Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2015; 21(33): 9785-9792
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9785
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9785
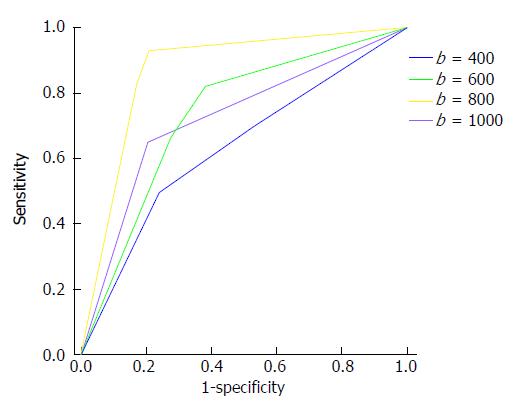
Figure 1 Accuracy of diffusion-weighted imaging hyperintensity from various b values to detect endoscopic inflammation.
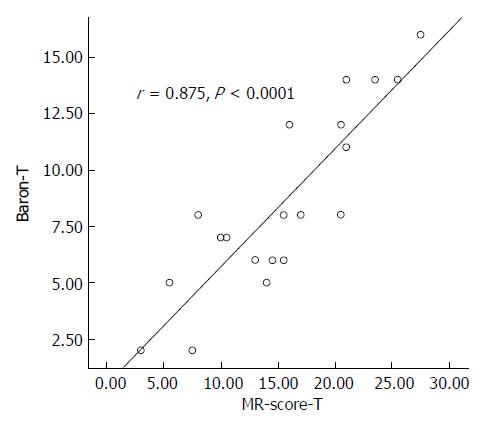
Figure 2 Correlation between total magnetic resonance score and total modified Baron score.
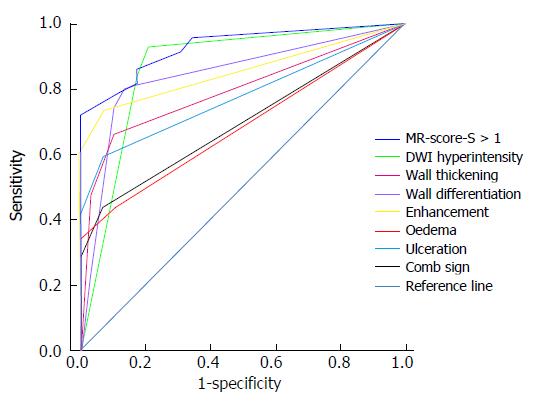
Figure 3 Accuracy of segmental magnetic resonance score and seven signs indicating endoscopic inflammation.
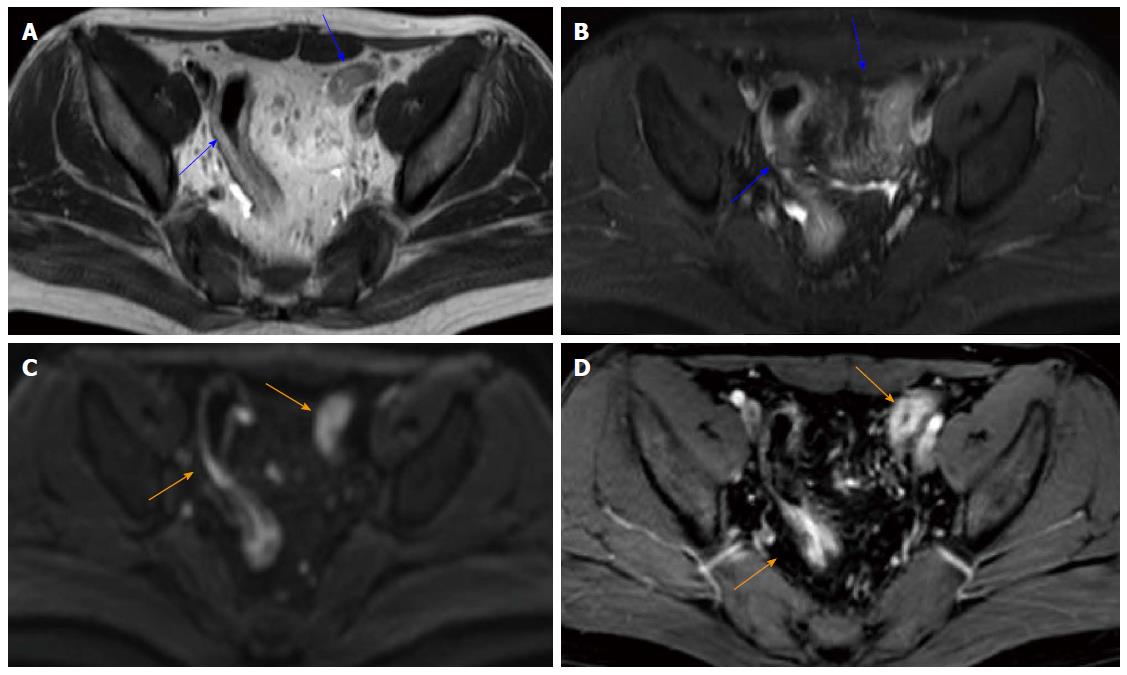
Figure 4 A 22-year-old woman with known ulcerative colitis involving the rectum and the sigmoid colon.
Mayo index = 8; total modified Baron score = 12; total MR-score = 22; T2WI without fat saturation (A) and T2WI with fat saturation (B) show a mild thickening of the sigmoid colon wall (blue arrows); DWI hyperintensity (C; b = 800 s/mm2; orange arrows); rapid gadolinium enhancement (D; orange arrows).
- Citation: Yu LL, Yang HS, Zhang BT, Lv ZW, Wang FR, Zhang CY, Chen WB, Zhang HM. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging without bowel preparation for detection of ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(33): 9785-9792
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i33/9785.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9785