Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2016; 22(45): 9921-9932
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9921
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9921
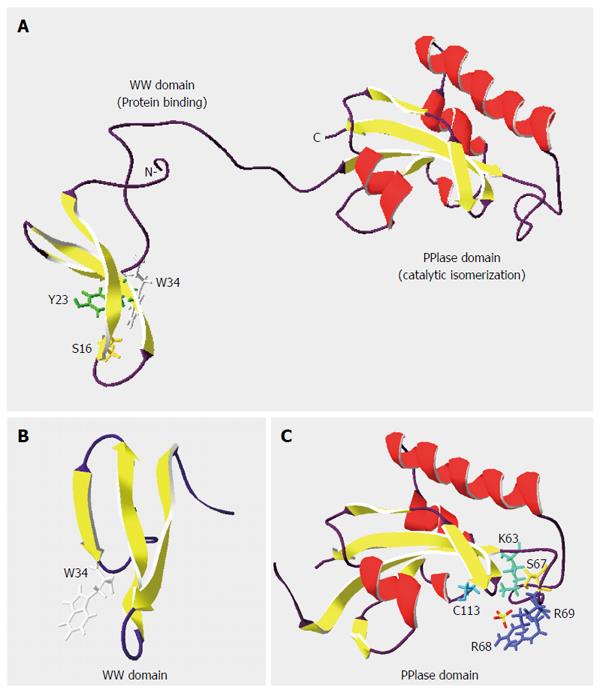
Figure 1 Structure of peptidyl-prolyl-isomerase PIN1 protein.
Ribbon diagrams of (A) PIN1 (NCBI Structure No. 1NMV), (B) WW binding domain (NCBI Structure No. 1I8H), and (C) PPIase catalytic domain (NCBI Structure No. 1NMW) were drawn with the Swiss-Pdb Viewer[11,15,115,116]. α-helices and β-strands are denoted by coils and arrows, respectively. Residues Ser(S)16, Tyr(Y)23 and Trp(W)34 in the WW domain are critical for phospho-protein binding, while residues Lys(K)63, Ser(S)67, Arg(R)68/69 and Cys(C)113 contribute to the PPIase activity. Adapted from thesis: Identification and characterization of PIN1 binding partners, HKU 2010.
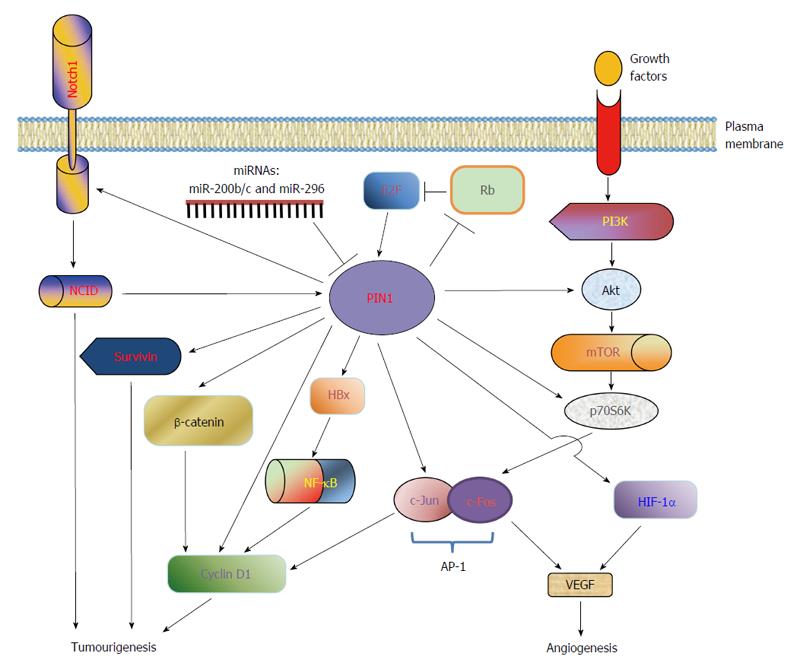
Figure 2 PIN1 dysregulation and targets in hepatocellular carcinoma.
PIN1 functions as an amplifier to augment the oncogenic activities of key phosphoproteins involved in HCC tumourigenesis. PIN1 gene expression is up-regulated by various transcription factors, including E2F family and activated NOTCH1 intracellular domain (NCID), but is down-regulated by miRNAs (miR-200b/c and miR-296). In addition, PIN1 inactivates retinoblastoma protein (Rb), resulting in the release of E2F for activation of PIN1 expression. Through phosphorylation-dependent prolyl isomerization, PIN1 activates the β-catenin/cyclin D1 signalling pathway by induction of β-catenin transcriptional activity and stabilization of cyclin D1 protein. In parallel, PIN1 increases the transcriptional activities of c-Jun and NF-κB, leading to an increase in cyclin D1 transcription. Furthermore, PIN1 stabilizes hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) and enhances its transactivating activity on downstream target nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), which in turn increases cyclin D1 transcription. Up-regulation of cyclin D1 leads to uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumourigenesis. In addition, PIN1 increases the antiapoptotic function of survivin to inhibit apoptosis and contribute to tumourigenesis. Through interaction with Akt and ribosomal S6 kinase (p70S6K), PIN1 also activates the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway to promote tumourigenesis. PIN1 enhances the transcriptional activities of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and activator protein (AP)-1, resulting in up-regulation of angiogenic factor vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and promotion of angiogenesis.
- Citation: Cheng CW, Leong KW, Tse E. Understanding the role of PIN1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(45): 9921-9932
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i45/9921.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9921