Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2016; 22(2): 823-832
Published online Jan 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i2.823
Published online Jan 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i2.823
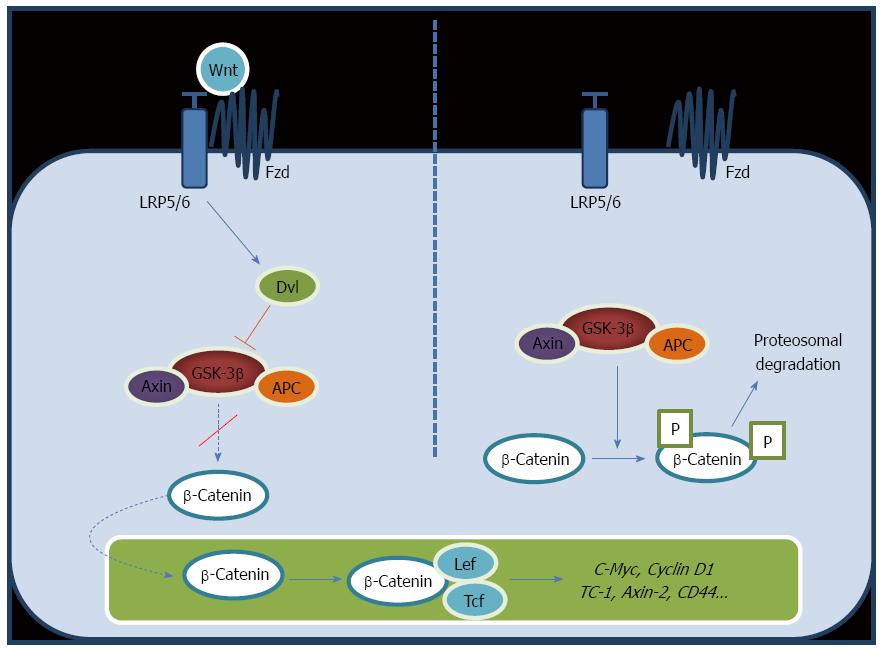
Figure 1 Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway.
Binding of Wnt protein initiates a cascade, which results in activation of β-catenin, its accumulation in the cytoplasm and translocation into the nucleus to enhance the transcription of target genes (Left); When Fz/LRP receptors are not engaged, CK1 and GSK3B sequentially phosphorylate Axin-bound β-catenin. Consequently, β-catenin is ubiquitinated and targeted for rapid destruction by the proteasome (Right).
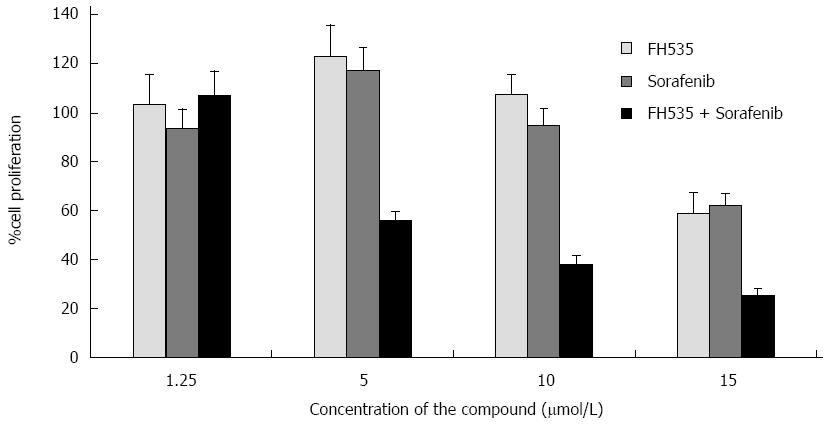
Figure 2 Synergistic inhibition of proliferation of liver cancer stem cells targeting β-catenin and Ras/Raf/MAPK pathways.
FH535 and Sorafenib combination on inhibition of [3H]-Thymidine incorporation in liver cancer stem cells (CD133+, CD44+ and CD24+) Calculated combination index (CI) of less than 1. From Galuppo et al[12] with permission of Anticancer Research.
- Citation: Vilchez V, Turcios L, Marti F, Gedaly R. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(2): 823-832
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i2/823.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i2.823