Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2015; 21(25): 7916-7920
Published online Jul 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7916
Published online Jul 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7916
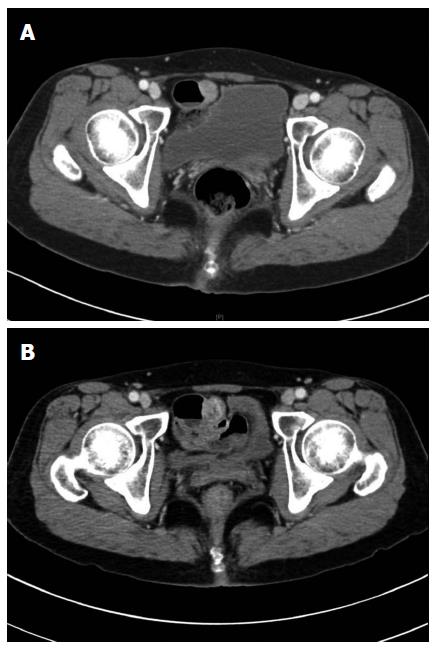
Figure 1 Abdominopelvic computed tomography in 2011 and B: 2014.
A: Contrast enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan shows 1.7 cm sized enhancing mass arising in small bowel; B: Follow up CT shows a slightly increased size to 2.2 cm and new appearance of low density areas in the mass suggests necrotic change.
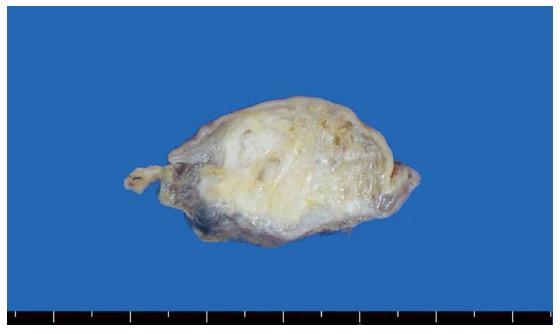
Figure 2 Cut surface shows a fibrotic and cystic lesion in the submucosa.
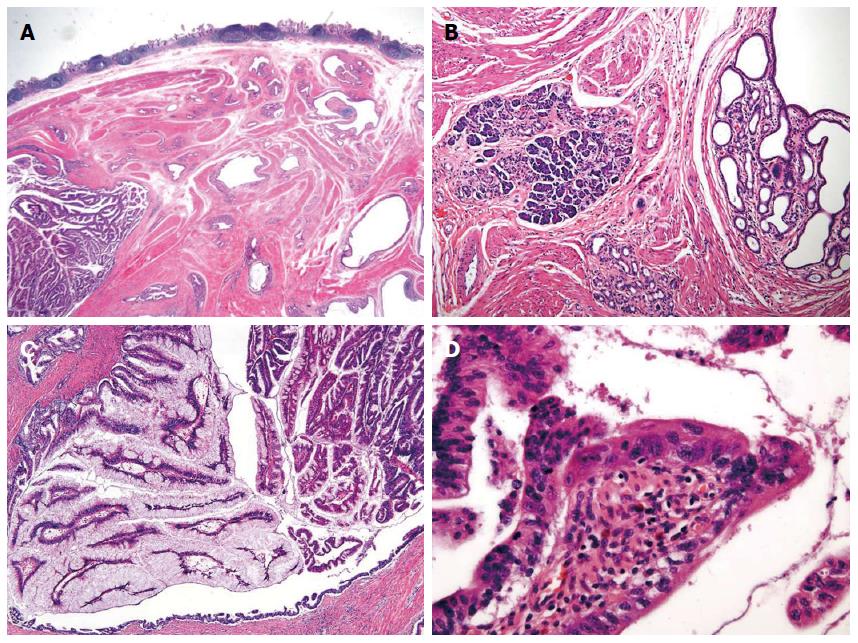
Figure 3 Microscopic findings.
A: Microscopic examination shows dilated ducts [hematoxylin-eosin (HE) stain, original magnification × 40] with B: pancreas acini (HE stain, original magnification × 100); C: The ducts are filled with papillary neoplasm. The epithelium is covered with tall columnar cells that have abundant intracytoplasmic mucin (HE stain, original magnification × 100); D: Some of the epithelial cells have enlarged nuclei with nucleoli and irregular nuclear membrane consistent with high grade nuclear atypia (HE stain, original magnification × 400).
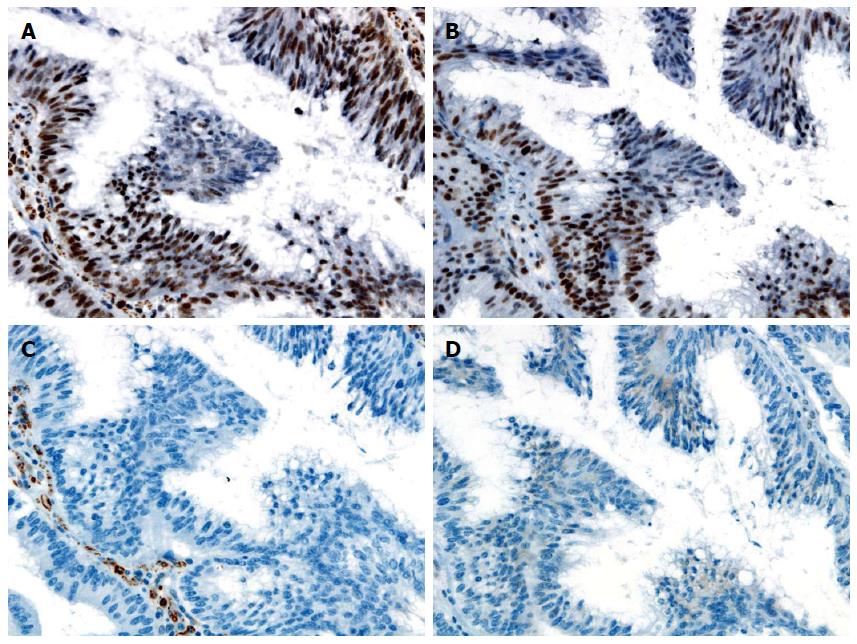
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical staining.
A: Immunohistochemical stain is positive for MLH1; B: PMS2; C: Negative for MSH2; D: MSH6. Magnification × 400 (A-D).
- Citation: Lee SH, Kim WY, Hwang DY, Han HS. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the ileal heterotopic pancreas in a patient with hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(25): 7916-7920
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i25/7916.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7916