Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2016; 22(41): 9196-9204
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9196
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9196
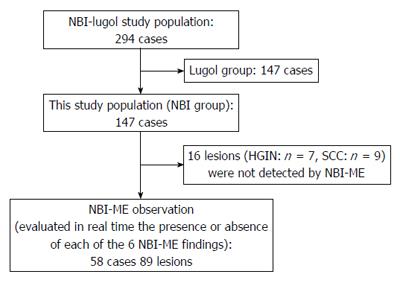
Figure 1 Overview of the study design.
HGIN: High-grade intraepithelial neoplasia; SCC: Squamous cell carcinoma; NBI-ME: Narrow Band Imaging magnifying endoscopy.
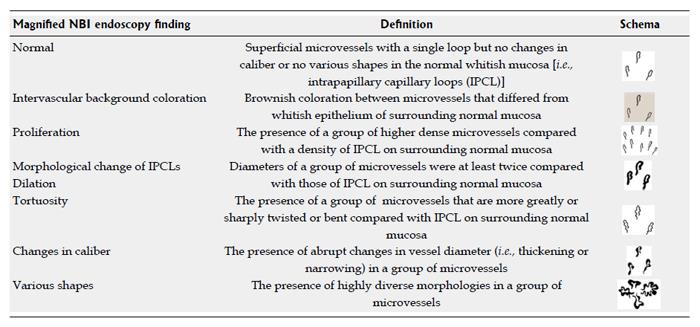
Figure 2 Definitions of Narrow Band Imaging magnifying endoscopy findings.
NBI: Narrow Band Imaging; IPCL: Intrapapillary capillary loop.
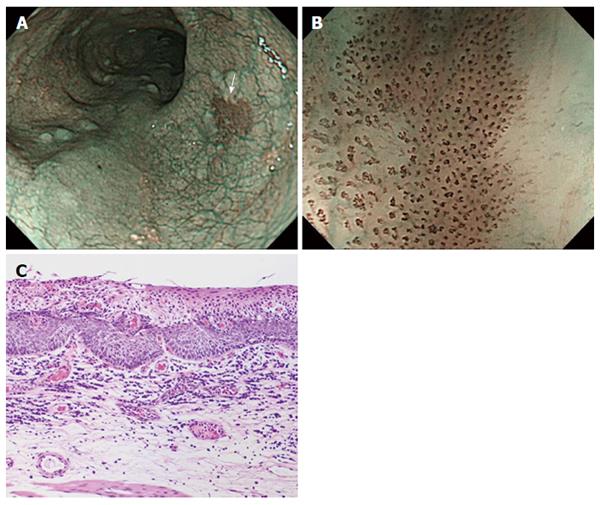
Figure 3 Representative case of superficial squamous cell carcinoma.
A: On non-magnifying NBI endoscopy, the lesion demonstrated a well-demarcated brownish area; B: The lesion has all six of the diagnostic findings obtained by using NBI-ME; C: Histology from endoscopic submucosal dissection showing squamous cell carcinoma invading up to the lamina propria mucosae. NBI: Narrow Band Imaging; NBI-ME: Narrow Band Imaging combined with magnifying endoscopy.
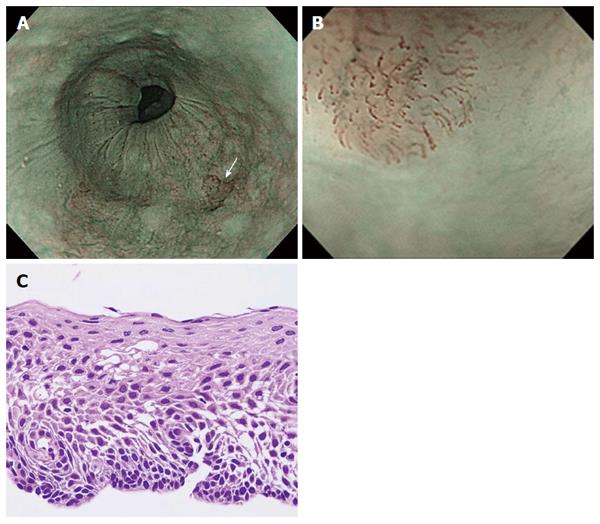
Figure 4 Representative case of low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia.
A: On non-magnifying NBI endoscopy, the lesion demonstrated a well-demarcated brownish area; B: Under magnifying NBI observation, the lesion had only two of the six findings, “intervascular background coloration” and “dilation” of IPCLs; C: The histology from biopsy showed low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia. NBI: Narrow Band Imaging; IPCL: Intrapapillary capillary loop.
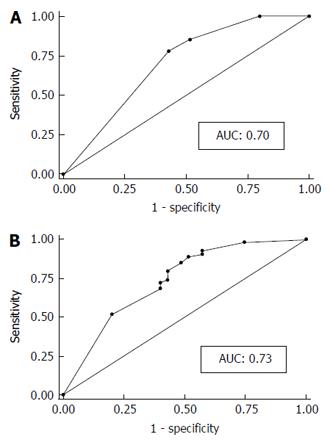
Figure 5 Diagnostic performance based on the receiver operating characteristic analysis.
The area under the curve of the simplified dyad criteria (A) was 0.70 and that of Inoue’s tetrad criteria was 0.73 (B). No significant difference was found between them. AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Dobashi A, Goda K, Yoshimura N, Ohya TR, Kato M, Sumiyama K, Matsushima M, Hirooka S, Ikegami M, Tajiri H. Simplified criteria for diagnosing superficial esophageal squamous neoplasms using Narrow Band Imaging magnifying endoscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(41): 9196-9204
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i41/9196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9196