Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2016; 22(30): 6851-6863
Published online Aug 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i30.6851
Published online Aug 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i30.6851
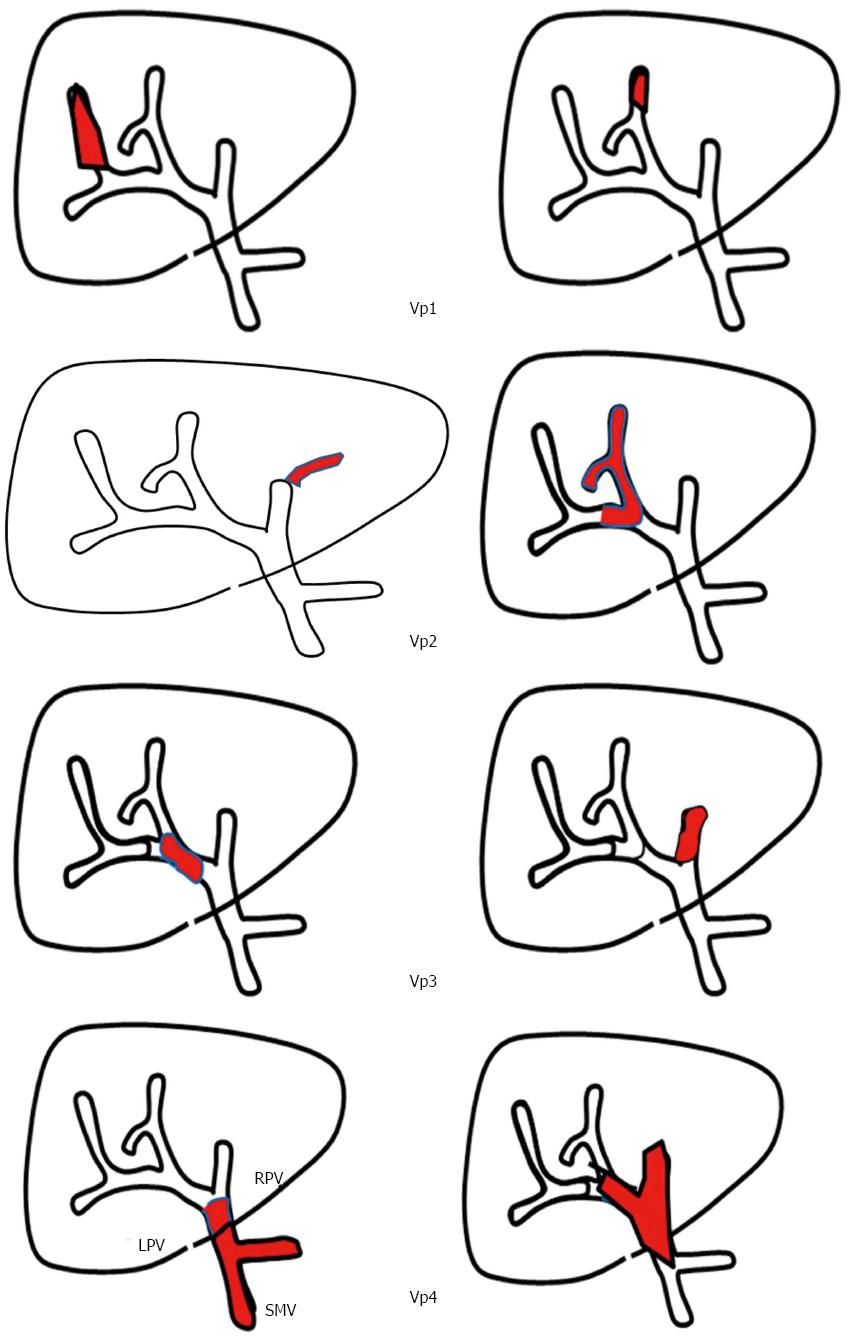
Figure 1 Classification of portal vein tumor thrombosis.
PVTT is classified into four categories according to the site of tumor thrombus as suggested by the Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. PVTT: Portal vein tumor thrombosis.
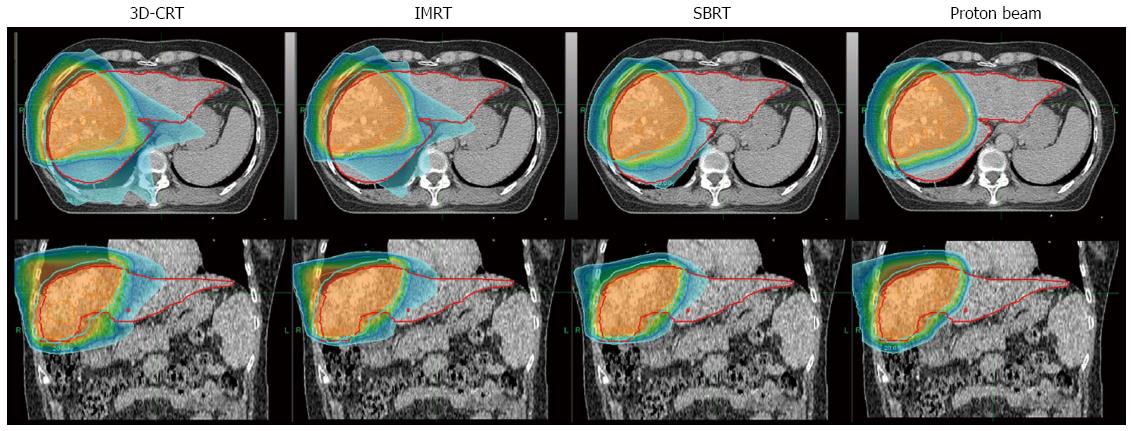
Figure 2 Radiation dose distribution according to radiotherapy technique.
More conformal dose delivery to the main mass and tumor thrombosis with a reduced liver dose is achievable with 3D-CRT, IMRT, and SABR, as well as to an even greater extent with proton beam RT. 3D-CRT: Three-dimensional conformal RT; IMRT: Intensity-modulated RT; SABR: Stereotactic body ablative RT. RT: Radiotherapy technique.
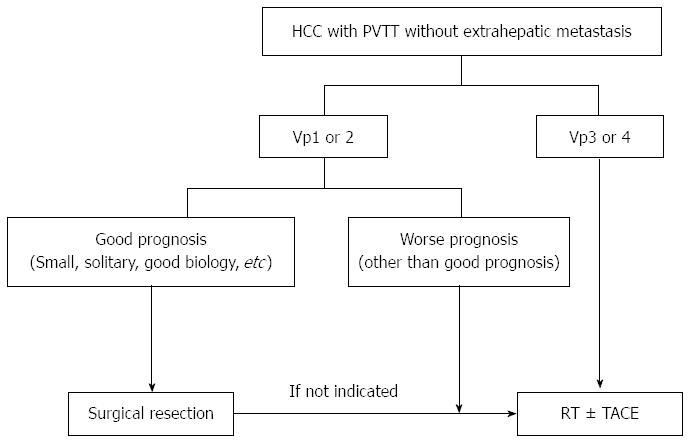
Figure 3 Suggested local treatment modalities for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis according to portal vein tumor thrombosis classification.
To rapidly eliminate tumor thrombosis, RT with or without TACE could be considered, except in the case of technically resectable Vp1/2 disease with a favorable prognosis. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; PVTT: Portal vein tumor thrombosis; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Trans-arterial chemoembolization.
- Citation: Yu JI, Park HC. Radiotherapy as valid modality for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(30): 6851-6863
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i30/6851.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i30.6851