Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2015; 21(9): 2645-2650
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2645
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2645
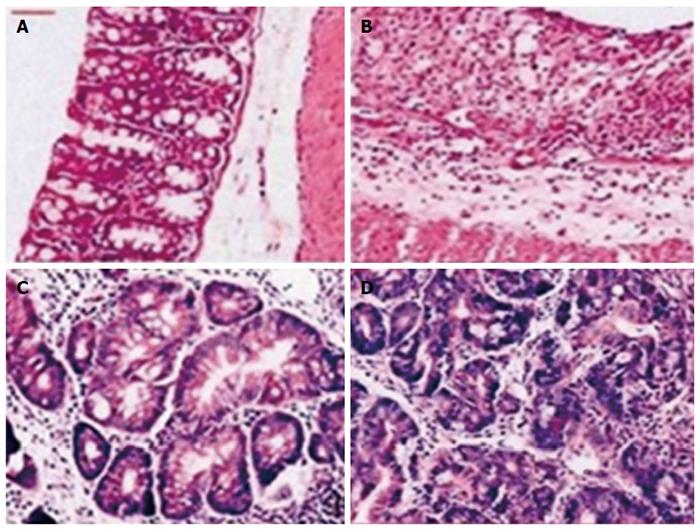
Figure 1 Hematoxylin and eosin staining of colons obtained from rats in each group.
A: Normal colonic histology (× 20); B: Colonic histology from a rat with ulcerative colitis (× 20); C: Dysplastic lesion in a rate with colorectal cancer (× 200); D: Cancer lesion in a rat with colorectal cancer (× 200).
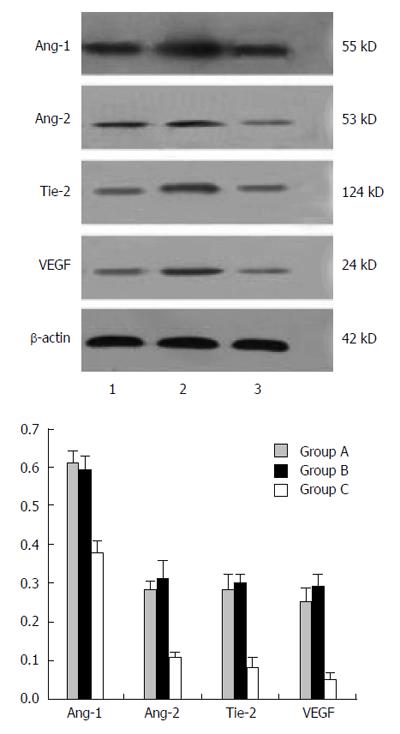
Figure 2 Protein expression in colorectum.
Representative Western blots and quantitation of angiopoietin (Ang)-1, Ang-2, tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin-like and EGF-like domains-2 (Tie-2), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) (normalized to β-actin). Lane 1: Group A (colorectal cancer); Lane 2: Group B (ulcerative colitis); Lane 3: Group C (control). Error bars represent standard deviation.
- Citation: Liu WX, Gu SZ, Zhang S, Ren Y, Sang LX, Dai C. Angiopoietin and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colorectal disease models. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(9): 2645-2650
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i9/2645.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2645