Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2015; 21(26): 8089-8095
Published online Jul 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8089
Published online Jul 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8089
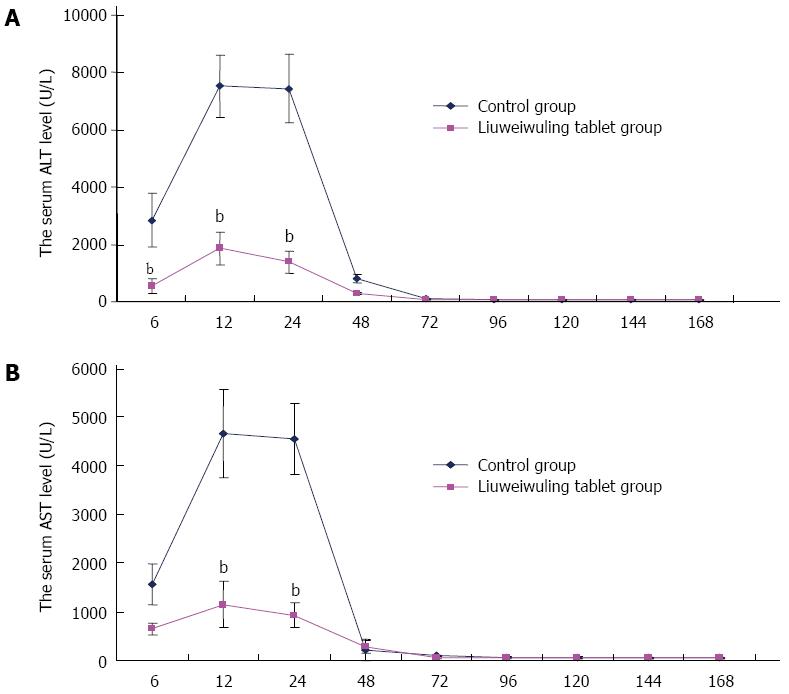
Figure 1 Liuweiwuling tablets significantly decrease serum alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransaminase levels in mice with acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury.
A: The levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in the Liuweiwuling tablet group were decreased significantly at 6, 12 and 24 h compared with the control group (t = 8.20, 15.89 and 16.76, respectively; bP < 0.01 vs control); B: The levels of aspartate aminotransaminase (AST) in the Liuweiwuling tablet group were also decreased significantly at 6, 12 and 24 h compared with the control group (t = 7.09, 11.75 and 16.28, respectively; bP < 0.01 vs control). The above experiments were repeated more than 3 times.
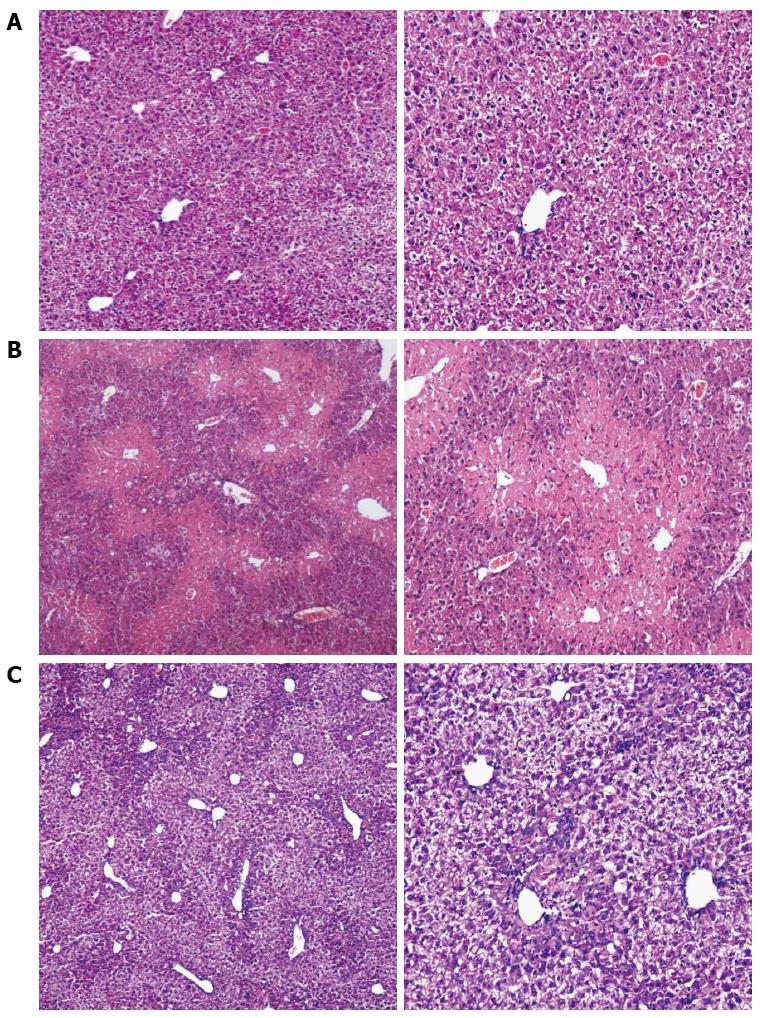
Figure 2 Influence of Liuweiwuling tablets on the central necrosis of hepatic lobules in mice with acute liver injury (magnification, × 10 and × 100, respectively).
A: Normal mice; B: Evident necrosis in the central hepatic lobule in the acute liver injury group; C: Slight necrosis in liver tissue in the Liuweiwuling tablet group.
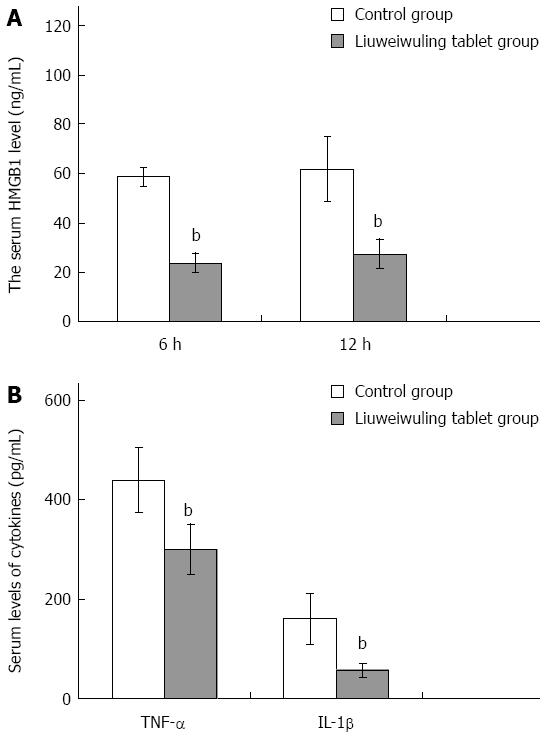
Figure 3 Liuweiwuling tablets decrease the level of high mobility group box protein B1, tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β in mice with acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury.
A: There is a significant difference between the Liuweiwuling tablet group and the control group in HMGB1 levels at 6 and 12 h (t = 22.82 and 8.29, respectively; bP < 0.01 vs control); B: The levels of TNF-α and IL-1β between the two groups were also significantly different at 12 h (t = 5.99 and 6.88, respectively; bP < 0.01 vs control). The above experiments were repeated more than 3 times.
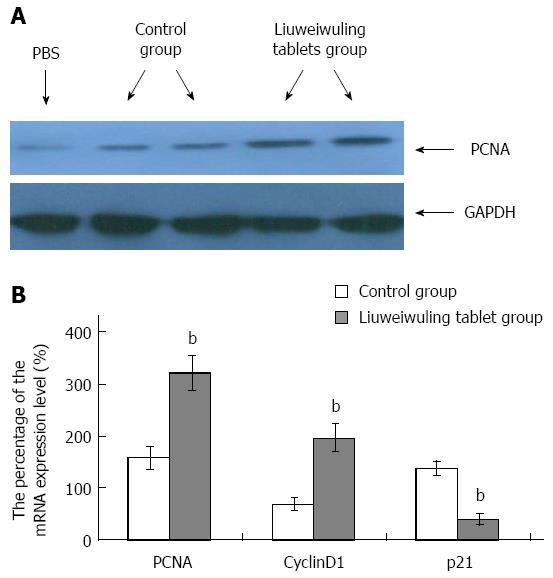
Figure 4 Liuweiwuling tablets accelerate liver regeneration in mice with acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury.
A: Immunoblotting assays were used to detect the expression of PCNA in different processes; B: Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction detection was used to detect mRNA expression. The levels of PCNA, CyclinD1 and p21 between the two groups were significantly different at 36 h (t = 14.37, 15.91 and 20.04, respectively; bP < 0.01 vs control). The above experiments were repeated more than 3 times and the results are expressed as percentages compared with the normal group.
- Citation: Lei YC, Li W, Luo P. Liuweiwuling tablets attenuate acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury and promote liver regeneration in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(26): 8089-8095
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i26/8089.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8089