Tβ4) prevented the colonic mucosal epithelia from undergoing apoptosis and thus led to decreased apoptotic indexes (AIs) in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)- (A and B) and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced (C and D) colitis in mice. The insets indicate the TUNEL-positive nuclear staining. Error bars indicate the SD. Scale bar: 50 μm and 25 μm (insets).
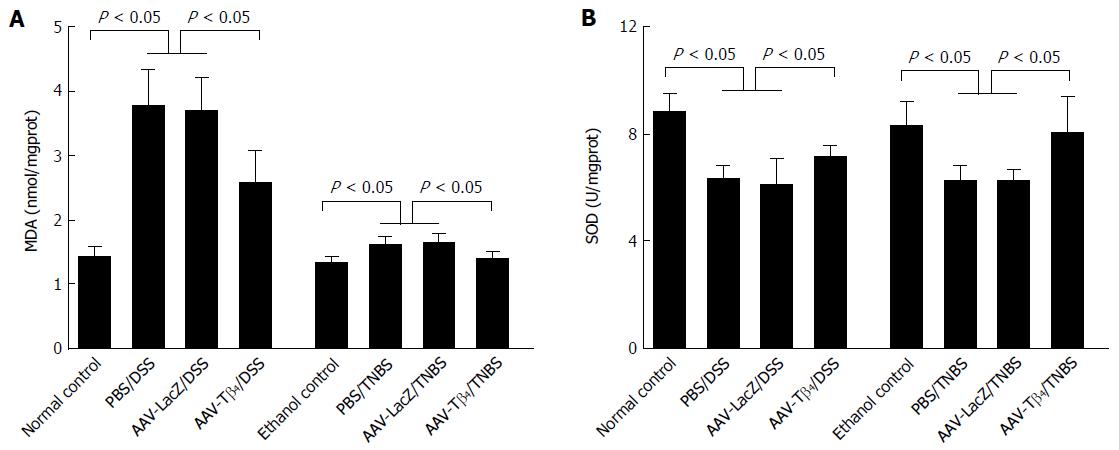
Figure 6 Adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 relieved colonic oxidant damage in the mice with colitis.
MDA content (A) and SOD activity (B) were determined using biochemical assays. Error bars indicate the SD. AAV: Adeno-associated virus; Tβ4: Thymosin β4.
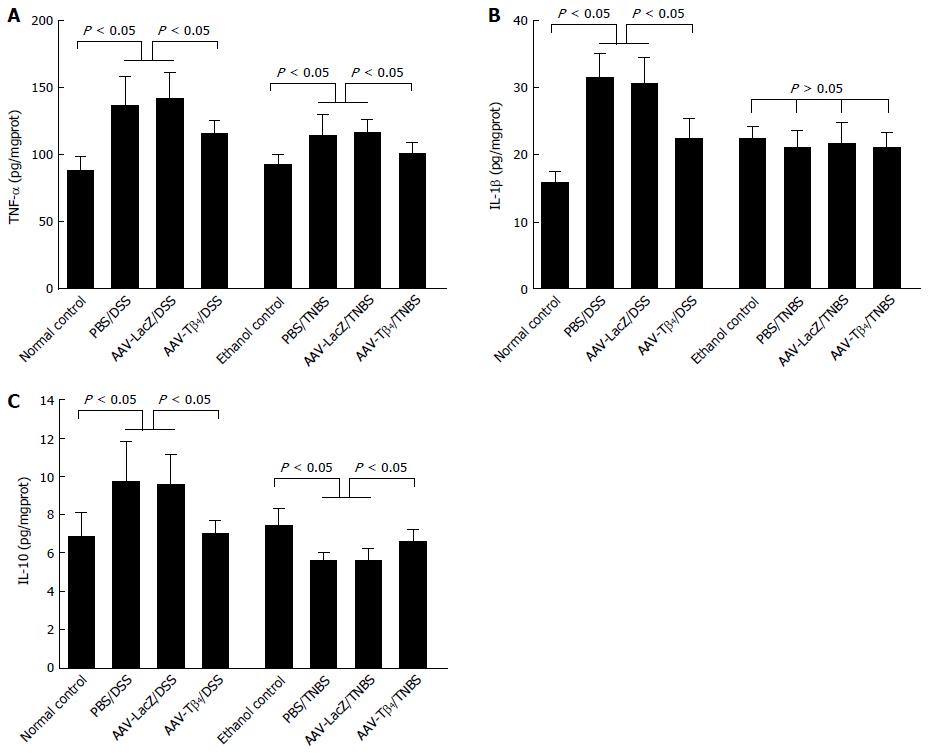
Figure 7 Adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 modulated colonic TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-10 levels in dextran sulfate sodium and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid models.
Colonic TNF-α (A), IL-1β (B) and IL-10 (C) levels were determined by ELISA. Error bars indicate the SD. AAV: Adeno-associated virus; Tβ4: Thymosin β4; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; TNBS: 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.
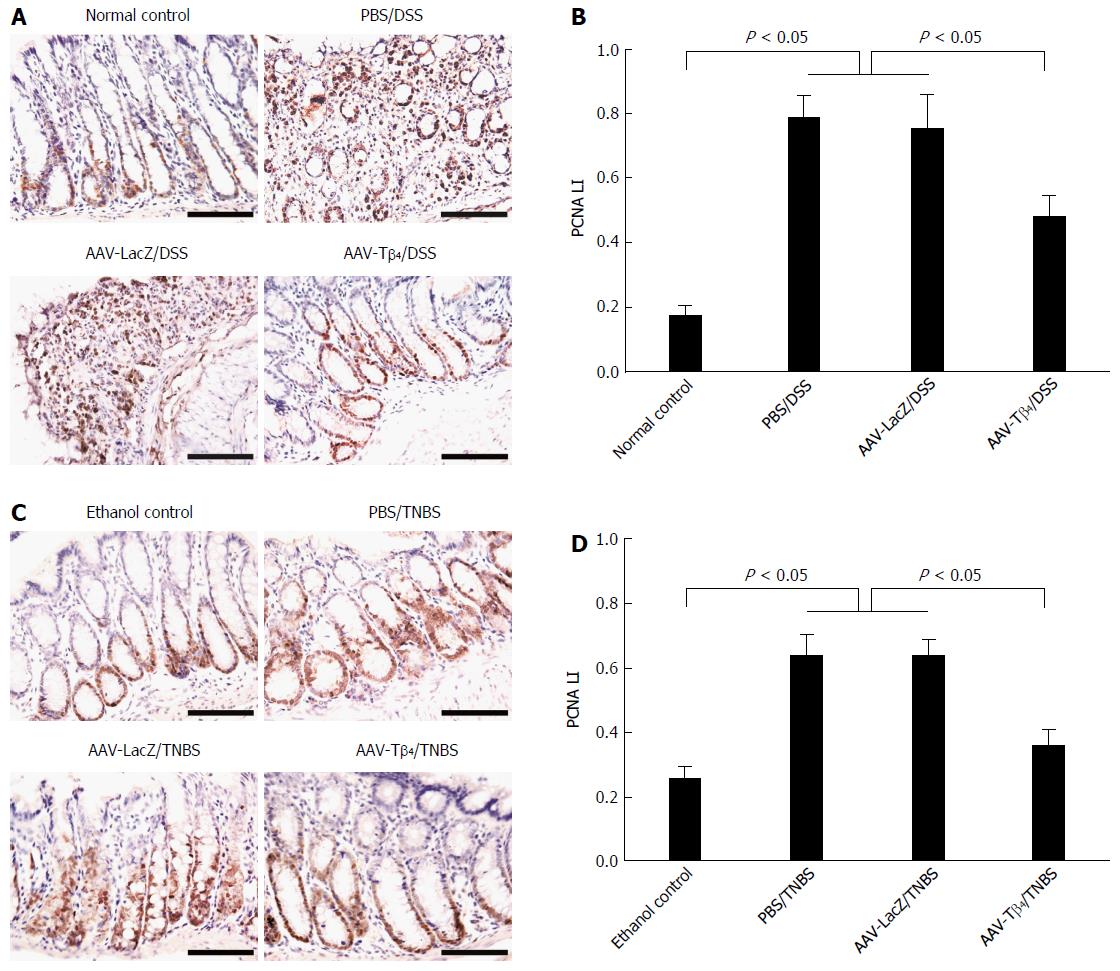
Figure 8 Adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 attenuated the acceleration of colonic mucosal cell proliferation following dextran sulfate sodium and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid treatments.
Colonic cell proliferation was determined by PCNA immunostaining in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) (A) and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) models (C). PCNA label indexes (PCNA LIs) of the DSS model (B) and TNBS model (D) were calculated. Error bars indicate the SD. Scale bars = 50 μm. AAV: Adeno-associated virus; Tβ4: Thymosin β4.
- Citation: Zheng XY, Lv YF, Li S, Li Q, Zhang QN, Zhang XT, Hao ZM. Recombinant adeno-associated virus carrying thymosin β4 suppresses experimental colitis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(2): 242-255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i2/242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i2.242