Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2015; 21(44): 12696-12708
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12696
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12696
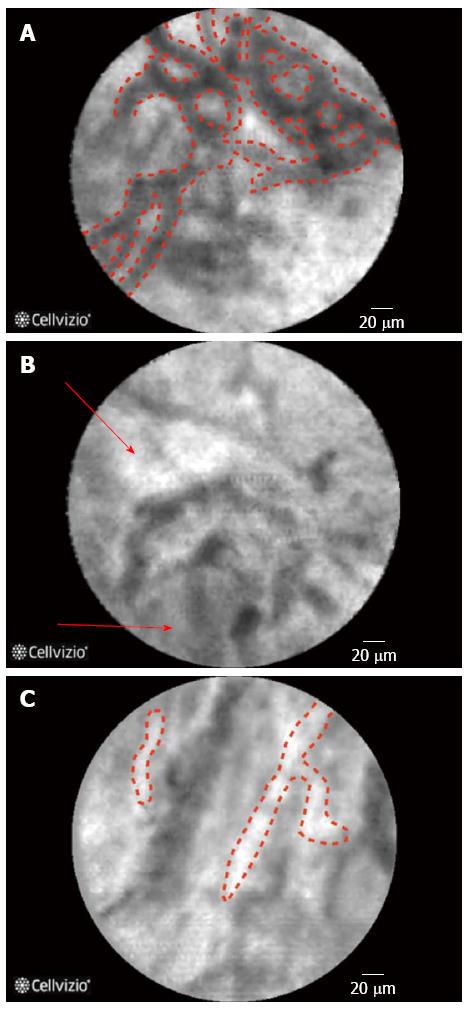
Figure 1 Confocal laser endomicroscopy images for a normal bile duct.
A: Reticular network of thin dark branching bands (< 20 μm); B: Light grey background; C: Normal blood vessels (< 20 μm).
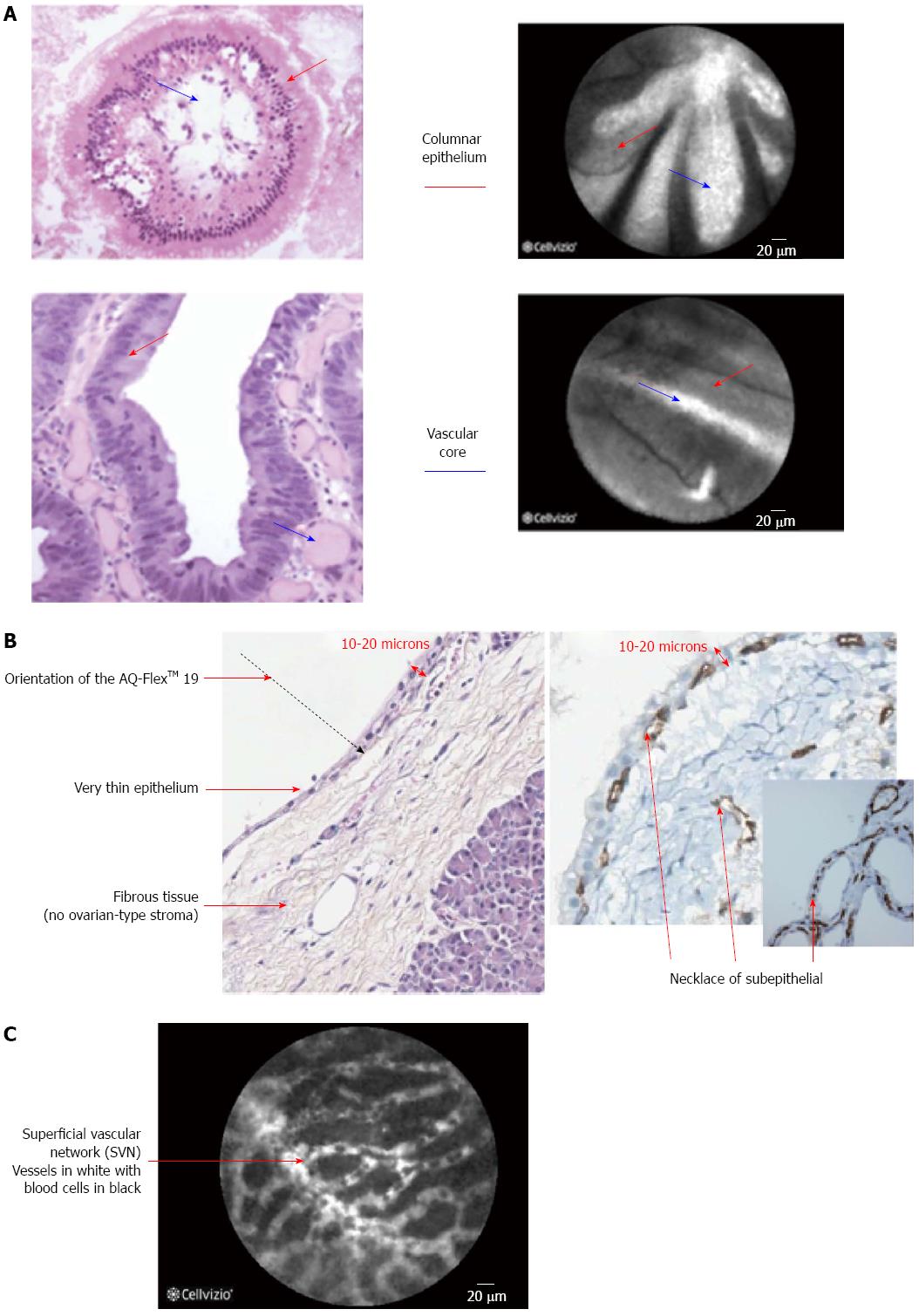
Figure 2 Wall of the intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms is composed of villous structures consisting of columnar epithelium and a vascular core (A); Histological specimen of a serous cystadenoma that is composed of a thin epithelium lining and underlying fibrous tissue and is characterized by the presence of a necklace of subepithelial vessels all around the cyst (B); Confocal laser endomicroscopy image of a serous cystadenoma (C).
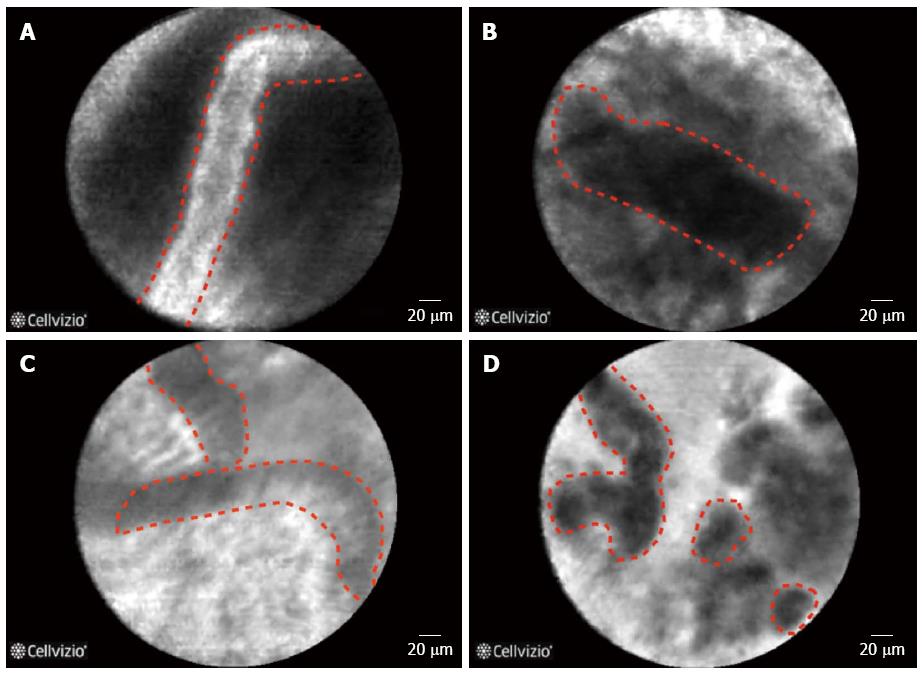
Figure 3 Features of malignant bile duct strictures on confocal laser endomicroscopy.
A: Thick white bands (> 20 μm); B: Thick dark bands (> 40 μm); C: Epithelium; D: Dark clumps.
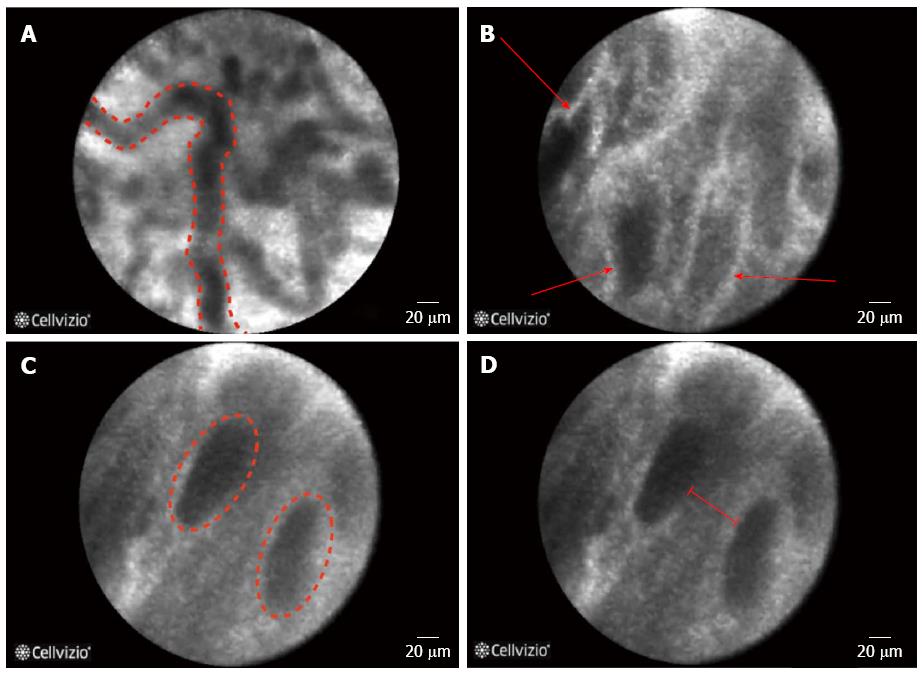
Figure 4 Features of inflammatory bile duct strictures on confocal laser endomicroscopy.
A: Thickened reticular structures; B: Multiple white bands; C: Dark granular pattern in scales; D: Increased spaces between scales.
- Citation: Almadi MA, Neumann H. Probe based confocal laser endomicroscopy of the pancreatobiliary system. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(44): 12696-12708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i44/12696.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12696