Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2016; 22(20): 4860-4867
Published online May 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4860
Published online May 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4860
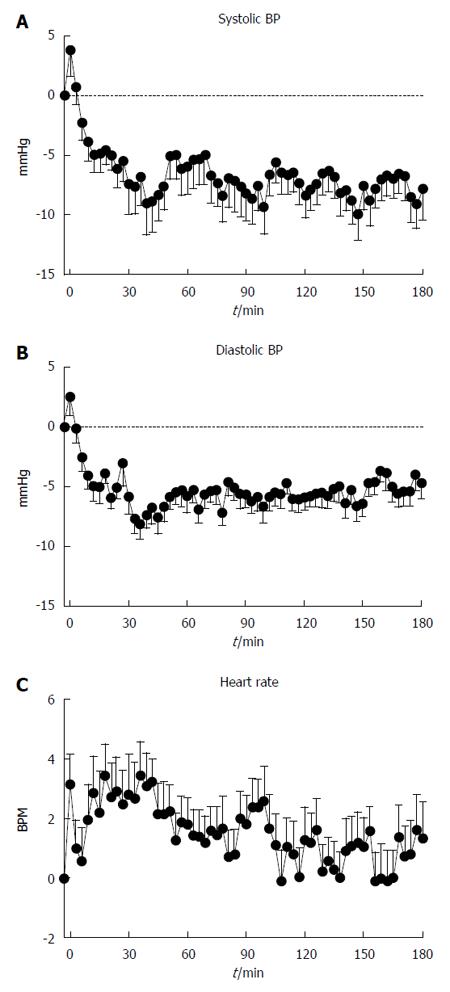
Figure 1 Systolic blood pressure (A), diastolic blood pressure (B) and heart rate (C) immediately before and after 75 g oral glucose load in 21 patients with Parkinson’s disease.
BP: Blood pressure.
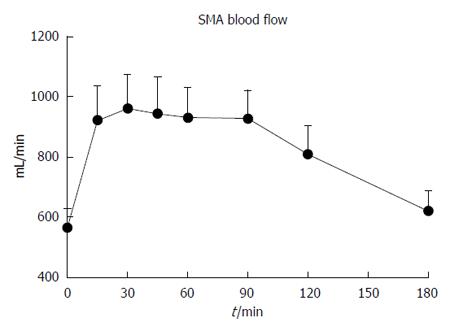
Figure 2 Superior mesenteric artery blood flow immediately before and after 75 g oral glucose load in 21 patients with Parkinson’s disease.
SMA: Superior mesenteric artery.
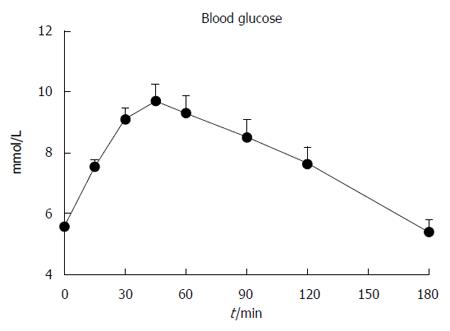
Figure 3 Blood glucose immediately before and after 75 g oral glucose load in 21 patients with Parkinson’s disease.
Figure 4 Relationship between gastric half emptying time (GE T50) and autonomic nerve function score (R = 0.
55, P < 0.01). ANF: Autonomic nerve function.
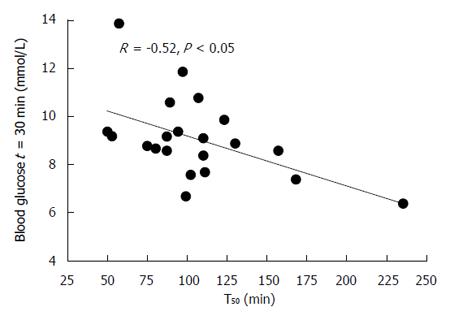
Figure 5 Relationship between the absolute blood glucose at t = 30 min with the gastric half emptying time (GE T50) (R = -0.
52, P < 0.05).
- Citation: Trahair LG, Kimber TE, Flabouris K, Horowitz M, Jones KL. Gastric emptying, postprandial blood pressure, glycaemia and splanchnic flow in Parkinson’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(20): 4860-4867
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i20/4860.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4860