Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2015; 21(9): 2858-2861
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2858
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2858
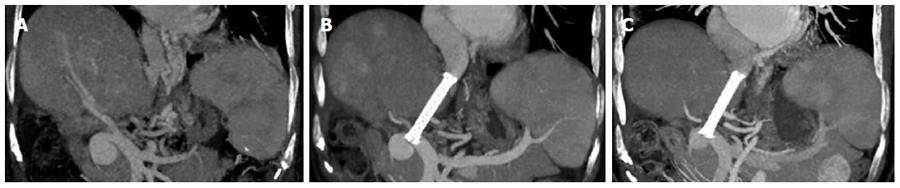
Figure 1 Coronal reformatted computed tomography images of the portal vein aneurysm.
A: A coronal reformatted computed tomography (CT) image obtained before transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) shows a saccular aneurysm located at the extrahepatic portal vein main branch measuring 3.2 cm in height and 2.5 cm × 2.4 cm in diameter; B: A coronal reformatted CT image obtained at 3 mo after TIPS shows the aneurysm has decreased in size to 2.4 cm in height and 2.0 cm × 1.9 in diameter; C: A coronal reformatted CT image obtained at 1 year after TIPS shows the aneurysm has further decreased in size to 1.9 cm in height and 1.6 cm × 1.5 cm in diameter.
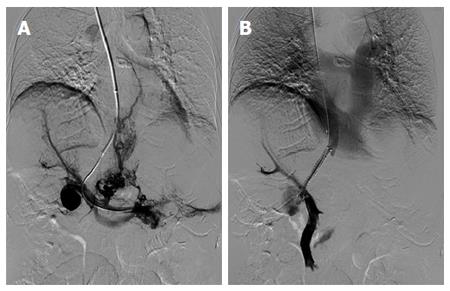
Figure 2 Portograms obtained before and after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
A: A portogram obtained before transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) shows a saccular aneurysm located at the main portal vein, extensive intrahepatic portal vein thrombosis, and small splenorenal varices; B: A portogram obtained after TIPS shows a widely patent shunt and markedly decreased aneurysm filling.
- Citation: Tsauo J, Li X. Portal vein aneurysm associated with Budd-Chiari syndrome treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(9): 2858-2861
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i9/2858.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2858