Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2015; 21(31): 9273-9285
Published online Aug 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9273
Published online Aug 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9273
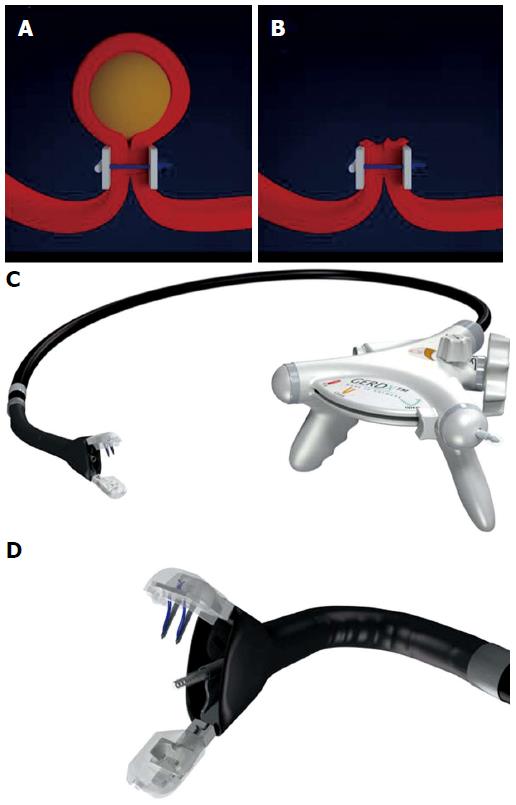
Figure 1 Endoscopic full-thickness resection with prior transmural suturing.
A: Transmural sutures are placed underneath a subepithelial tumor (schematic illustration); B: The sutures are securing gastric wall patency after full-thickness resection; C: The GERDXTM device (G-Surg, Seeon, Germany); D: The tip of GERDXTM device with opened branches and the central tissue retractor.
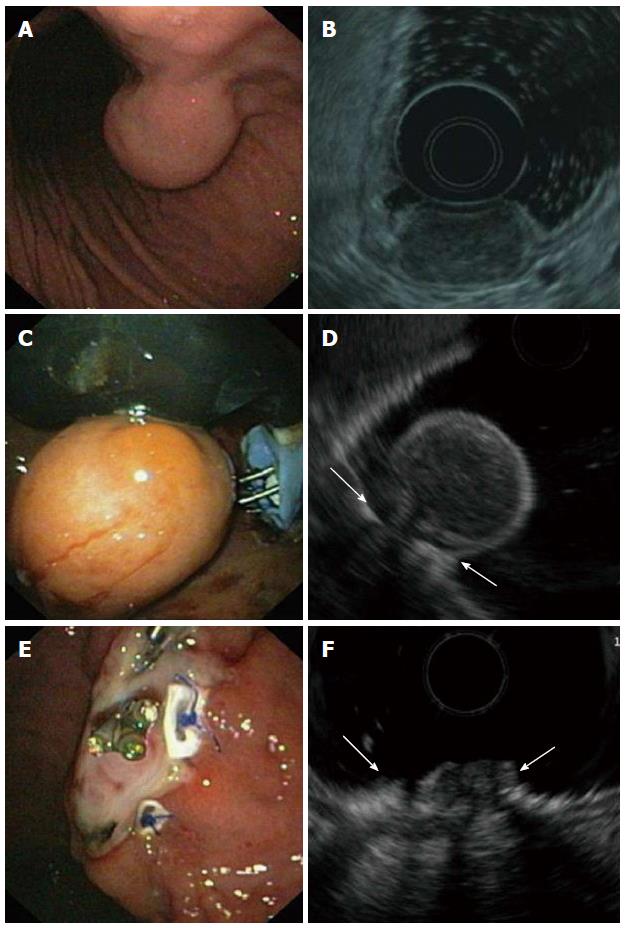
Figure 2 Endoscopic full-thickness resection of a gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors after prior transmural suturing.
A: Endoscopic image of the subepithelial tumor in the gastric corpus; B: EUS-image showing an inhomogeneous tumor arising from the muscularis propria; C: Two transmural sutures are deployed underneath the tumor using the PlicatorTM suturing device; D: EUS image after suturing. The PTFE pledges are indicated with arrows; E: Resection site. The transmural sutures are securing gastric wall patency; F: EUS image of the resection site. The PTFE pledges are indicated with arrows. EUS: Endoscopic ultrasonography.
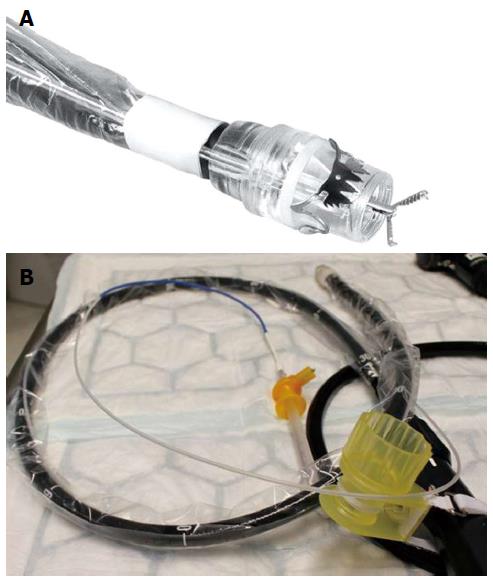
Figure 3 Full thickness resection device (Ovesco Endoscopy, Tuebingen, Germany).
A: Tip of a colonoscope with the mounted FTRD. A grasping forceps is advanced through the working channel of the scope; B: The assembled FTRD on a colonoscopy. FTRD: Full thickness resection device.
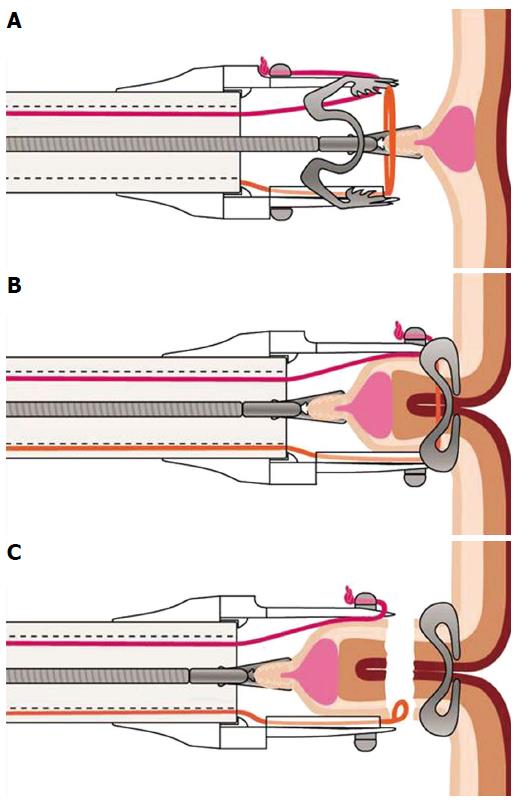
Figure 4 Schematic image of the resection procedure with the full-thickness resection device.
A: The lesion is grasped with a forceps and pulled into the cap thereby creating a full-thickness duplication of the colonic wall; B: The over-the-scope clip is deployed; C: The tissue above the clip is resected with the integrated snare.
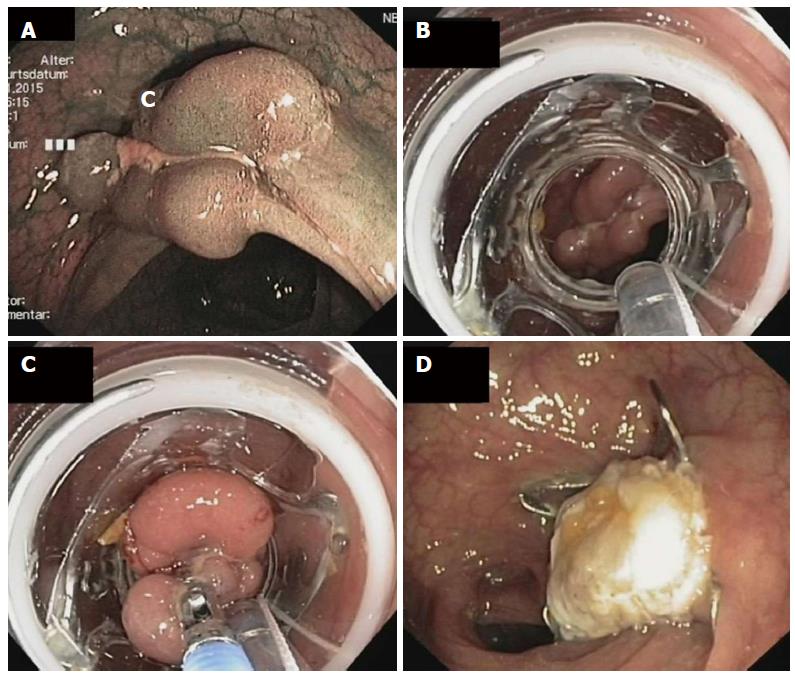
Figure 5 Endoscopic full thickness resection of a non-lifting recurrent adenoma in a patient with a polyposis syndrome.
A: Endoscopic image showing a polypoid and centrally depressed non-lifting adenoma (2.5 cm) in the sigmoid (Narrow band imaging mode); B: View with the mounted full thickness resection device (FTRD, Ovesco Endoscopy, Tübingen, Germany); C: The lesion is pulled into the cap with a forceps; D: Resection site. The over-the-scope clip is securing gastric wall patency.
- Citation: Schmidt A, Meier B, Caca K. Endoscopic full-thickness resection: Current status. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(31): 9273-9285
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i31/9273.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9273