Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2016; 22(38): 8459-8471
Published online Oct 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8459
Published online Oct 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8459
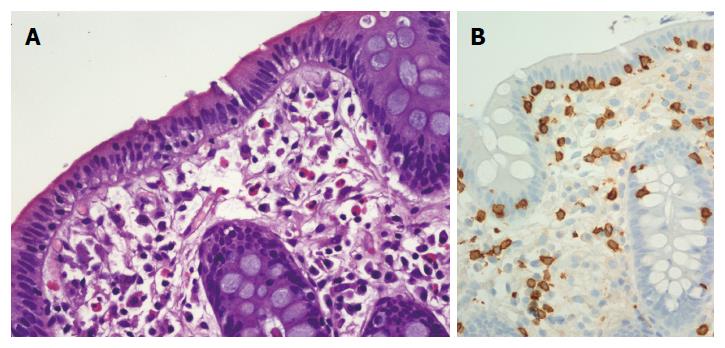
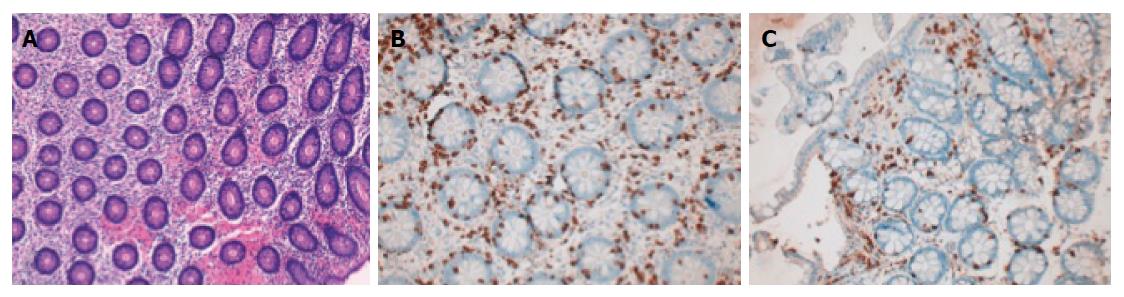
Figure 1 Photomicrographs of a colonic specimen from a lymphocytic colitis patient showing inflammatory hypercellularity in the lamina propria of colonic mucosa and clear presence of a greater number of intraepithelial lymphocyte cells.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification × 200; B: More evident with the CD3 staining, magnification × 200.
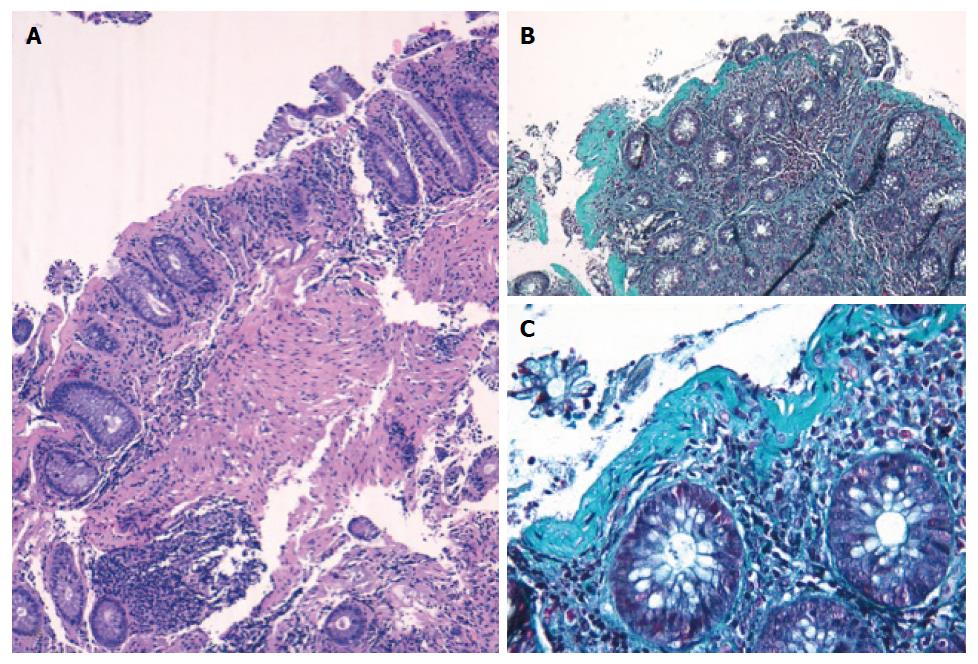
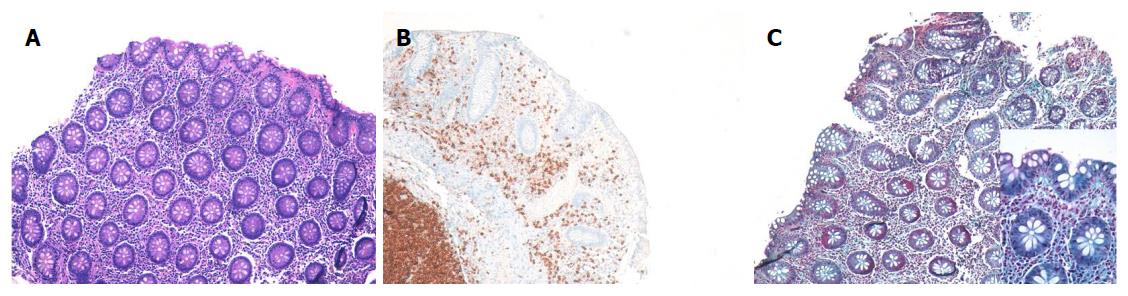
Figure 2 Photomicrographs of a colonic specimen from a collagenous colitis patient showing detachment of superficial epithelium.
Hematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification × 100 (A) and thick subepithelial collagen band, Gomori’s Trichrome staining (B and C, magnification × 100, × 400, respectively).
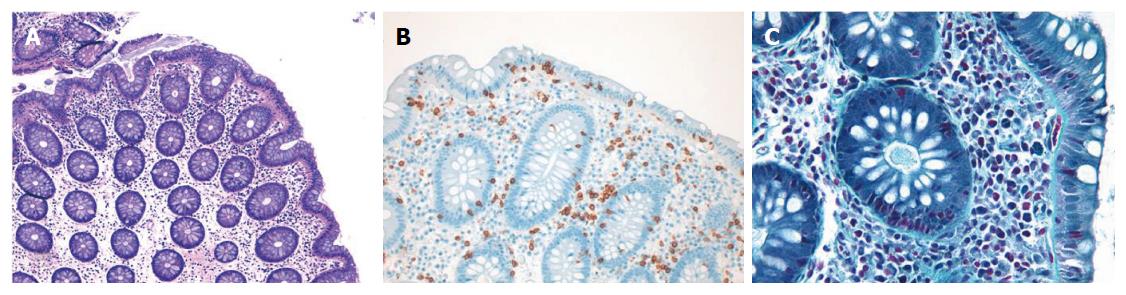
Figure 3 Photomicrographs of a colonic specimen from an incomplete lymphocytic colitis patient.
Hematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification × 100 (A) with a mild increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes cells (B, CD3, magnification × 200) and a regular collagen band (C, Gomori’s Trichrome staining, magnification × 400).
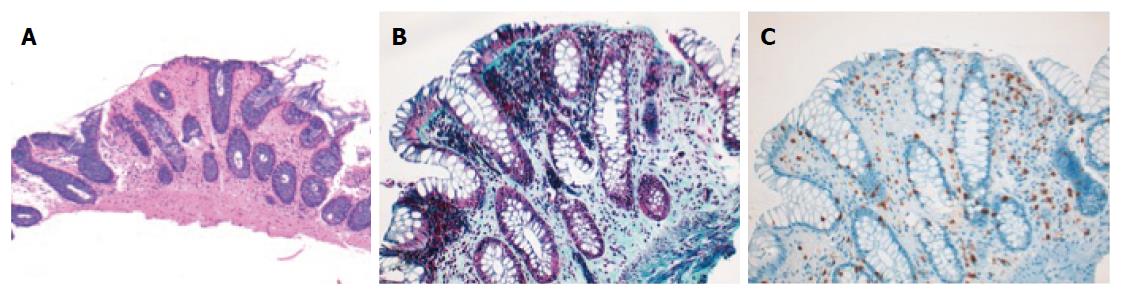
Figure 4 Photomicrographs of a colonic specimen from an incomplete collagenous colitis patient.
Hematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification × 100 (A) with slight enhancement of subepithelial collagen band (B, Gomori’s Trichrome staining, magnification × 200) without increased intraepithelial lymphocyte cells infiltration (C, CD3 inmunostaining, magnification × 200).
Figure 5 Photomicrographs of a colonic specimen from a cryptal lymphocytic colitis patient.
Hematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification × 100 (A) showing only the presence of cryptal lymphocytosis (B, CD3, magnification × 200) and lack of intraepithelial lymphocytosis (C, CD3, magnification × 200).
Figure 6 Photomicrographs of a colonic specimen from a healthy donor.
Hematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification × 100 (A) showing low number (usually less than 5) of intraepithelial lymphocyte cells, which can be easily identified by CD3 immunohistochemistry marker (B, magnification × 100). The subepithelial collagen band is tiny and regular (C, Gomori’s Trichrome staining, magnification × 10 and inset, Gomori’s Trichrome staining, magnification × 400).
- Citation: Guagnozzi D, Landolfi S, Vicario M. Towards a new paradigm of microscopic colitis: Incomplete and variant forms. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(38): 8459-8471
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i38/8459.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8459