Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2016; 22(1): 37-49
Published online Jan 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.37
Published online Jan 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.37
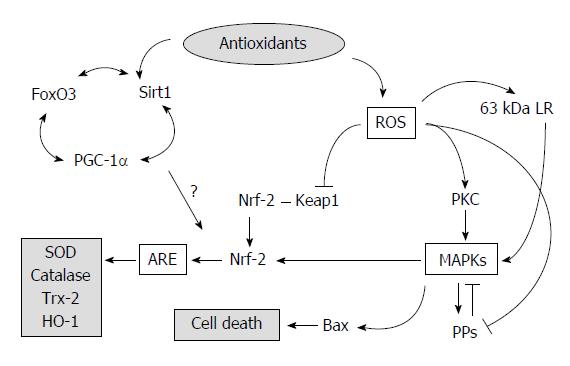
Figure 1 Oxidative stress-stimulating signaling pathways.
The oval with the gray indicates the start point; gray boxes indicate consequences; other boxes indicate key substances. ARE: Antioxidant responsive element; FoxO3: Forkhead winged-helix box class O3 transcription factor; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; Keap1: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; LR: Laminin receptor; MAPK: Mitogen-activating protein kinase; Nrf2: NF-E2-related factor-2; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated responsive element γ coactivator-1α; PKC: Protein kinase C; PP: Protein phosphatase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; Sirt1: Sirtuin 1; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; Trx: Thioredoxin.
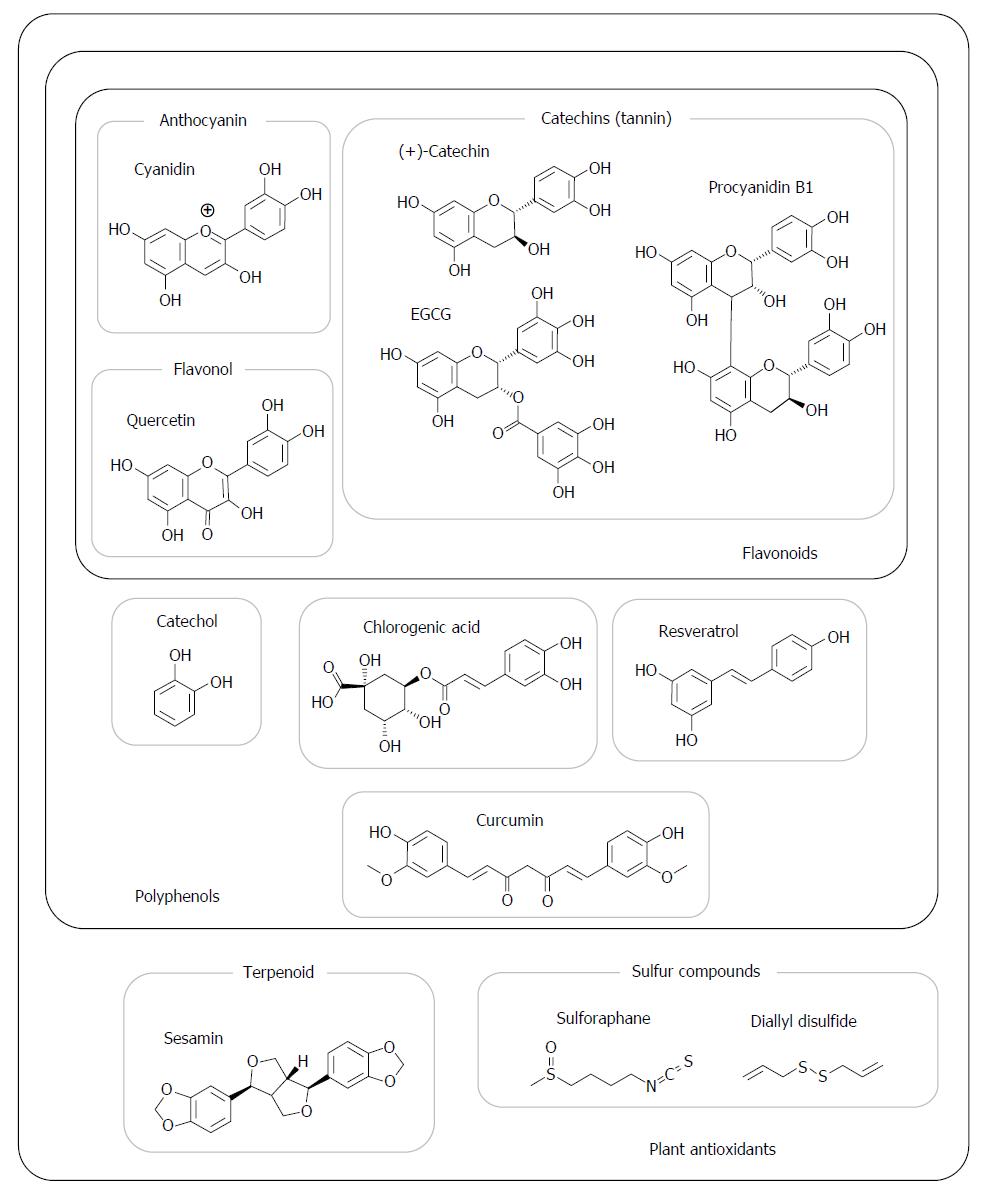
Figure 2 Structures of representative plant antioxidants and their classification.
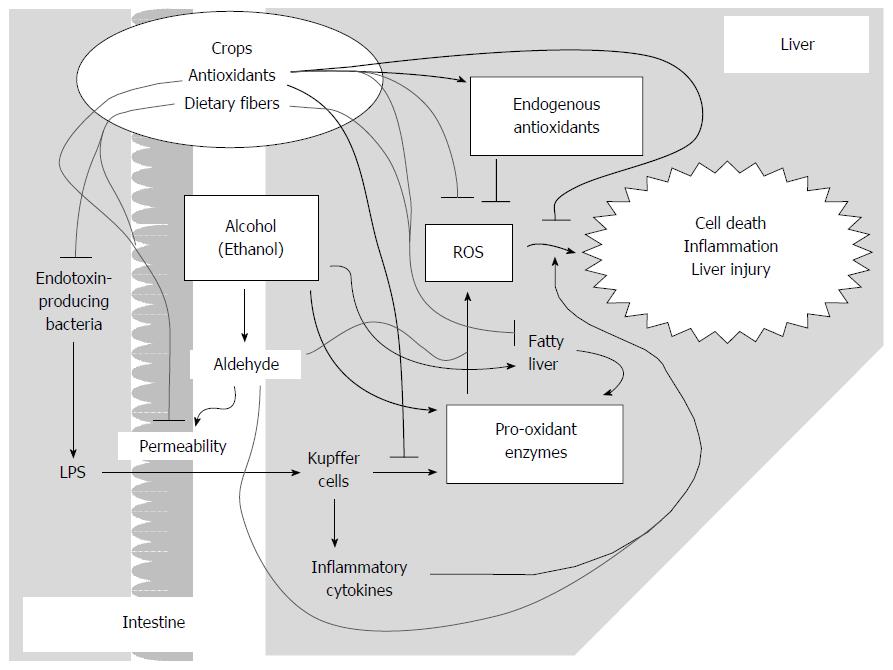
Figure 3 Potential multiple effects of crop components on alcoholic liver disease.
LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Han KH, Hashimoto N, Fukushima M. Relationships among alcoholic liver disease, antioxidants, and antioxidant enzymes. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(1): 37-49
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i1/37.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.37