Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2016; 22(5): 1811-1825
Published online Feb 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i5.1811
Published online Feb 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i5.1811
Figure 1 The RS-ALC system: A conventional endoscope is mounted onto electromechanical control wheels.
Control of the system is through a joystick device. Courtesy of Dr Pullens, Meander MC, Netherlands.
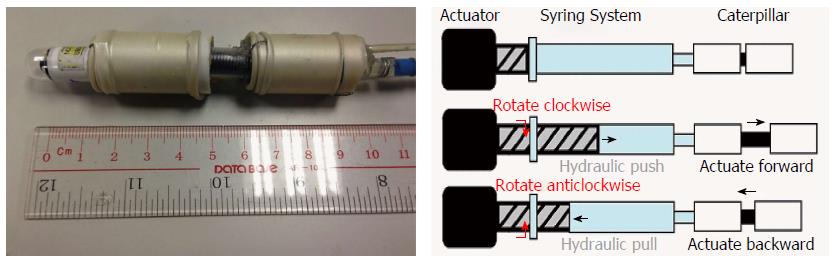
Figure 2 EOR version 3.
The system consists of various actuators to execute forward/backward, rotational, up/down, left/right movement of a conventional endoscope. Courtesy of Professor Kume, Kyushu University, Japan.
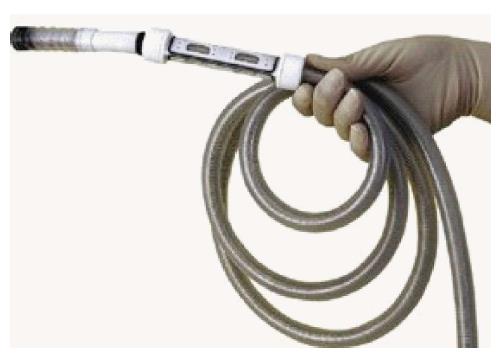
Figure 3 Invendoscope.
The scope design is akin to a conventional endoscope. The scope is protected by a disposable inverted sheath which unfurls when the endoscope is pushed forward by the actuating wheels (Invendo Medical Ltd).
Figure 4 Neoguide with its multiple bending segments enabling it to manoeuvre in a tail follow nose manner.
Eickhoff et al[47], 2007.
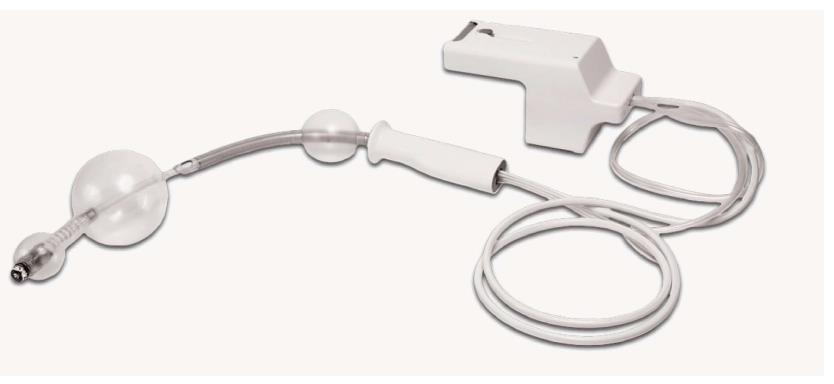
Figure 5 The Aeroscope relies on a balloon at the tip of the endoscope to form a seal with surrounding colonic wall.
A computerized pump system generates a pressure gradient proximal and distal to the balloon. This pressure gradient propels the device. Courtesy of GIview Ltd.
Figure 6 Endotics double balloon probe.
Locomotion is executed using the inch-worm mechanism. Courtesy of Endotics SRL, Italy.
Figure 7 CUHK double balloon endoscope with its proximal and distal balloon connected by an extension section.
A capsule endoscope is mounted at the tip of this endoscope prototype. Poon et al[53], 2015.
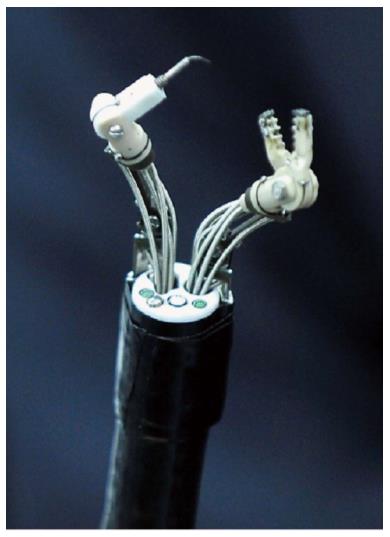
Figure 8 The MASTER system is a robotic arm system that can be mounted onto a conventional endoscope.
Phee et al[68], 2012.
Figure 9 ISIS-Scope/STRAS system is a electromechanically controlled ANUBISCOPE.
De Donno et al[72], 2013.
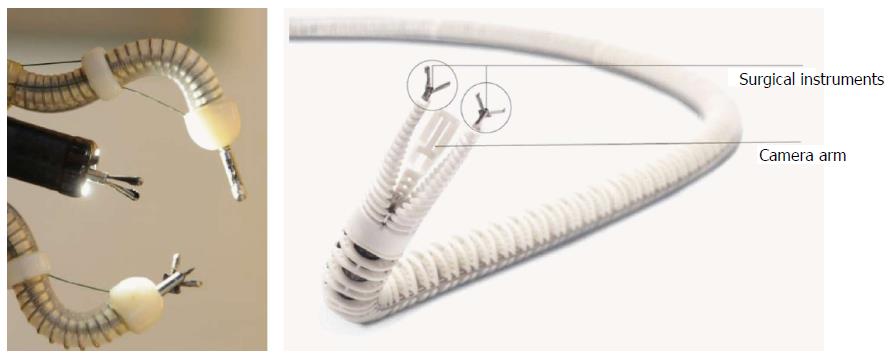
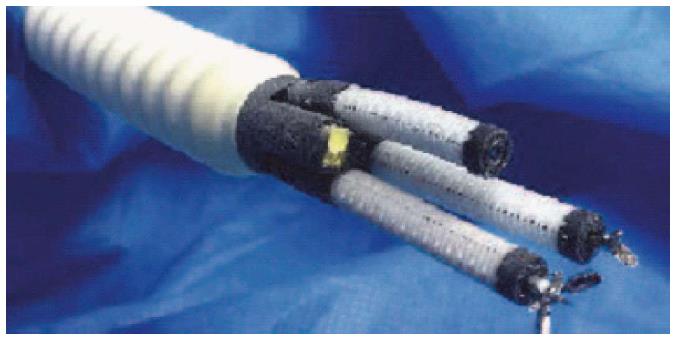
Figure 10 The Endomima system can be mounted onto a conventional endoscope.
The arms allow passage of conventional flexible instruments. Each arm has up to 3 DOF of movement (Endotools Therapeutics). Roppenecker et al[129].
Figure 11 Scorpion like endoscopic robot is an externally mountable robot arms system.
It is actuated by external actuators through traction cables (right). Suzuki et al[74], 2010.
Figure 12 On the left, the endoscope and the viacath robotic arms are integrated using an overtube.
Abbott et al[75], 2007.
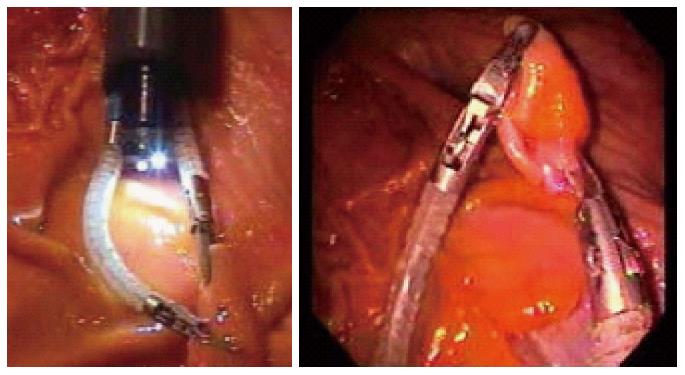
Figure 13 CUHK robotic arm prototype.
Poon et al[77], 2014.
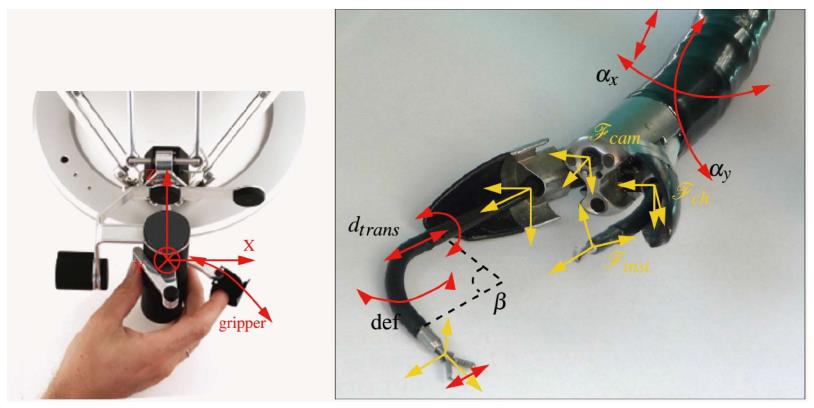
Figure 14 Imperial College robotic arm prototype.
Seneci et al[80], 2014.
- Citation: Yeung BPM, Chiu PWY. Application of robotics in gastrointestinal endoscopy: A review. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(5): 1811-1825
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i5/1811.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i5.1811