Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2015; 21(3): 854-861
Published online Jan 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.854
Published online Jan 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.854
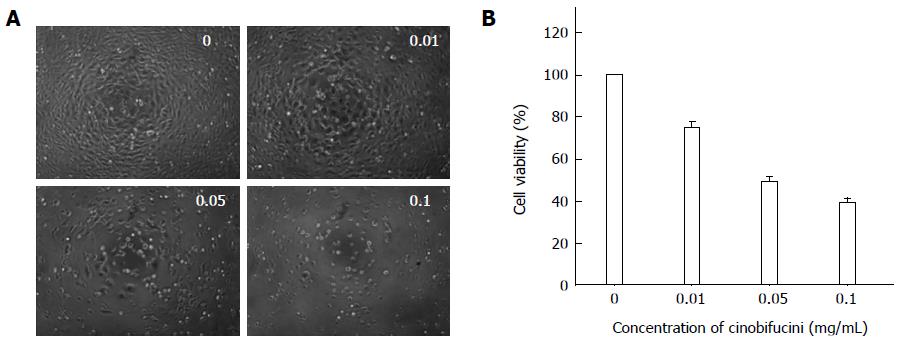
Figure 1 Growth inhibitory effect of cinobufacini on HepG2 cells.
Cells were treated with different concentrations (0-0.1 mg/mL) of cinobufacini for 48 h. A: Changes in morphology observed under a phase microscope; B: Viability of HepG2 cells measured by methylthiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT) assay. The results reveal that the cytotoxic effect of cinobufacini on HepG2 cells was dose dependent. All studies are representative of at least three independent experiments.
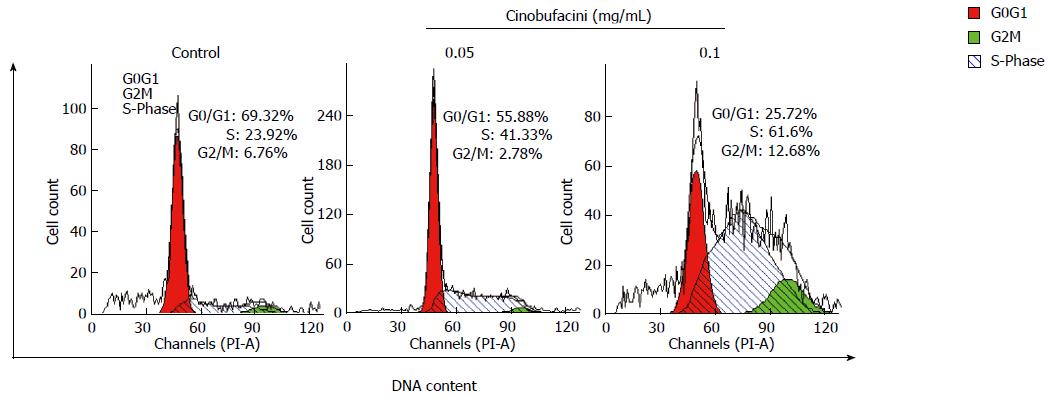
Figure 2 Cell cycle distribution of HepG2 cells analyzed by flow cytometry.
Cells were incubated with cinobufacini (0, 0.05 or 0.1 mg/mL) for 48 h. Cell cycle was arrested at S phase.
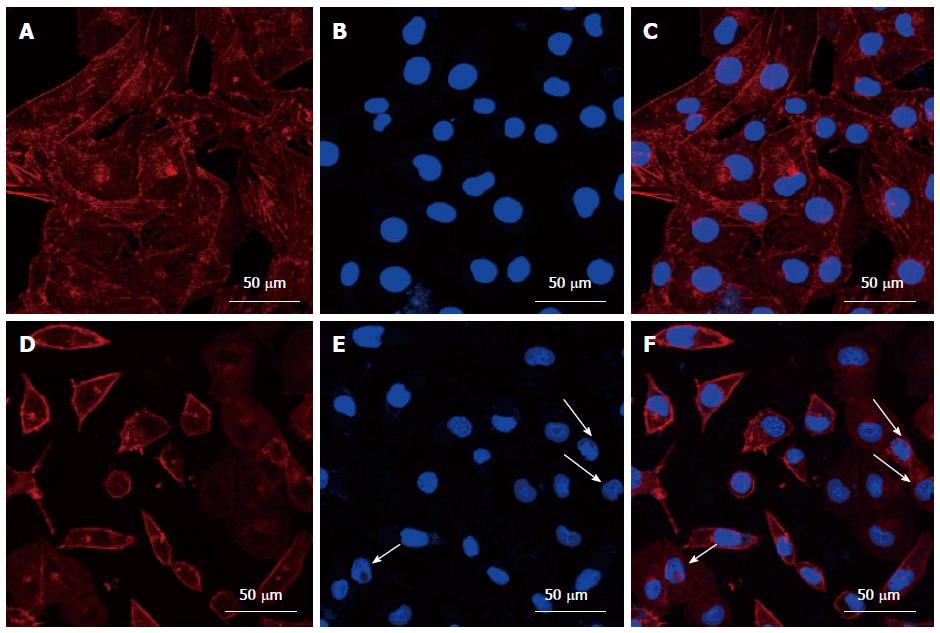
Figure 3 Morphology of the cytoskeleton and nuclei in HepG2 cells before (A-C) and after (D-F) treatment with cinobufacini.
The cytoskeleton and nuclei were stained with rhodamine-phalloidin and DAPI. (C) and (F) were merged images of (A, B) and (D, E). White arrow: Fragmented nuclei.
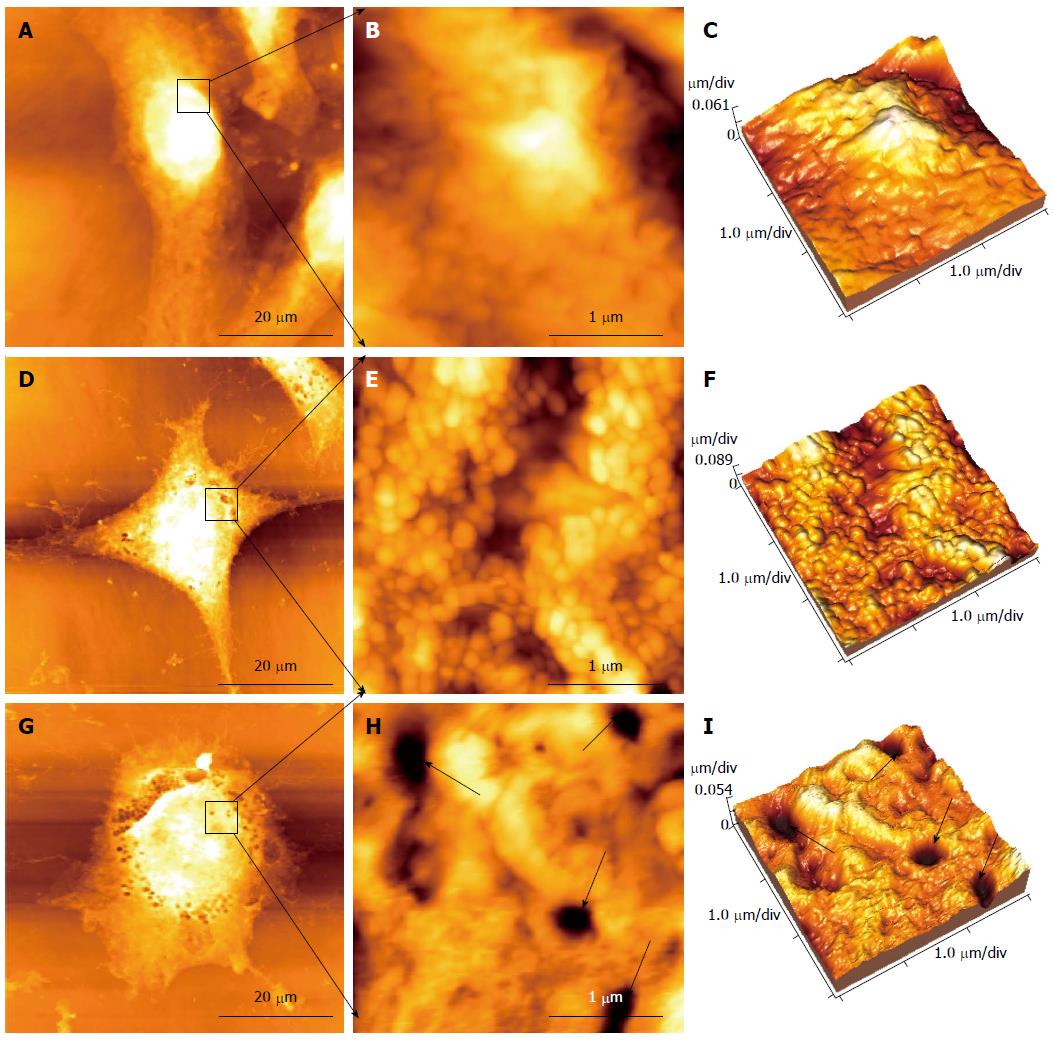
Figure 4 Changes in morphology and ultrastructure of HepG2 cells detected by atomic force microscopy.
A-C: Control HepG2 cells; D-F: HepG2 cells treated with 0.05 mg/mL cinobufacini for 48 h; G-I: HepG2 cells treated with 0.1 mg/mL cinobufacini for 48 h; A, D and G: Morphology of HepG2 cells (60 μm × 60 μm); B, E and H: Ultrastructure images (3 μm × 3 μm) on corresponding cell region indicated by black frame; C, F and I: Corresponding 3D images of ultrastructure in B, E and H. Black arrows: Some pores in the cell membrane.
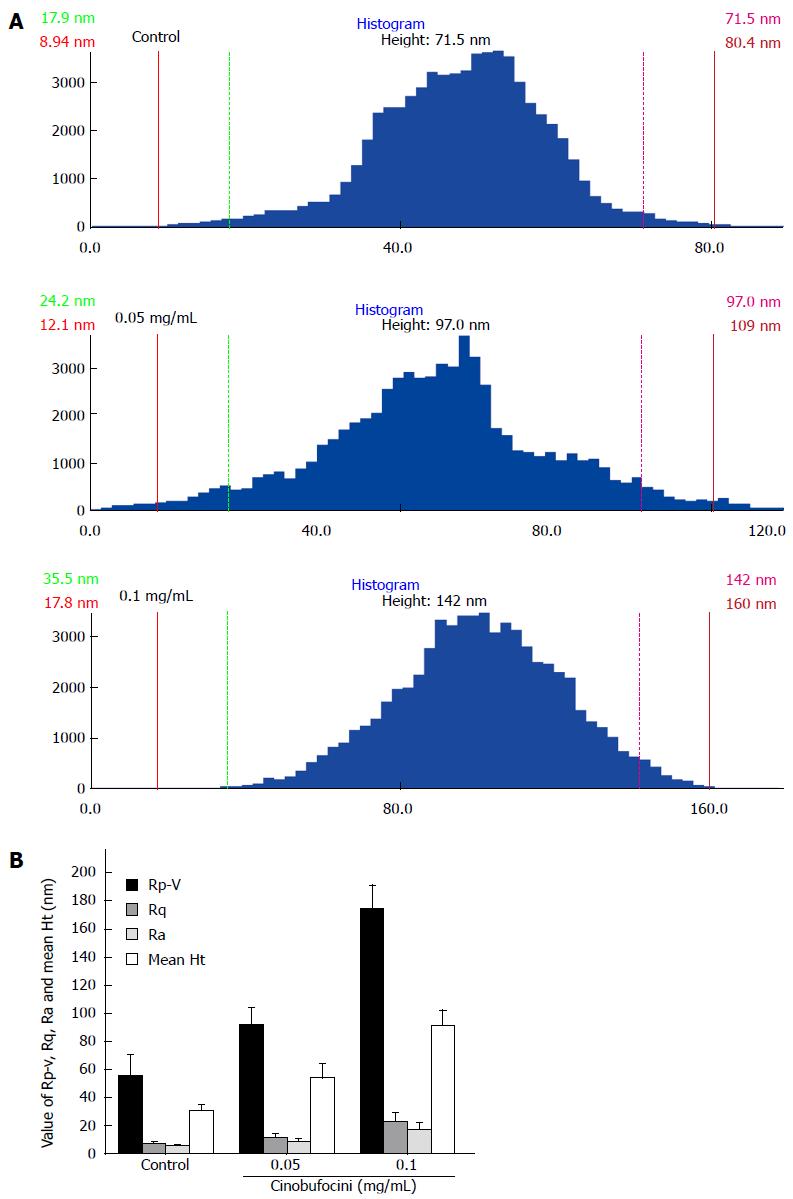
Figure 5 Average size of surface particles on control HepG2 cells.
A: Histograms of cell membrane particle size distributions of ultrastructure in Figure 4; B: Statistical analysis of the membrane Rp-v, Rq, Ra and mean Ht of HepG2 cell surface; these values increased as cinobufacini concentration increased (P = 0.000). The data showed that cinobufacini treatment induced rougher cell membranes.
- Citation: Wu Q, Lin WD, Liao GQ, Zhang LG, Wen SQ, Lin JY. Antiproliferative effects of cinobufacini on human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells detected by atomic force microscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(3): 854-861
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i3/854.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.854