Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2016; 22(44): 9727-9733
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9727
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9727
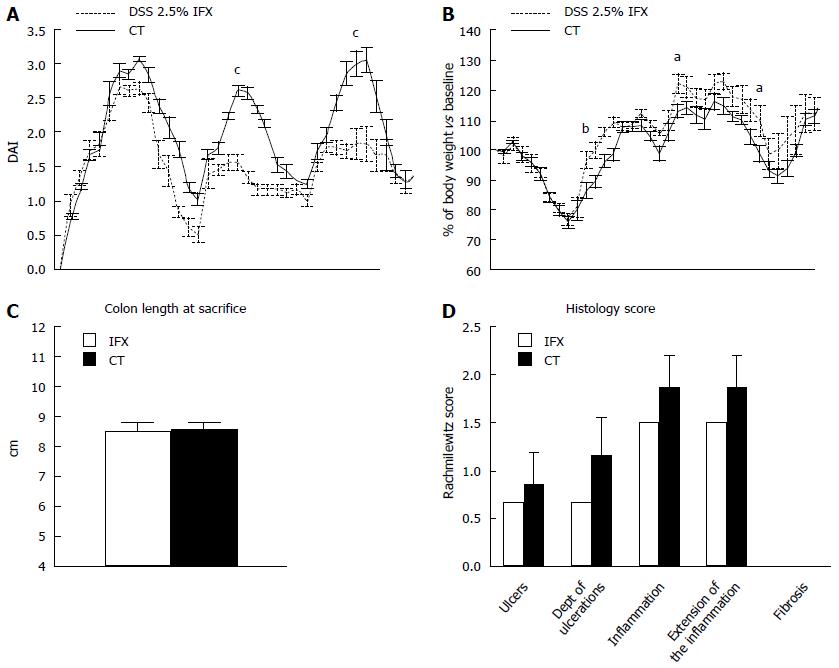
Figure 1 Effect of Infliximab on dextran sodium sulphate induced chronic colitis in mice.
A: Disease activity index (DAI) in infliximab (IFX) treated animals compared with controls (CT); B: Body weight variation in IFX treated animals compared with CT; C: Colon length at sacrifice in IFX treated mice compared with CT; D: Histology assessment in IFX treated mice compared with CT. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs controls.
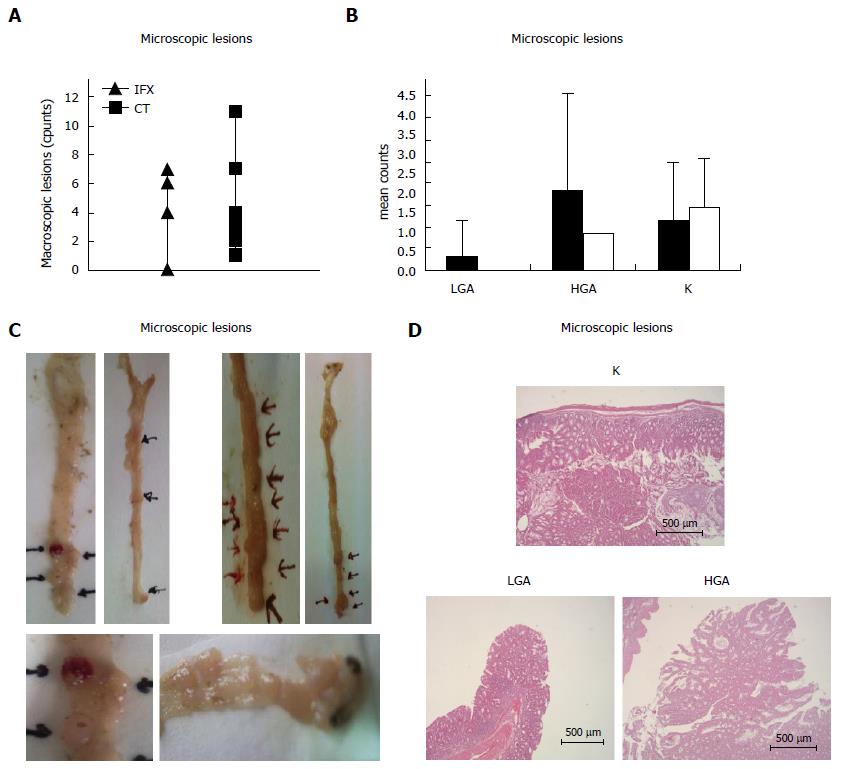
Figure 2 Effect of Infliximab on colonic cancer lesions associated to chronic colitis in mice.
A: Macroscopic lesion number in Infliximab treated mice compared with controls; B: Microscopic colon lesions classified as carcinoma (K), high grade-dysplasia adenoma (HGA) and low grade-dysplasia adenoma (LGA); C: Macroscopic colon lesions (Infliximab treated on the left and controls on the right); D: Histological photos of carcinoma (K), high grade-dysplasia adenoma (HGA) and low grade-dysplasia adenoma (LGA).
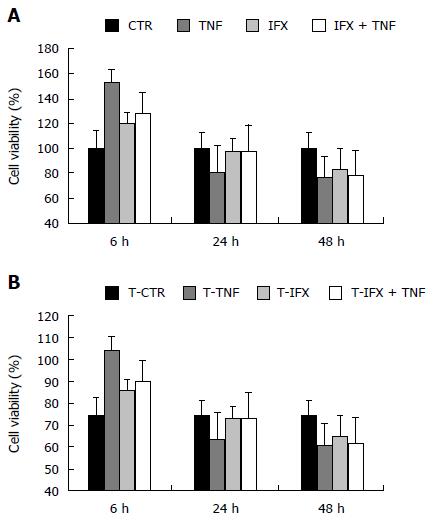
Figure 3 Effect of Infliximab on proliferation and vitality of colonic cancer cell line CT26: MTT assay.
A: MTT performed without cell pre-treatment; B: MTT performed following 24 h cell pre-incubation with TNFα.
- Citation: Lopetuso LR, Petito V, Zinicola T, Graziani C, Gerardi V, Arena V, Caristo ME, Poscia A, Cammarota G, Papa A, Cufino V, Sgambato A, Gasbarrini A, Scaldaferri F. Infliximab does not increase colonic cancer risk associated to murine chronic colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(44): 9727-9733
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i44/9727.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9727