Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2016; 22(10): 3031-3037
Published online Mar 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.3031
Published online Mar 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.3031
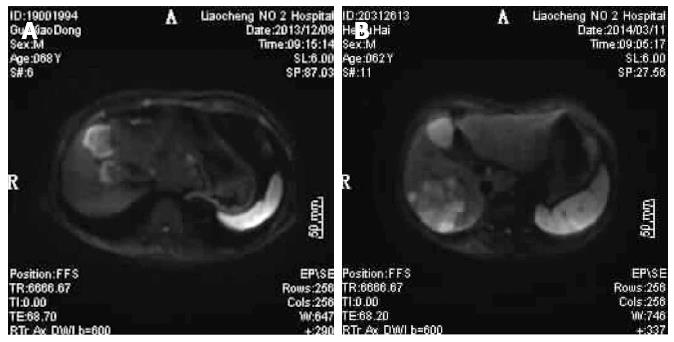
Figure 1 Diffusion-weighted imaging results for patients with liver metastasis of gastrointestinal tract cancer.
A: Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) figure shows right anterior lobe of liver with surrounding high signal, clear boundary, and significant contrast; B: DWI figure shows the right posterior lobes of livers with huge and irregular high signal intensity; surrounding small satellite focus were visible with a blending tendency, clear boundary, and significant contrast.
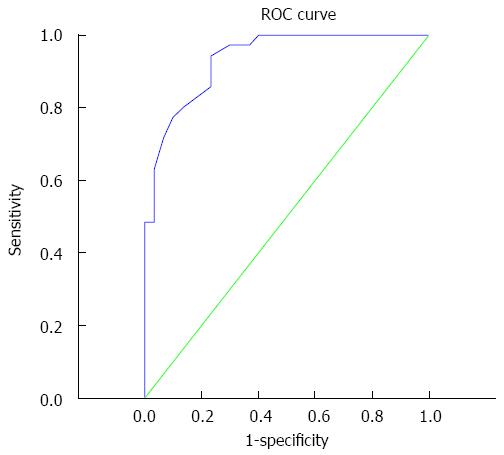
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curve.
Area under the curve is 0.934, the optimal diagnostic point is 1.14 × 10-3 mm2/s, and sensitivity and specificity are 94.3% and 76.7%, respectively.
- Citation: Zheng DX, Meng SC, Liu QJ, Li CT, Shang XD, Zhu YS, Bai TJ, Xu SM. Predicting liver metastasis of gastrointestinal tract cancer by diffusion-weighted imaging of apparent diffusion coefficient values. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(10): 3031-3037
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i10/3031.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.3031