Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2015; 21(8): 2433-2442
Published online Feb 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2433
Published online Feb 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2433
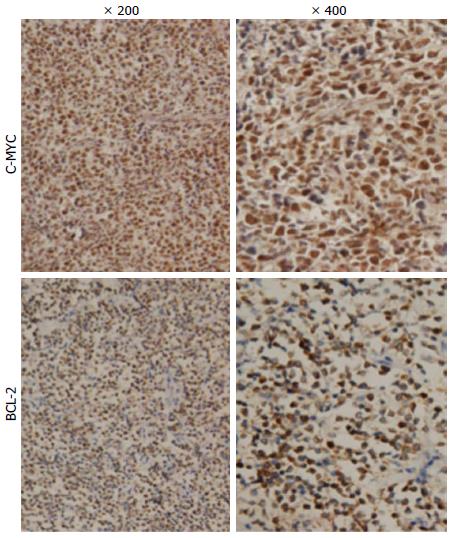
Figure 1 MYC and BCL-2 expression in primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry (magnification × 200 and × 400, respectively).
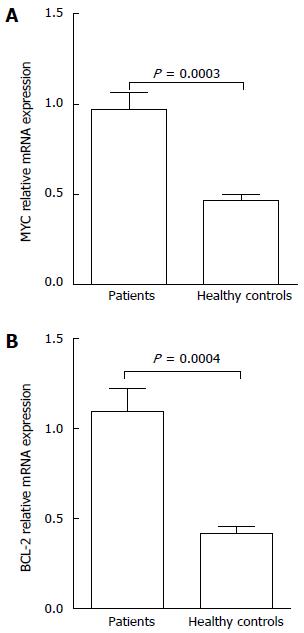
Figure 2 mRNA expression of MYC and BCL-2 in primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients.
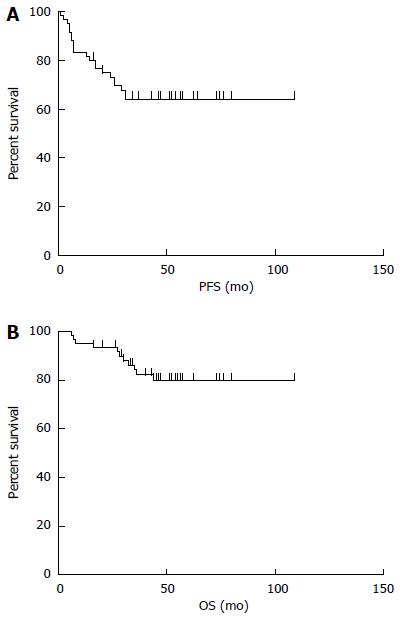
Figure 3 Survival curves for the entire population of patients with primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
A: Progression-free survival (PFS); B: Overall survival (OS).
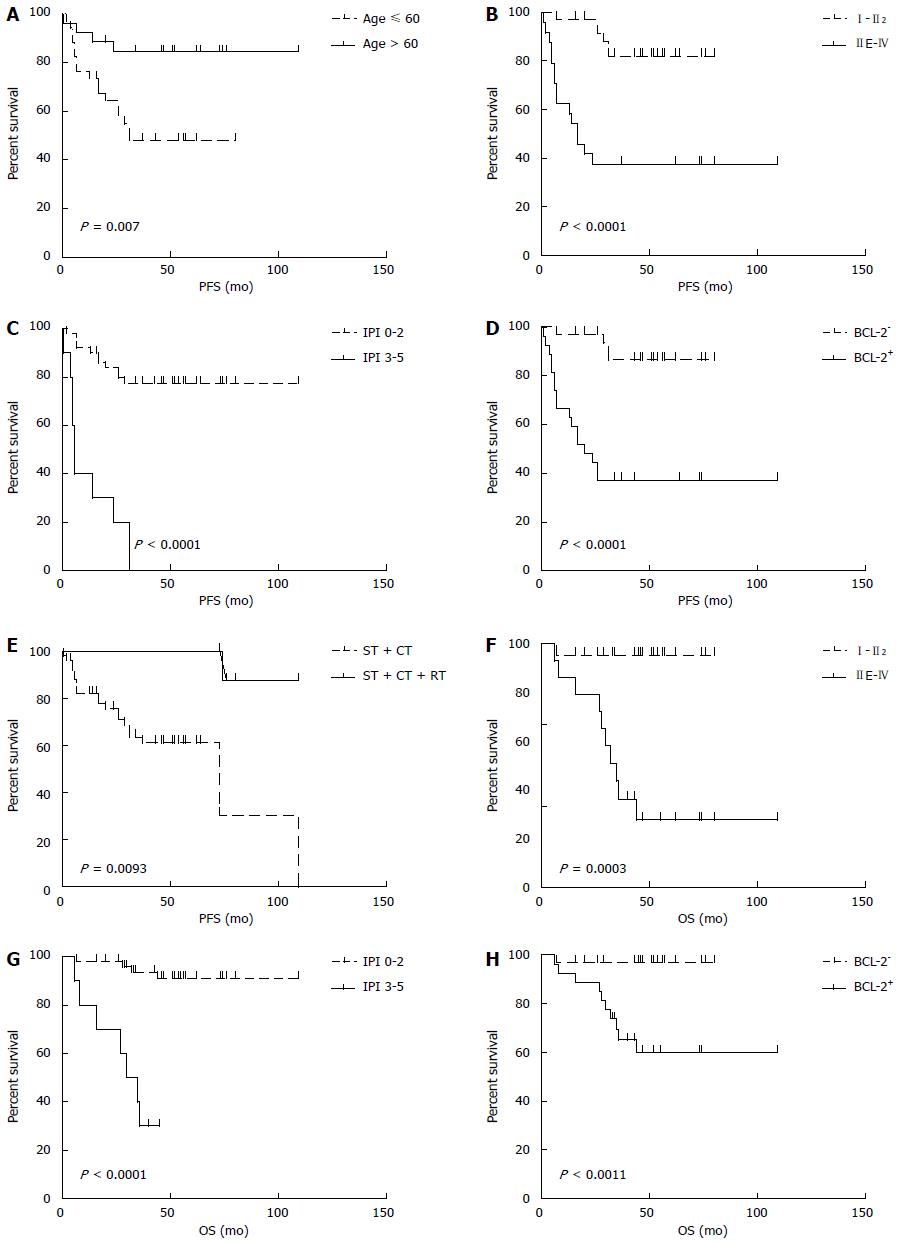
Figure 4 Survival analysis of primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
The effects of age (A), Lugano stage (B), IPI score (C), the expression of BCL-2 protein (D), and treatment (E) on progression-free survival (PFS); And the effects of Lugano stage (F), IPI score (G) and BCL-2 protein expression (H) on overall survival (OS). ST: Surgery; CT: Chemotherapy; RT: Radiotherapy; IPI: International prognostic index.
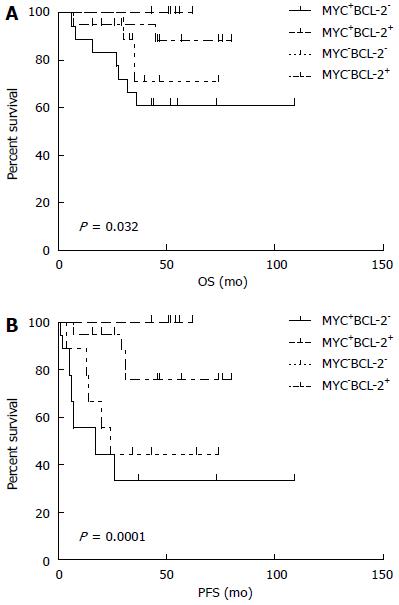
Figure 5 Kaplan-Meier curves represent overall survival (OS) (A) and progression-free survival (B) according to presence of MYC and BCL-2 protein expression.
OS: Overall survival; PFS: Progression-free survival.
-
Citation: Xia B, Zhang L, Guo SQ, Li XW, Qu FL, Zhao HF, Zhang LY, Sun BC, You J, Zhang YZ. Coexpression of
MYC andBCL-2 predicts prognosis in primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(8): 2433-2442 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i8/2433.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2433