Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2015; 21(44): 12653-12659
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12653
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12653
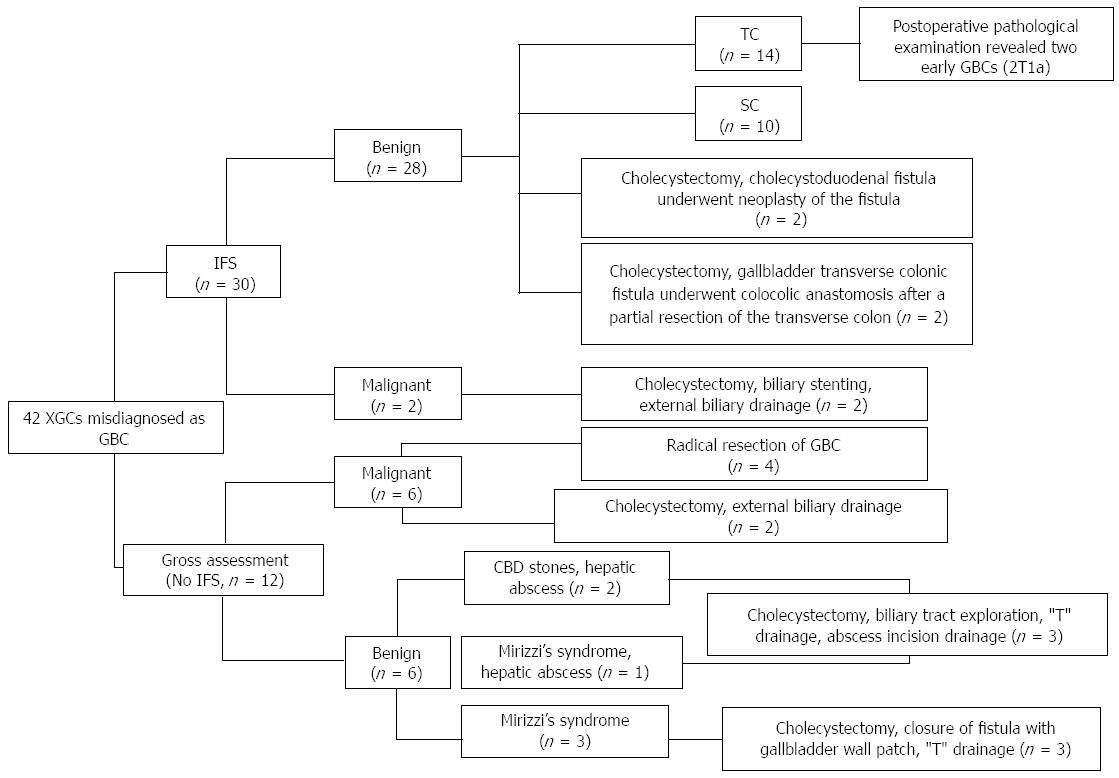
Figure 1 The surgical procedures for the 42 cases of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis.
XGC: Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis; GBC: Gallbladder carcinoma; IFS: Intra-operative frozen section analysis; TC: Total cholecystectomy; SC: Subtotal cholecystectomy; CBD: Common bile duct.
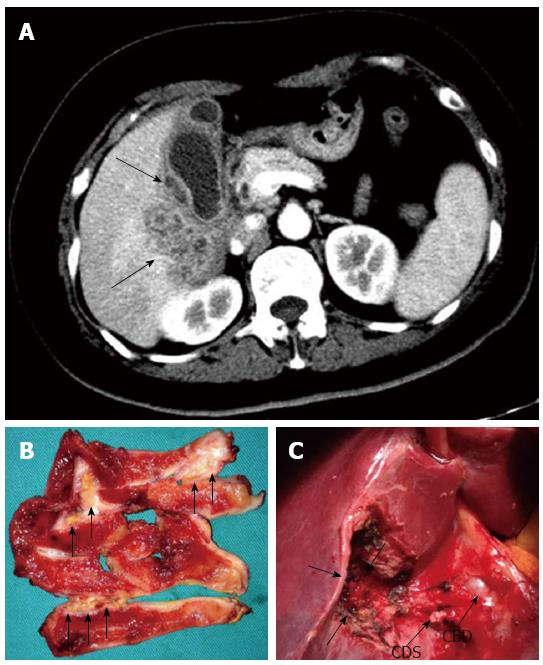
Figure 2 A 50-year-old woman with xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis misdiagnosed as gallbladder carcinoma based on computed tomography findings.
A: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography shows the diffuse gallbladder wall thickening with intramural hypo-attenuated nodules (arrows) and heterogeneous enhancement in hepatic parenchyma neighboring gallbladder, indicating gallbladder carcinoma with direct liver invasion; B: Macroscopic examination of gallbladder specimen revealed multiple yellow nodules and bands in the wall (arrows). The gallbladder was sent for intra-operative frozen section (FS) analysis and demonstrated inflammatory lesions; C: Based on the FS diagnosis, a simple cholecystectomy was performed. Note that no macroscopic hepatic invasion was found (arrows). Ultimately, xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis was diagnosed by the pathological examination. CDS: Cystic duct stump; CBD: Common bile duct.
- Citation: Deng YL, Cheng NS, Zhang SJ, Ma WJ, Shrestha A, Li FY, Xu FL, Zhao LS. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis mimicking gallbladder carcinoma: An analysis of 42 cases. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(44): 12653-12659
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i44/12653.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12653