Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2016; 22(3): 1224-1235
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1224
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1224
Figure 1 Structural features of the group I and group II p21-activated kinases family members.
PAK: p21-activated kinase; PBD: p21-binding domain; AID: Autoinhibitory domain.
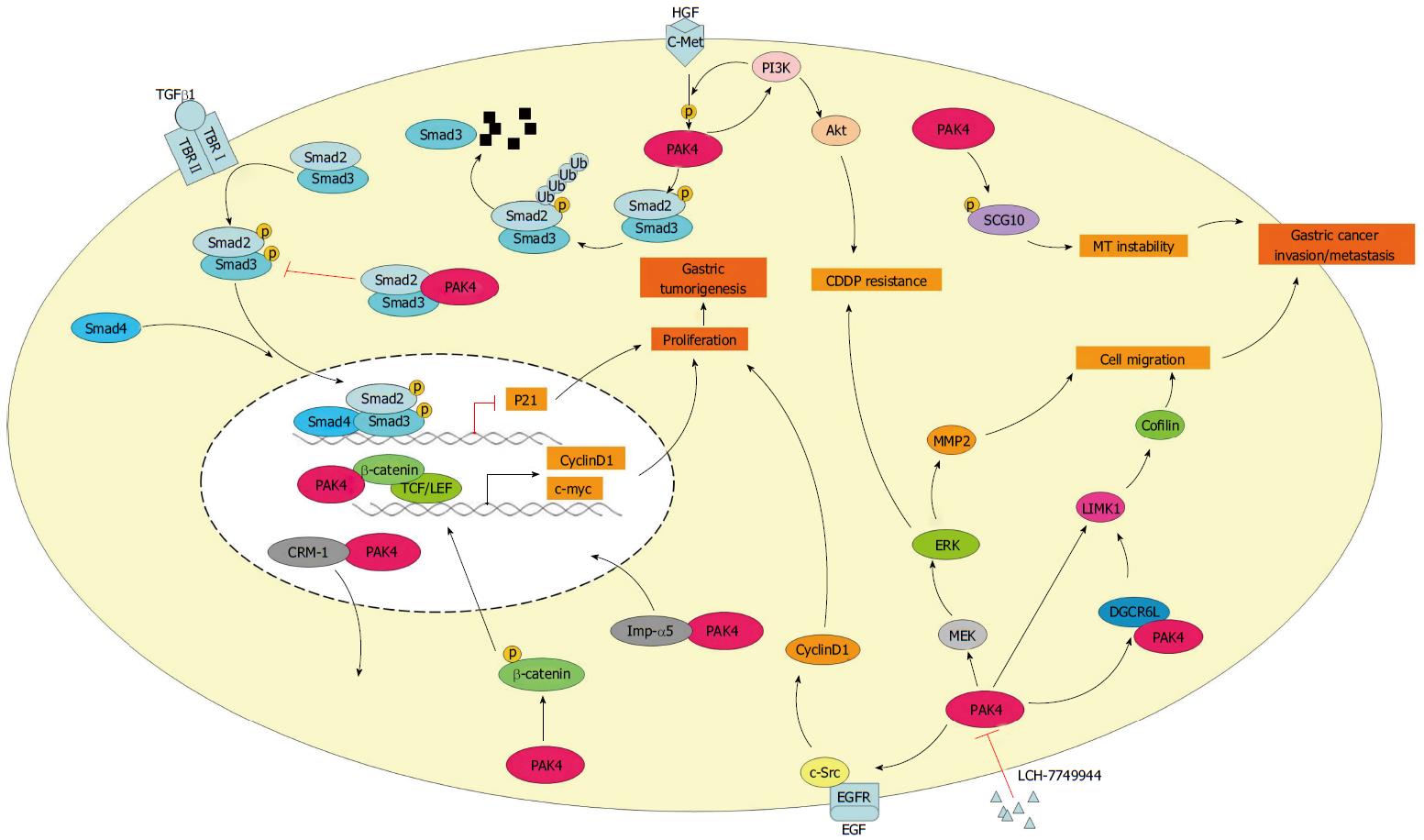
Figure 2 p21-activated kinase 4 signaling pathways in gastric cancer.
Schematic depicting some of the signaling cascades mediated by PAK4. PAK4 is a nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling protein that is exported by the CRM-1-dependent pathway and imported into the nucleus in an importin α5-dependent manner. We have demonstrated that PAK4 contributes to gastric tumorigenesis and gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by phosphorylating Smad2, SCG10 or β-catenin or by interacting with DGCR6L. PAK4-mediated substrate phosphorylation is indicated by the letter P. PAK4 activation and inhibition of proteins are depicted using arrows and blocked lines, respectively. Specific details of the pathways are described in the text. CRM-1: Chromosome region maintenance-1; Imp-α5: Importin α5; SCG10: Superior cervical ganglia 10; DGCR6L: DiGeorge critical region 6 L; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B or PKB; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, MAPKK; ERK: Extracellular-signal regulated protein kinase; MT: Microtubule; LIMK1: LIM domain kinase 1; MMP2: Matrix metallopeptidase 2; CDDP: Cisplatin or cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II).
- Citation: Shao YG, Ning K, Li F. Group II p21-activated kinases as therapeutic targets in gastrointestinal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(3): 1224-1235
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i3/1224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1224