Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2015; 21(30): 9002-9020
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9002
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9002
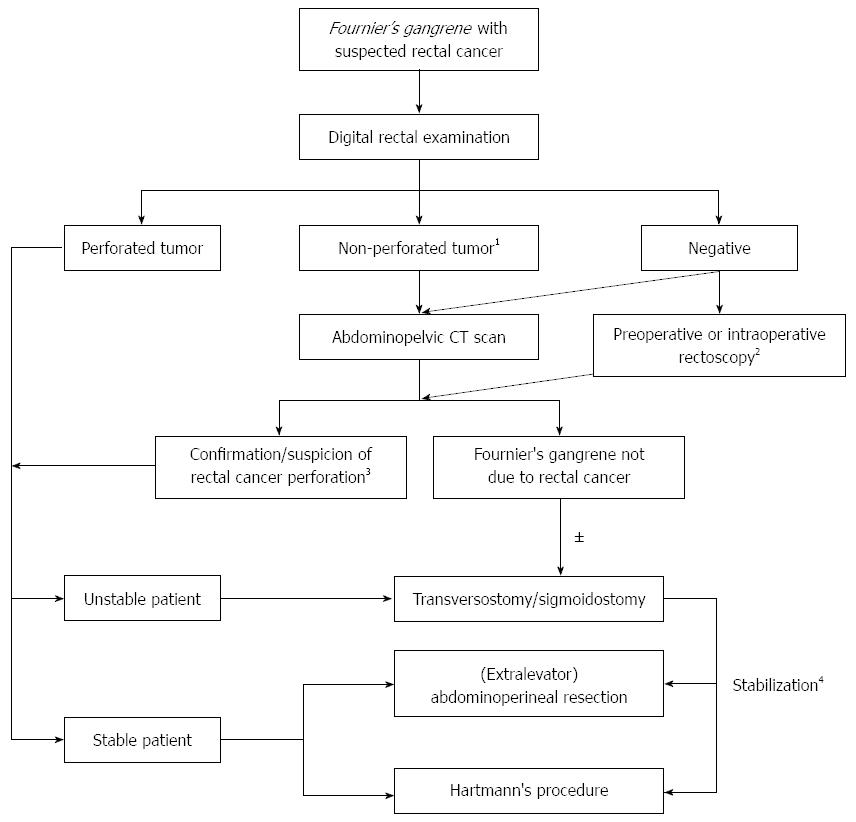
Figure 1 Diagnostic-therapeutic algorithm for suspected/proven Fournier’s gangrene due to rectal cancer.
Perioperative management and necrosectomy are excluded which are standard procedures in Fournier’s gangrene treatment in all patients. 1Impalpable perforation does not exclude microperforation; 2(1) Blood (any form) on digital rectal examination; (2) history and other/previous diagnostic modalities refer to rectal carcinoma; (3) urogenital and dermatological causes excluded; (4) bacteria highly specific for (intestinal) rectal malignancy such as Clostridium septicum; and (5) fever or sepsis of unknown origin with perianal symptoms/signs; 3Increased soft tissue density with abscess and/or gas bubbles around the tumor; 4After confirmation of rectal cancer, definitive oncological operation is performed after stabilization and neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy if indicated. Reconstructive surgery after consultation with plastic surgeon.
- Citation: Bruketa T, Majerovic M, Augustin G. Rectal cancer and Fournier’s gangrene - current knowledge and therapeutic options. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(30): 9002-9020
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i30/9002.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9002