Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2016; 22(4): 1607-1616
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1607
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1607
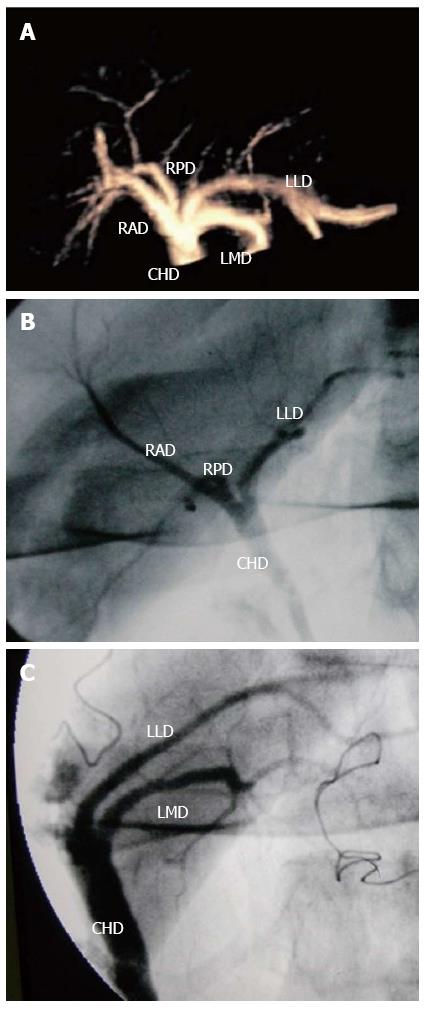
Figure 1 Three-dimensional contrast-enhanced ultrasonic cholangiography for displaying the biliary tree.
A 21-year-old living donor liver with normal biliary anatomy. A: On the anterior-posterior 3D contrast-enhanced ultrasonic cholangiography image delineating the biliary system, the common hepatic duct (CHD), right posterior duct (RPD), right anterior duct (RAD), left lateral duct (LLD) and left median duct (LMD) are well seen; B: IOC image also shows CHD, RPD, RAD and LLD before hepatectomy; C: IOC image shows CHD, LLD and LMD after hepatectomy. IOC: intraoperative cholangiography.
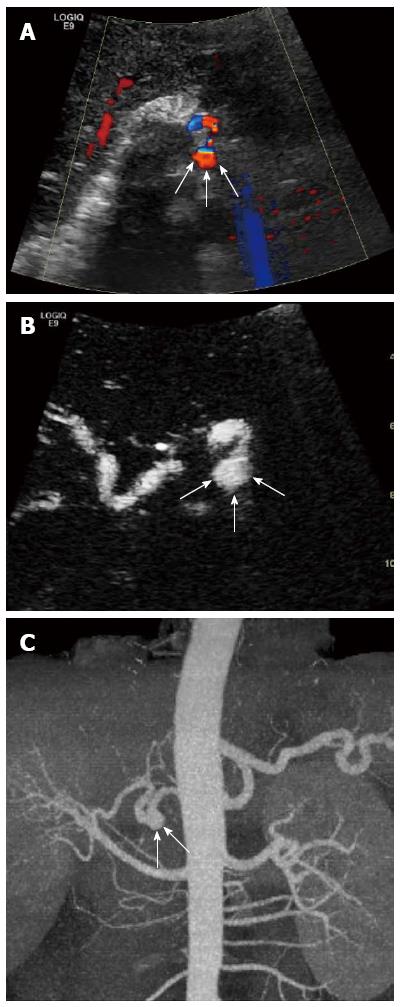
Figure 2 Aneurysm of the hepatic artery.
A 52-year-old recipient with aneurysm of the hepatic artery at the anastomosis between the donor and recipient hepatic artery. A: Color Doppler ultrasound shows a swirl of color signal (arrows); B: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound demonstrates continuing patency of the aneurysm in the arterial phase (arrows); C: Computed tomography angiography confirms it (arrows).
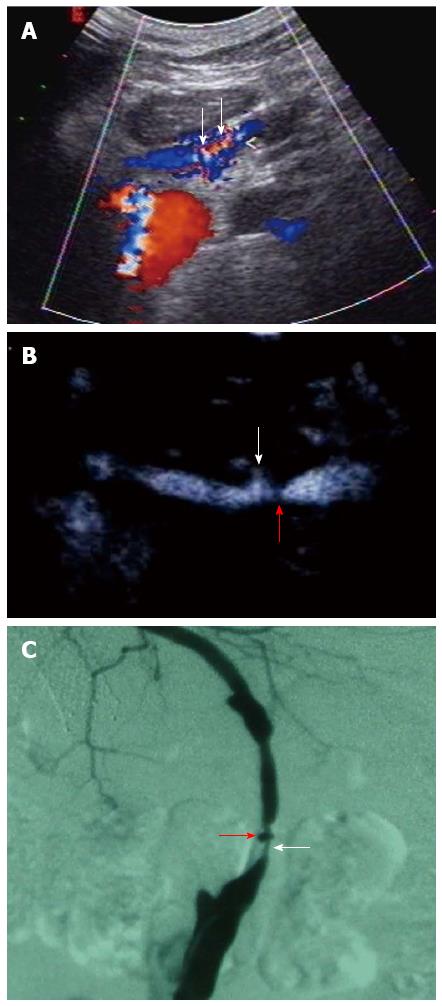
Figure 3 Hepatic artery stenosis and pseudo-aneurysm.
A 43-year-old recipient with arterial bypass arising from the infrarenal aorta through the transverse mesocolon with an iliac artery graft tunneled. A: Color Doppler ultrasound shows turbulent flow of the graft artery (arrows); B: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound shows stenosis at the graft artery (arrows) and continuing patency of the pseudo-aneurysm with adjacent site of stenosis (red arrow); C: Conventional angiography confirms hepatic artery stenosis (arrow) and pseudo-aneurysm (red arrow).
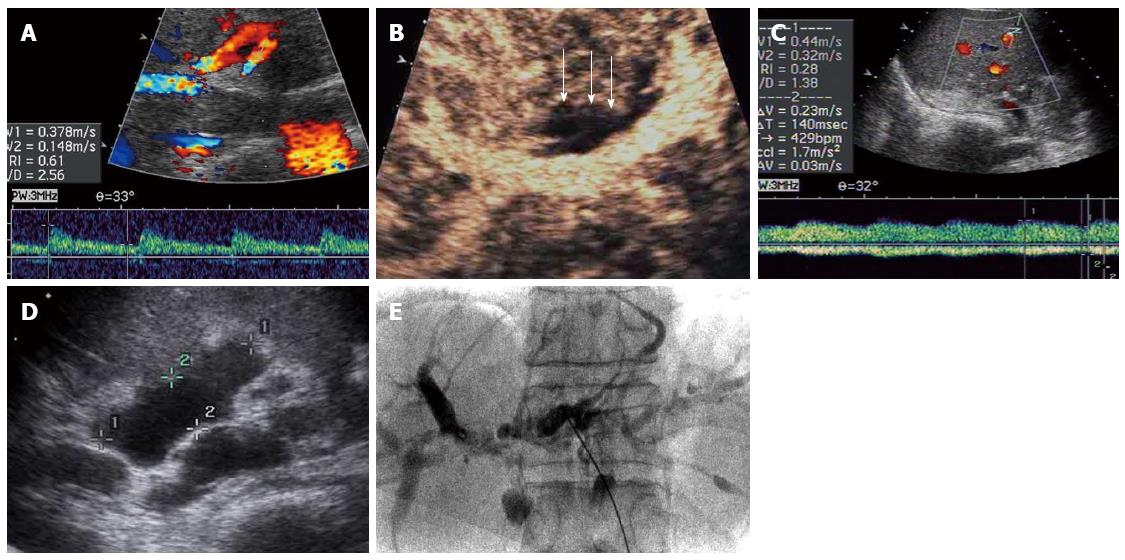
Figure 4 Ischemic-type biliary lesions.
A 38-year-old recipient with ischemic-type biliary lesion (ITBL) after liver transplantation. On 17 d after liver transplantation, color Doppler ultrasound (CDUS) shows the normal intrahepatic arterial waveform (A) while contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) of hilar bile duct walls shows no enhancement compared with the surrounding liver parenchyma in arterial phase (arrows) (B). In 2 mo after liver transplantation, CDUS shows the tardus-parvus intrahepatic arterial waveform (C) with biliary leakage in the portal hepatis on US (D). In 1 year after liver transplantation, ITBL is confirmed on cholangio-pancreatography (E). CEUS may have potential value in the early prediction of ITBL after liver transplantation.
- Citation: Ren J, Wu T, Zheng BW, Tan YY, Zheng RQ, Chen GH. Application of contrast-enhanced ultrasound after liver transplantation: Current status and perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(4): 1607-1616
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i4/1607.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1607