Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2016; 22(4): 1461-1476
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1461
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1461
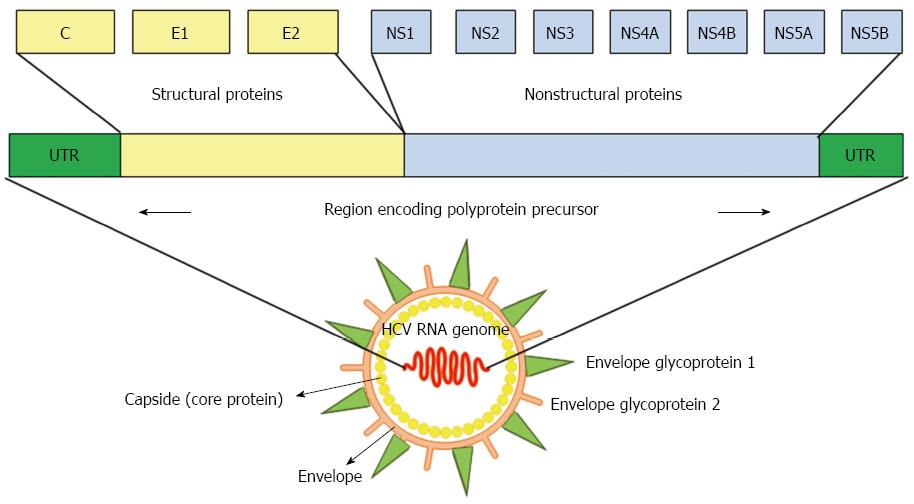
Figure 1 Diagram of the hepatitis C viral genome.
Hepatitis C virus is a single-stranded RNA virus, and its genomic organization shows highly conserved 5’ and 3’ nonstructural proteins. UTR: Untranslated region; C: Core protein; E1 and E2: Envelope glycoprotein 1 and 2; NS: Nonstructural protein.
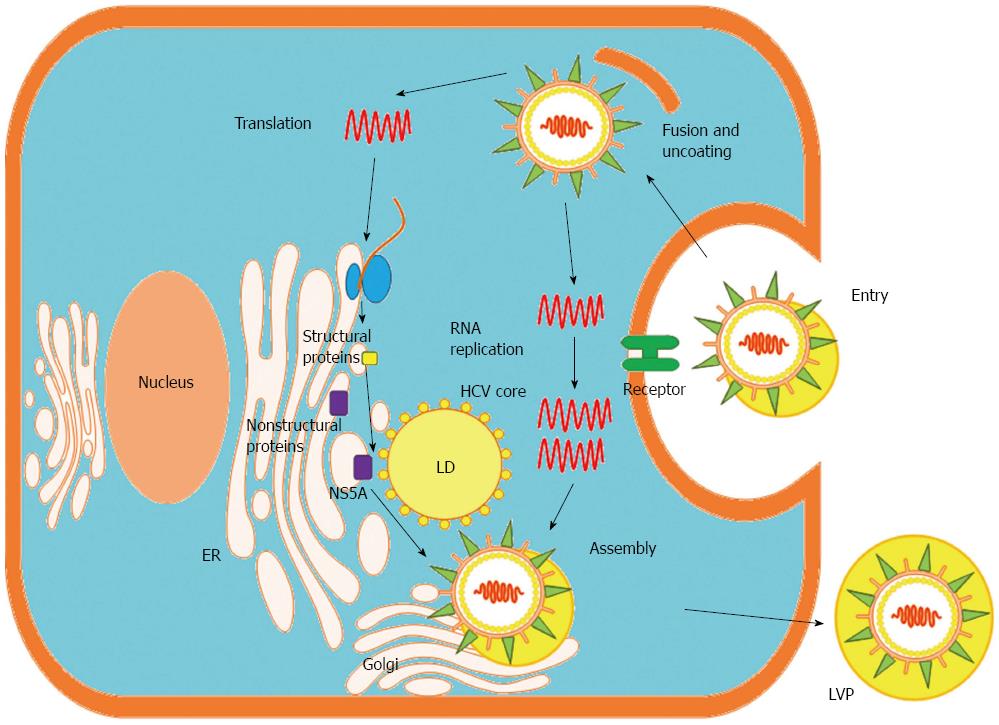
Figure 2 Life cycle of hepatitis C virus in the hepatocyte.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) LVPs enter hepatocytes via receptor-mediated endocytosis. Released viral RNA is translated at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), producing a single polyprotein precursor that is cleaved by host and viral proteases. The viral NS proteins (e.g., NS5A protein) form RNA replication complexes in lipid rafts, where positive-strand RNA is replicated via a negative-strand intermediate. Newly synthesized positive-strand RNA is encapsidated by the HCV core protein in close proximity to LDs, and envelope glycoproteins are acquired through budding into the ER lumen. LVPs mature in the ER through interactions with lipoproteins and exit the cell via the cellular Golgi apparatus. LD: Lipid droplet; LVP: Lipoviral particle; Golgi: Golgi apparatus.
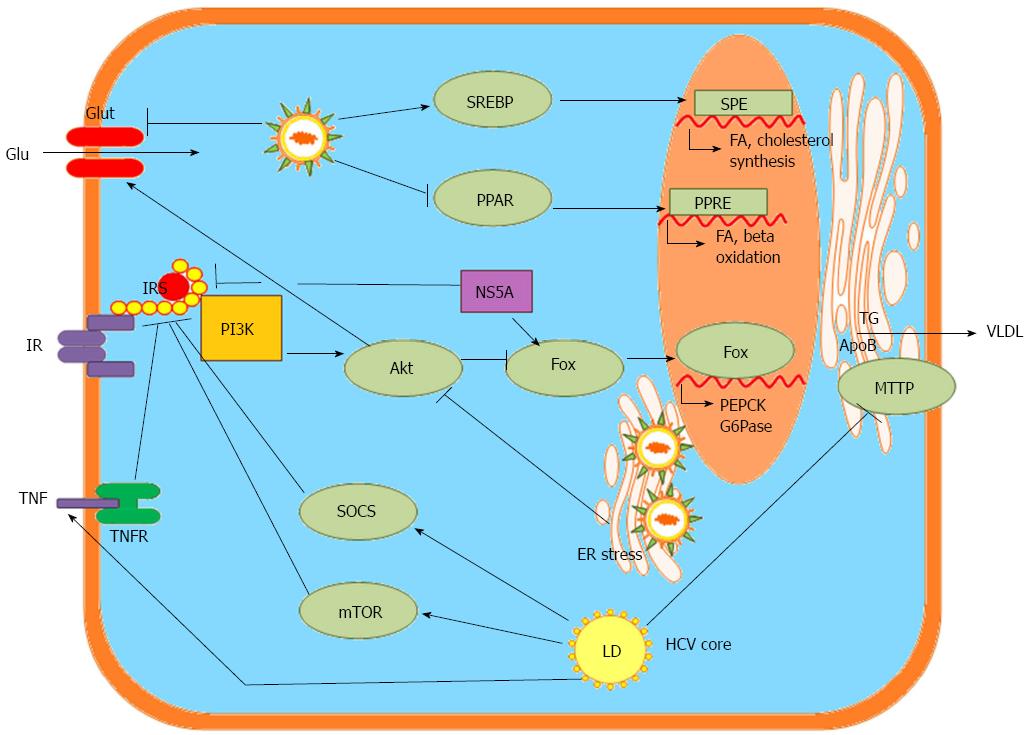
Figure 3 Hepatitis C virus-associated metabolic alterations in the hepatocyte, data from bench studies.
SREBP: Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; Glu: Glucose; Glut: Glucose transporter; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; SRE: SREBP response element; FA: Fatty acid; PPRE: PPAR response element; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B: Fox: Transcription factor forkhead box; PEPCK: Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; G6Pase: Glucose 6-phosphatase; IR: Insulin receptor; IRS: Insulin receptor sustrate; NS5A: HCV nonstructural protein 5 A; TG: Triglyceride; ApoB: Apoliporptoein B; MTTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor; LD: Lipid droplet.
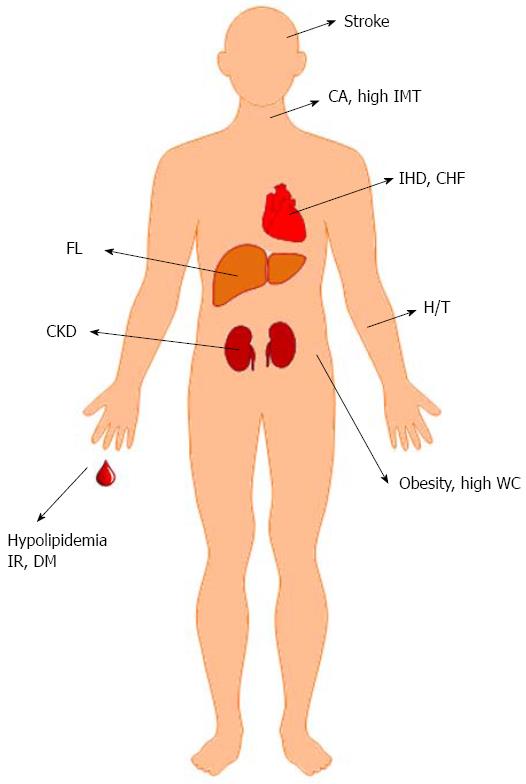
Figure 4 Hepatitis C virus-associated metabolic alterations and cardiovascular events, data from human studies.
CA: Carotid atherosclerosis; IMT: Intima-media thickness; IHD: Ischemic heart disease; CHF: Congestive heart failure; FL: Fatty liver; H/T: Hypertension; WC: Waist circumference; IR: Insulin resistance; DM: Diabetes; CKD: Chronic kidney disease.
- Citation: Chang ML. Metabolic alterations and hepatitis C: From bench to bedside. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(4): 1461-1476
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i4/1461.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1461