Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2015; 21(43): 12457-12467
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12457
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12457
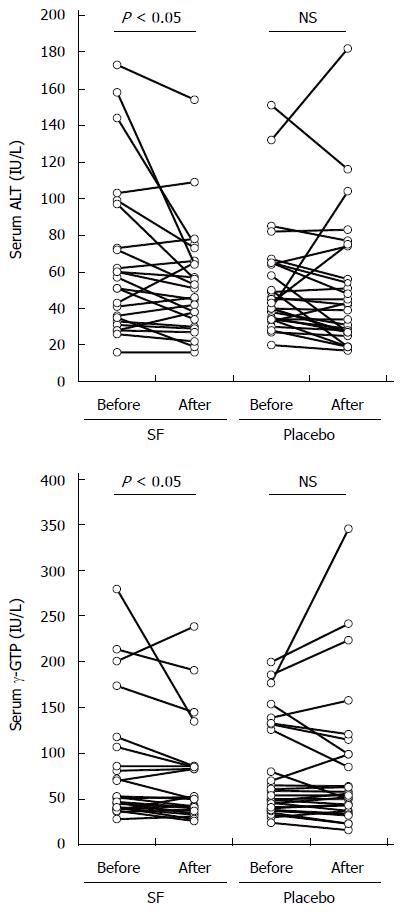
Figure 1 Effect of supplementation with broccoli sprout extract containing the sulforaphane precursor glucoraphanin on liver function markers in male participants with hepatic abnormalities.
A, B: Serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GTP) in sulforaphane (SF) and placebo group participants (n = 24 and 28, respectively) before and after 2 mo of intervention. Each line between the circle symbols represents individual change in serum levels of ALT and γ-GTP. P values were analyzed by using the Wilcoxon single rank test.
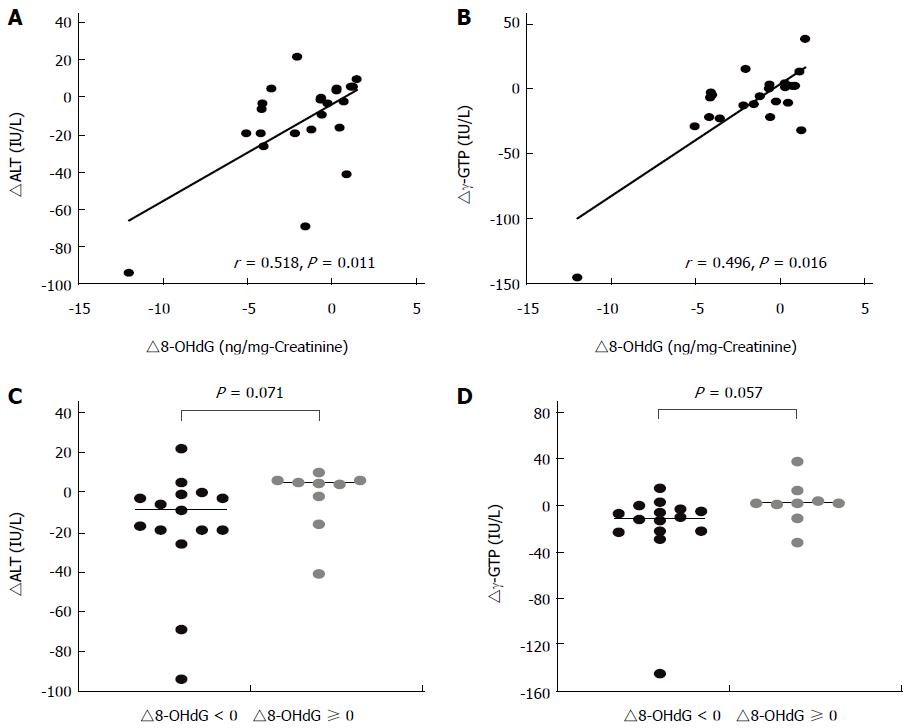
Figure 2 Parallel improvements of an oxidative stress marker and liver function markers in sulforaphane group participants.
A, B: Change levels of liver function markers, alanine aminotransferase and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (∆ALT and ∆γ-GTP) were respectively plotted against changes in levels of urinary 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (∆8-OHdG), an in vivo oxidative stress marker, in SF group participants (n = 24). Each circle represents individual data. Spearman r and P were determined; C, D: ∆ALT and ∆γ-GTP were compared between participants with ∆8-OHdG < 0 (n = 15) and ∆8-OHdG ≥ 0 (n = 9). Each circle symbol represents an individual data point. Bars in graphs represent median values. P values were obtained by using the Mann-Whitney U test.
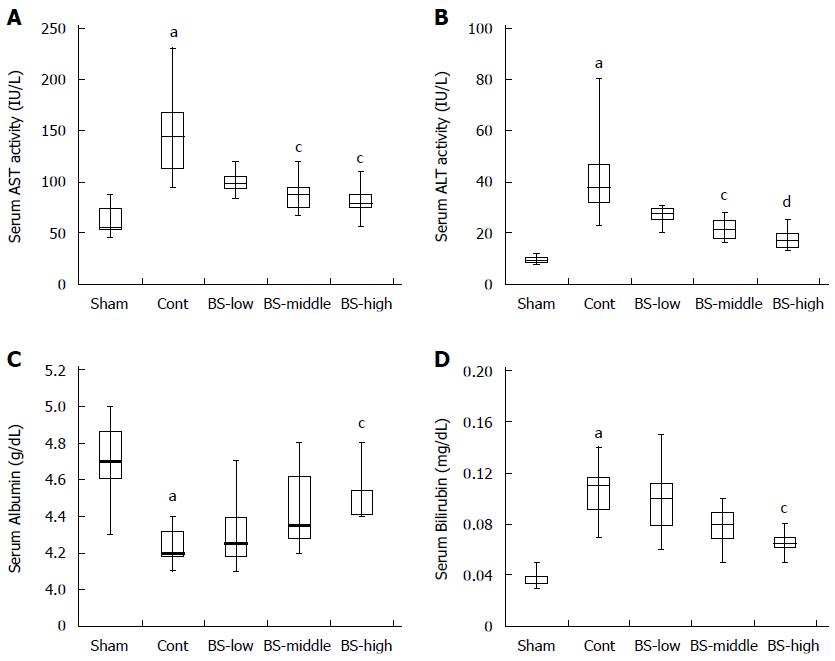
Figure 3 Effects of intake of broccoli sprout extract on liver function markers in serum from N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced chronic liver failure model rats.
A, B: Serum activities of aspartate-aminotransferases (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in male Sprague-Dawley rats who had received an AIN-76 diet containing no (sham, n = 6 and control, n = 8) or different amounts of BS extract at glucoraphanin (GR) doses of 62.5, 125, and 250 mg per 100 g diet (BS-low, BS-middle, and BS-high, respectively, n = 8) for 4 wk. All rats, except for the sham group, were intraperitoneally injected with N-nitrosodimethylamine (5 mg per kg body weight) on 3 consecutive days of the week for 4 wk; C, D: Serum levels of albumin and bilirubin in the rats. Data are shown as boxplots representing the minimum (bottom of the bar), 25th percentile (bottom of the box), median (horizontal line), 75th percentile (top of the box), and the maximum observations (top of the bar). aP < 0.05 vs sham; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs control (Steel-Dwass test). BS: Broccoli sprout.
Figure 4 Effects of intake of broccoli sprout extract on oxidative stress and enzyme activity of glutathione S-transferase in livers from N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced chronic liver failure model rats.
A: Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) levels were determined in livers from serum activities of alanine aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in male Sprague-Dawley rats who had received an AIN-76 diet containing no (sham, n = 6 and control, n = 8) or different amount of BS extract at glucoraphanin (GR) doses of 62.5, 125, and 250 mg per 100 g diet (BS-low, BS-middle, and BS-high, respectively, n = 8) for 4 wk. All rats, except for sham group, were intraperitoneally injected with NDMA (5 mg per kg body weight) in 3 consecutive days of the week for 4 wk; B: GST activities in rat livers were determined with 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) as substrate. Data are shown as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs sham, dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs control (A: Tukey Kramer; B: Dunnett test).
- Citation: Kikuchi M, Ushida Y, Shiozawa H, Umeda R, Tsuruya K, Aoki Y, Suganuma H, Nishizaki Y. Sulforaphane-rich broccoli sprout extract improves hepatic abnormalities in male subjects. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(43): 12457-12467
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i43/12457.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12457