Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2015; 21(48): 13566-13573
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13566
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13566
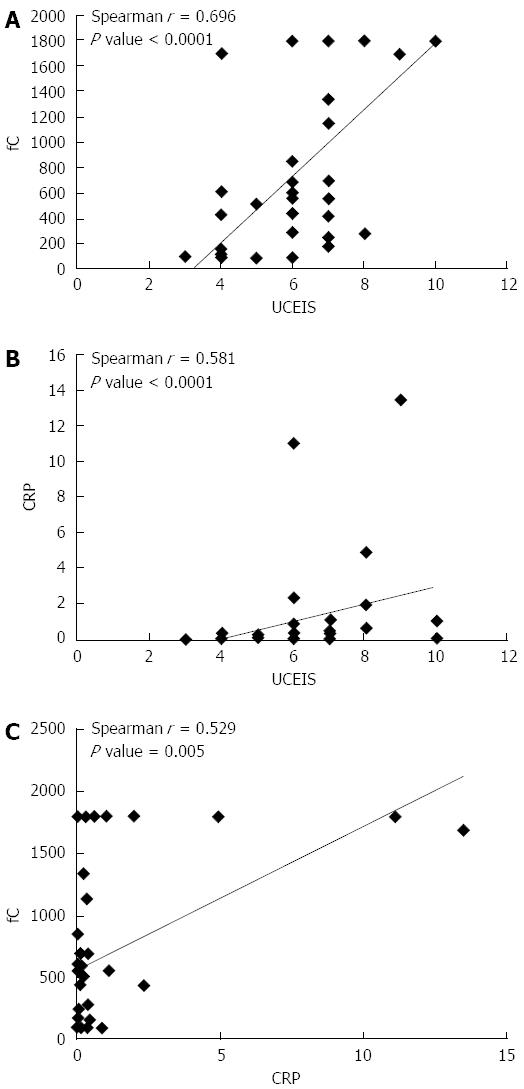
Figure 1 Correlations between (A) UCEIS and fecal calprotectin, (B) UCEIS and CRP, and (C) fecal calprotectin and CRP in ulcerative colitis patients.
UCEIS: Ulcerative colitis endoscopic index of severity; CRP: C-reactive protein; fC: Fecal calprotectin.
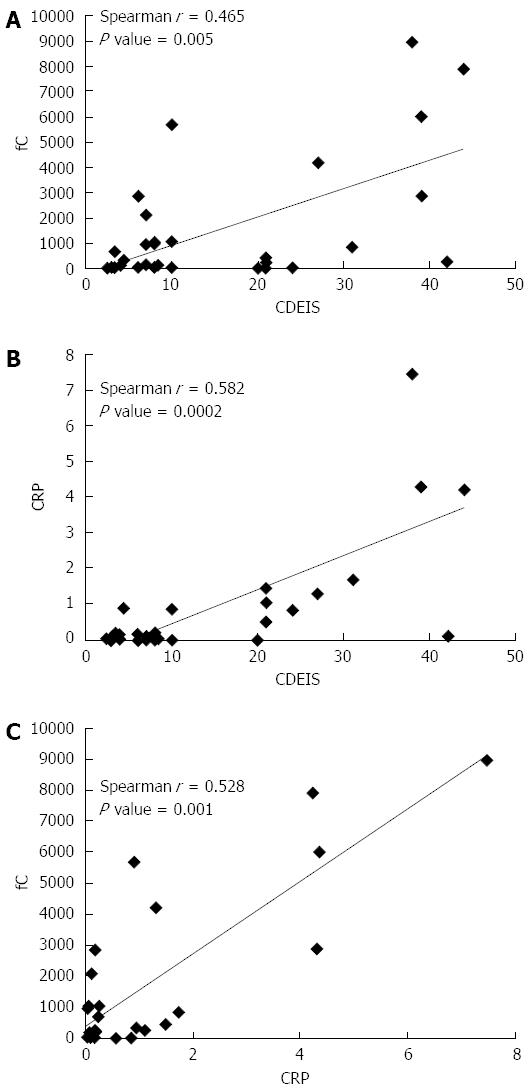
Figure 2 Correlations between (A) CDEIS and fecal calprotectin, (B) CDEIS and CRP, and (C) fecal calprotectin and CRP in Crohn's disease patients.
CDEIS: Crohn's disease endoscopic index of severity; CRP: C-reactive protein; fC: Fecal calprotectin.
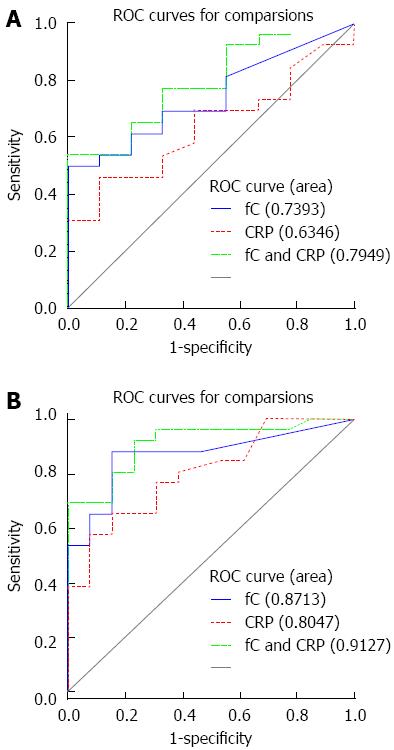
Figure 3 Comparison of receiver operating characteristic curves for Crohn's disease (A) and ulcerative colitis (B) patients.
ROC: Receiver operating characteristic. CRP: C-reactive protein; fC: Fecal calprotectin.
- Citation: Lin WC, Wong JM, Tung CC, Lin CP, Chou JW, Wang HY, Shieh MJ, Chang CH, Liu HH, Wei SC, Taiwan Society of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Multicenter Study. Fecal calprotectin correlated with endoscopic remission for Asian inflammatory bowel disease patients. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(48): 13566-13573
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i48/13566.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13566