Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2016; 22(34): 7742-7747
Published online Sep 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7742
Published online Sep 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7742
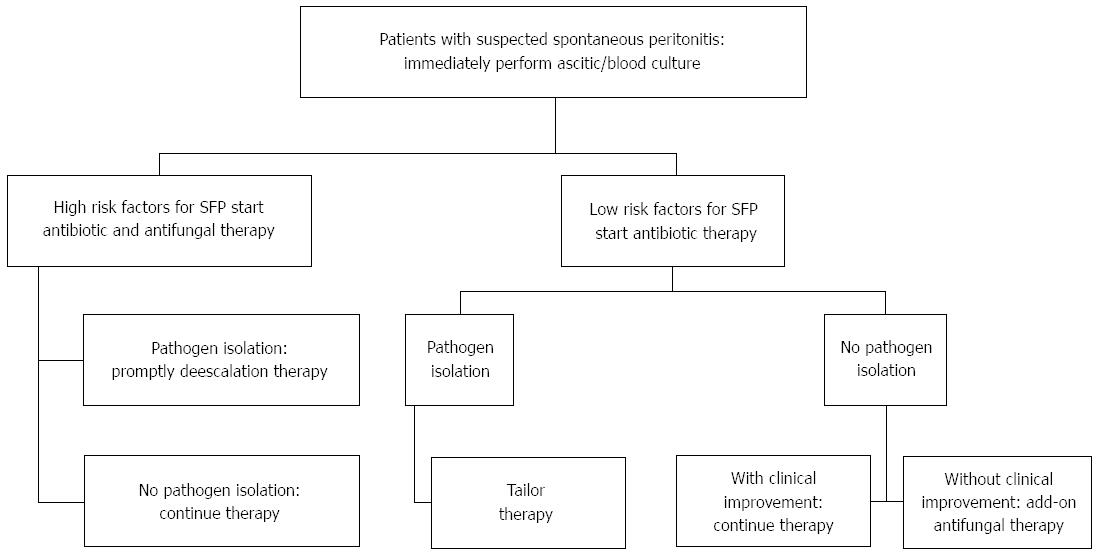
Figure 1 Spontaneous fungal peritonitis management algorithm.
Risk factors for fungal diseases[32]: Surgery, total parenteral nutrition, fungal colonisation, renal replacement therapy, infection and/or sepsis, mechanical ventilation, diabetes, and APACHE II or III score; Add-on: consider adding empiric antifungal therapy. APACHE: Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation.
- Citation: Fiore M, Leone S. Spontaneous fungal peritonitis: Epidemiology, current evidence and future prospective. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(34): 7742-7747
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i34/7742.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7742