Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2015; 21(32): 9588-9597
Published online Aug 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9588
Published online Aug 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9588
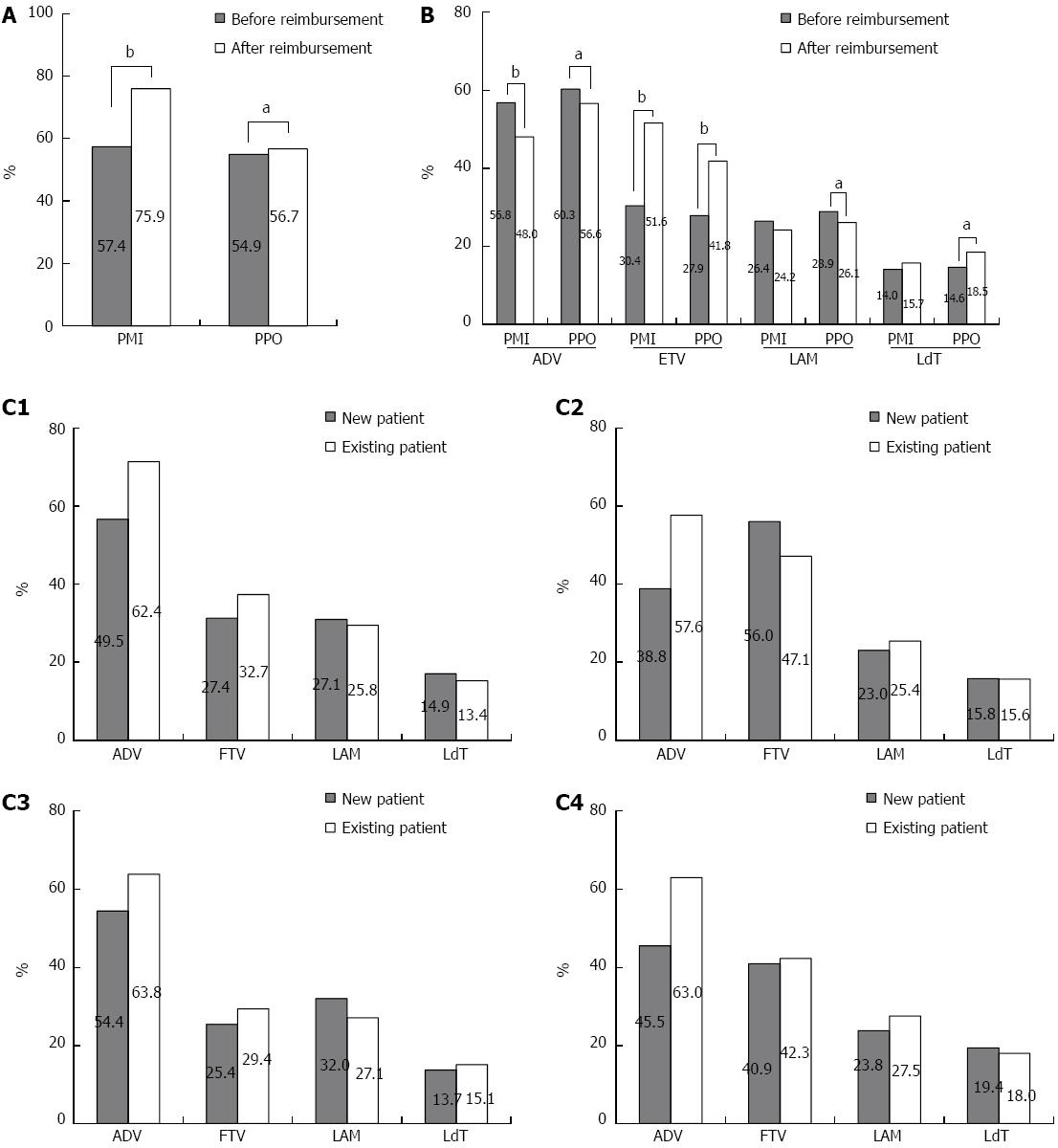
Figure 1 Antiviral agent utilization before and after reimbursement for patients with different characteristics.
A: Antiviral agent utilization before and after reimbursement for patients with different insurance types; B: Utilization of different NAs for PMI vs PPO before and after reimbursement C1: Utilization of specific antiviral among new and existing PMI before reimbursement; C2: Utilization of specific antiviral among new and existing PMI after reimbursement; C3: Utilization of specific antiviral among new and existing PPO before reimbursement; C4: Utilization of specific antiviral among new and existing PPO after reimbursement. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, before reimbursement vs after reimbursement. PMI: Patients with medical insurance; PPO: Patients paid out-of-pocket.
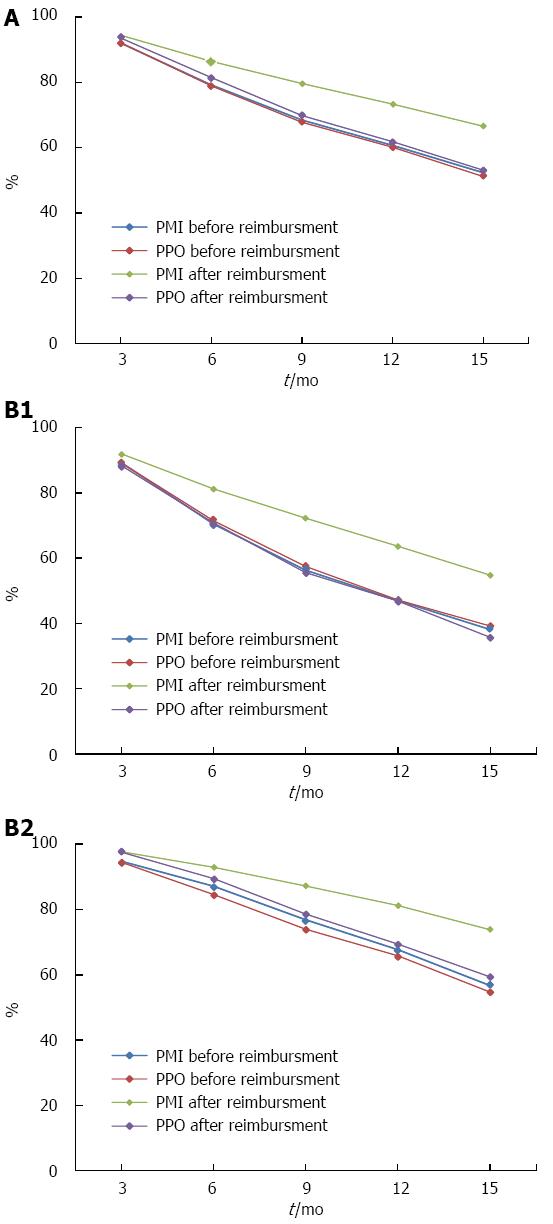
Figure 2 Persistence rate before and after reimbursement for patients with different characteristics.
A: Persistence rate before and after reimbursement for patients with different insurance types; B1: Persistence rate for new patients with different insurance types; B2: Persistence rate for existing patients with different insurance types. PMI: Patients with medical insurance; PPO: Patients who paid out-of-pocket.
- Citation: Qiu Q, Duan XW, Li Y, Yang LK, Chen Y, Li H, Duan ZP, Wang L. Impact of partial reimbursement on hepatitis B antiviral utilization and adherence. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(32): 9588-9597
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i32/9588.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9588