Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2015; 21(31): 9403-9412
Published online Aug 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9403
Published online Aug 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9403
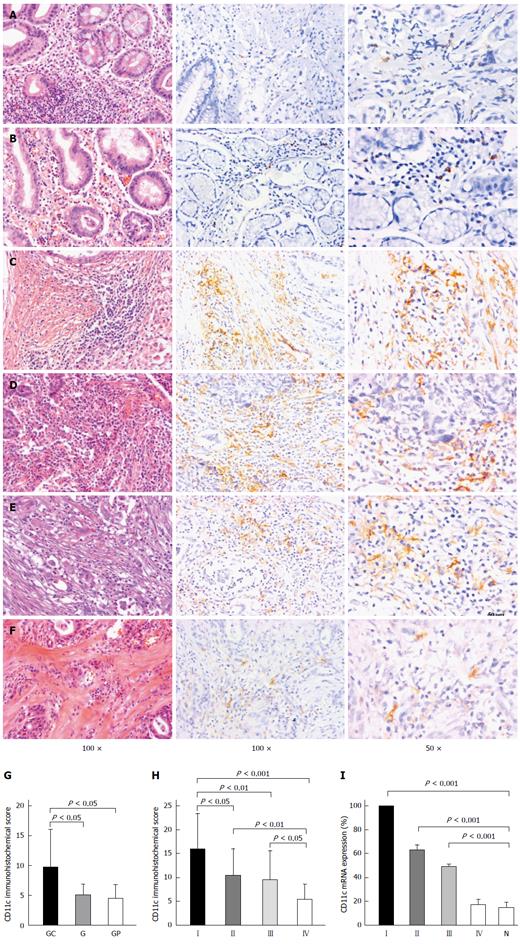
Figure 1 Validation of differentially expressed CD11c by IHC (magnification × 100) and qRT-PCR.
Representative IHC for gastritis tissues (A), gastric polyp tissues (B) and gastric cancer tissues at different stages I-IV (C-F) showed that high CD11c expression was present in UICC stage I, and the stain density of CD11c decreased progressively from UICC stage I to stage IV. CD11c showed differential expression in gastric cancer, gastritis, and gastric polyp tissues and the stain density of CD11c was significantly increased in gastric cancer tissue compared with gastritis and gastric polyp tissues (G). The expression of CD11c progressively decreased from UICC stage I to UICC stage IV (H). qRT-PCR using mRNA from gastric cancer at UICC stages I-IV and normal gastric tissue was conducted. Using CD11c expression of UICC stage I as 100%, CD11c expression levels were significantly different at UICC stages I-III compared with normal gastric tissue (I). GC: Gastric cancer; G: Gastritis; GP: Gastric polyp; N: Normal gastric tissue.
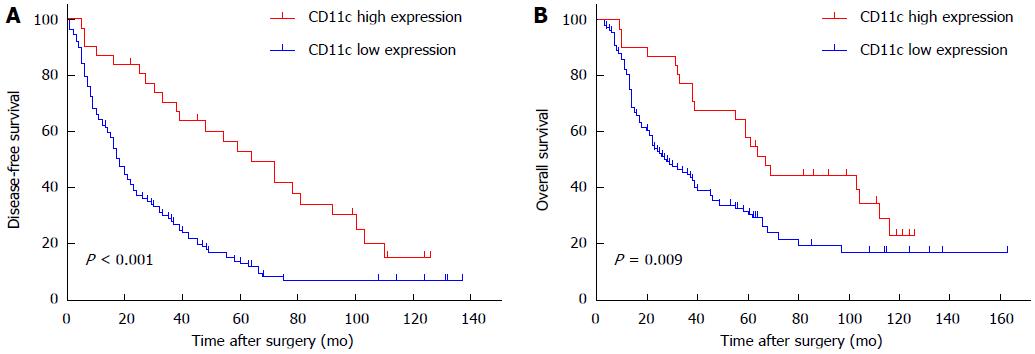
Figure 2 CD11c expression in gastric cancer tissues correlates with survival rate of patients.
Based on the minimum P value observed, patients were divided into two groups with low or high CD11c expression, respectively. The DFS of patients with low and high CD11c expression was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. Log-rank: P < 0.001 (A). The OS of patients with low and high CD11c expression was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. Log-rank: P = 0.009 (B).
- Citation: Wang Y, Xu B, Hu WW, Chen LJ, Wu CP, Lu BF, Shen YP, Jiang JT. High expression of CD11c indicates favorable prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(31): 9403-9412
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i31/9403.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9403