Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2015; 21(9): 2854-2857
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2854
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2854
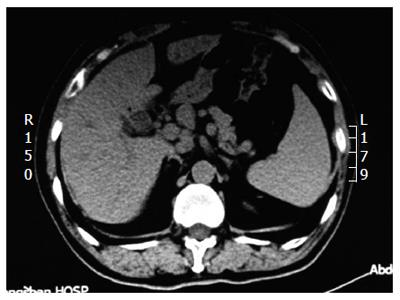
Figure 1 Computed tomography.
Cholecystectomy change, intrahepatic bile duct dilatation, fatty liver, splenomegaly.
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
Multiple stones in extrahepatic bile duct and common bile duct, dilated intrahepatic bile duct, and cholecystectomy change.
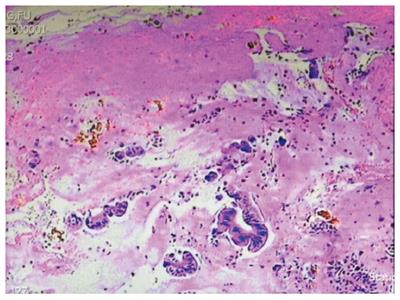
Figure 3 Pathology: Calcified biliary mucosa.
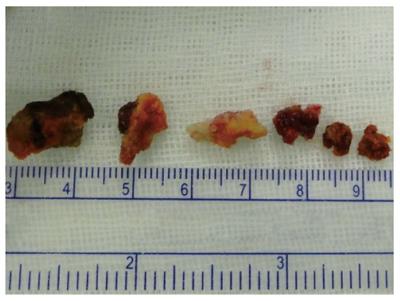
Figure 4 Morphology: Hard, grid-like solid fibrin glue.
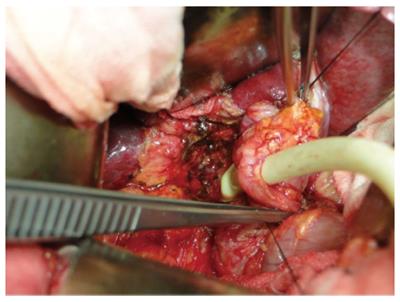
Figure 5 Common bile duct repaired by longitudinal, slivered, pedunculated liver round ligament with serous face towards the bile duct, and T-tube drainage from the middle of the liver round ligament.
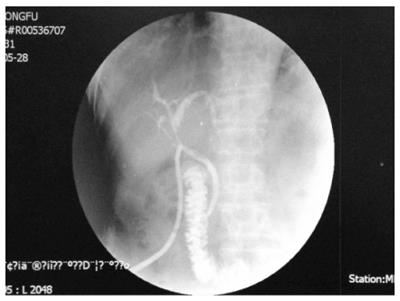
Figure 6 T-tube visualization: contrast agent introduced smoothly into the duodenum with no extravasation or bile duct stenosis.
- Citation: Yang YL, Zhang C, Zhang HW, Wu P, Ma YF, Lin MJ, Shi LJ, Li JY, Zhao M. Common bile duct injury by fibrin glue: Report of a rare complication. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(9): 2854-2857
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i9/2854.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2854