Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2015; 21(25): 7860-7868
Published online Jul 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7860
Published online Jul 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7860
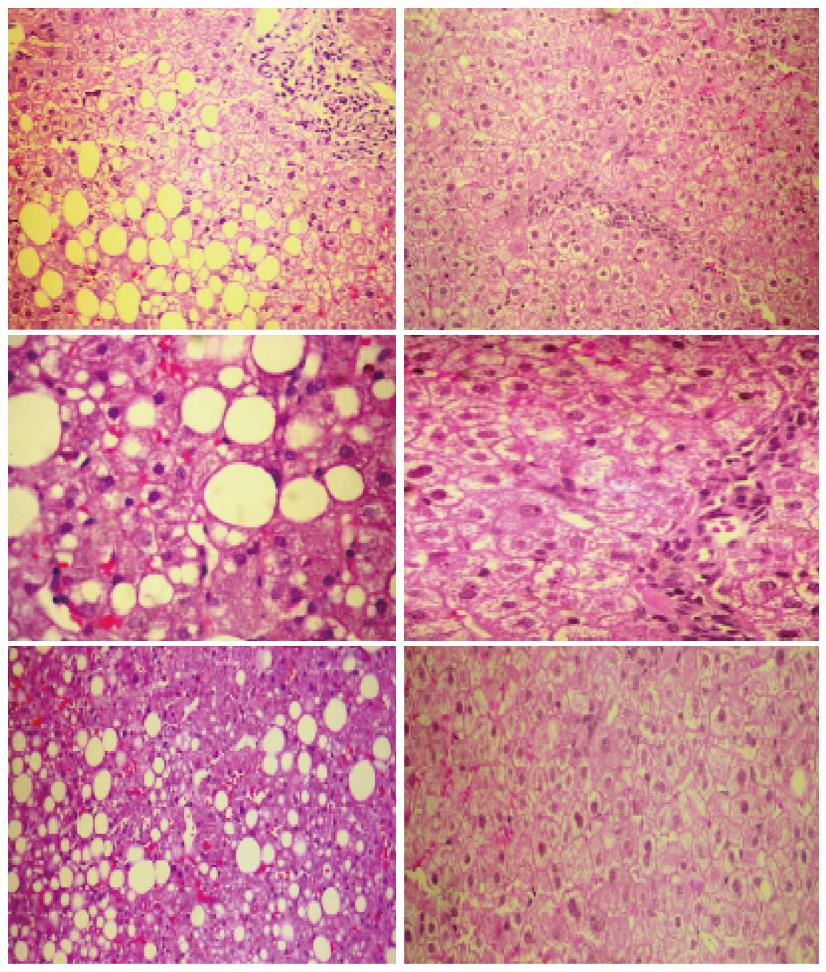
Figure 1 Presentation of the baseline and repeat liver biopsies in 3 metabolic syndrome patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis on rosuvastatin (10 mg/d) monotherapy for 12 mo.
On the left panel liver biopsies of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis presenting steatosis (fat content of the liver > 30%), hepatocyte ballooning degeneration, diffuse lobular mixed acute and chronic inflammation, and perivenular, perisinusoidal collagen disposition. On the right panel liver biopsies of the same 3 patients after one year monotherapy with 10 mg/d of rosuvastatin presenting total normal liver tissue.
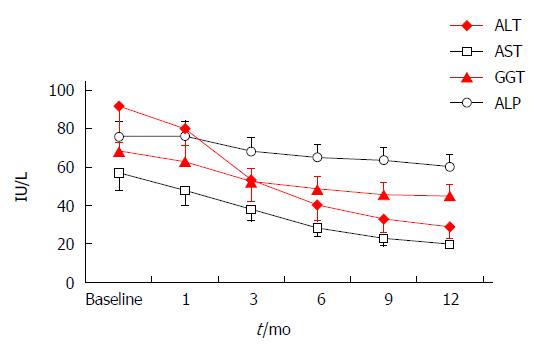
Figure 2 Liver enzyme changes in 20 patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis during the 12 mo of rosuvastatin (10 mg/d) monotherapy.
The reduction in serum alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST) and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) levels became statistical significant by the 3rd month of treatment (ANOVA for the 12 mo period P < 0.001) and for alkaline phosphatase (ALP) by the 6th mo of treatment (ANOVA for the 12 mo period P = 0.01).
- Citation: Kargiotis K, Athyros VG, Giouleme O, Katsiki N, Katsiki E, Anagnostis P, Boutari C, Doumas M, Karagiannis A, Mikhailidis DP. Resolution of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by rosuvastatin monotherapy in patients with metabolic syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(25): 7860-7868
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i25/7860.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7860