Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2015; 21(35): 10200-10207
Published online Sep 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10200
Published online Sep 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10200
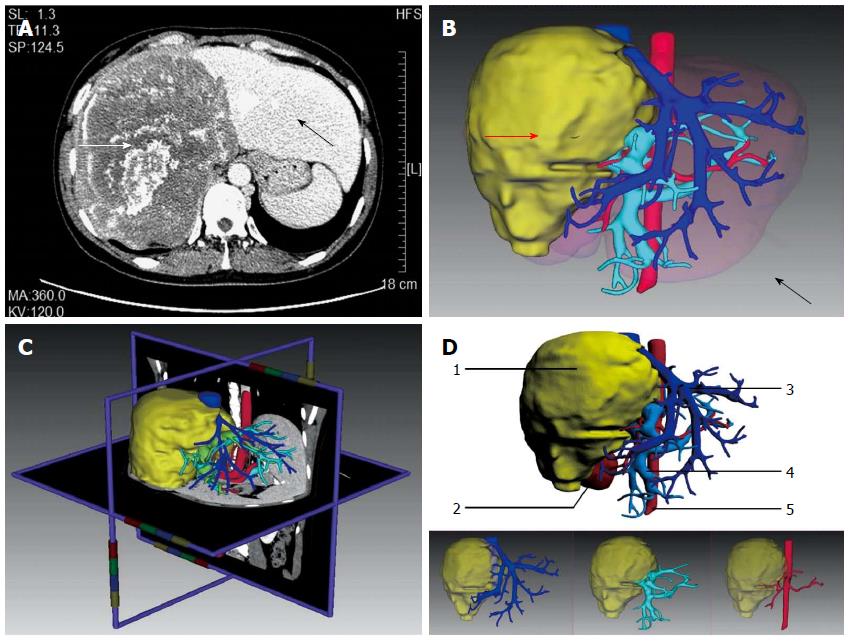
Figure 1 3D reconstruction and anatomical analysis.
A: Diagnosis of giant hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (HAE) by computed tomography; B: 3D reconstruction model of a liver showing the lesion (red arrow) and normal liver (black arrow); C: Real-time correction between the 3D model and 2D image; D: 3D reconstruction model of a liver showing the lesion as well as intrahepatic biliary and vascular networks. 1: Lesion; 2: Right kidney; 3: Hepatic vein (deep blue); 4: Portal vein (light blue); 5: Abdominal aorta (red).
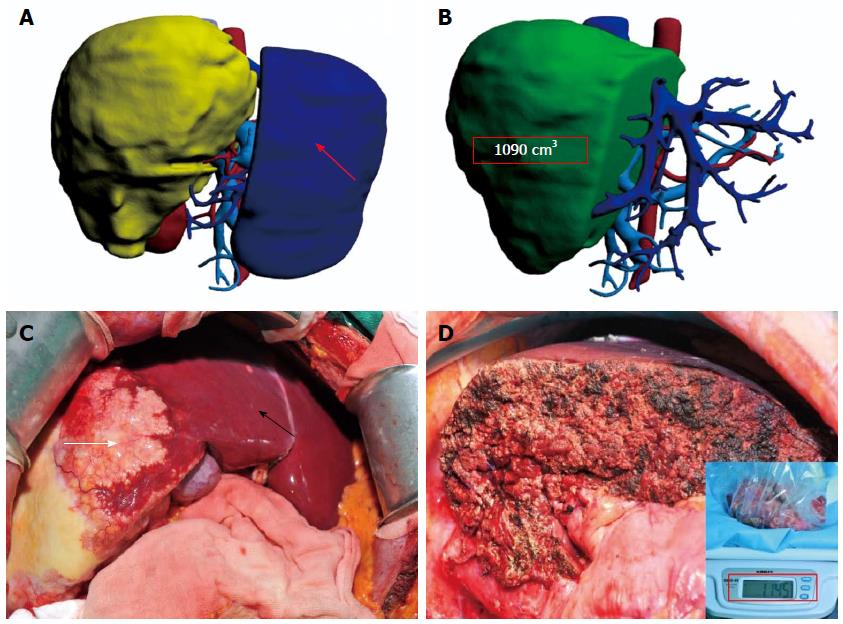
Figure 2 Liver.
A: 3D model of a liver showing virtual surgery and the remnant liver (red arrow); B: Remnant liver volume calculated in virtual surgery (1090 cm3); C: Actual surgery showing the lesion (the lesion and normal liver are marked by a white and a black arrow, respectively); D: Remnant liver in actual surgery (1145 g).
- Citation: He YB, Bai L, Aji T, Jiang Y, Zhao JM, Zhang JH, Shao YM, Liu WY, Wen H. Application of 3D reconstruction for surgical treatment of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(35): 10200-10207
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i35/10200.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10200