Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2015; 21(43): 12322-12333
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12322
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12322
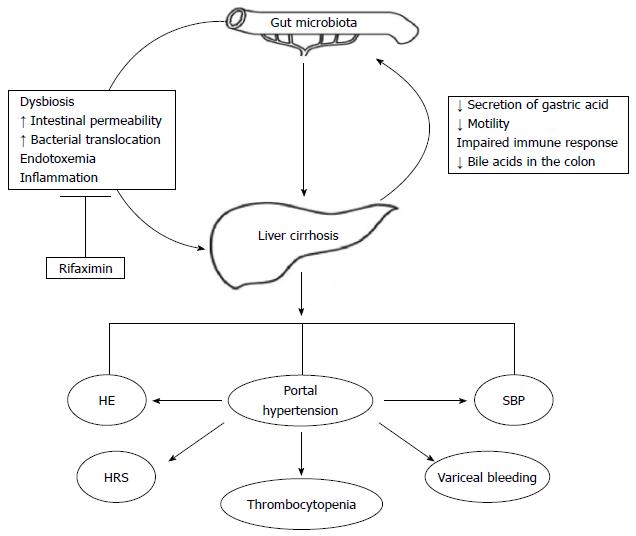
Figure 1 Effects of Rifaximin on gut-liver axis.
Rifaximin decreases endotoxemia and inflammation both directly and indirectly, by reducing bacterial translocation, counteracting bacterial overgrowth and modulating gut microbiota composition and function. Due to these peculiar effects, rifaximin is used for the treatment of advanced liver disease complications. HE: Hepatic encephalopathy; SIBO: Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth; SBP: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; HRS: Hepatorenal syndrome.
- Citation: Ponziani FR, Gerardi V, Pecere S, D’Aversa F, Lopetuso L, Zocco MA, Pompili M, Gasbarrini A. Effect of rifaximin on gut microbiota composition in advanced liver disease and its complications. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(43): 12322-12333
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i43/12322.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12322