Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2015; 21(24): 7488-7494
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7488
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7488
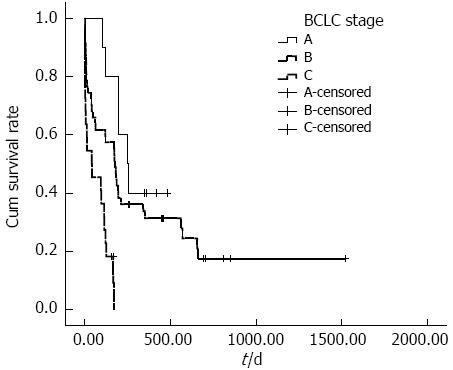
Figure 1 Cumulative survival according to Barcelona-Clinic Liver Cancer stage.
Cumulative survival rates of patients with ruptured HCC according to BCLC stage significantly differed; the median survival times of patients with HCC rupture and BCLC stage A, B and C disease were 251, 175 and 40 d, respectively (P < 0.001). BCLC: Barcelona-Clinic Liver Cancer; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
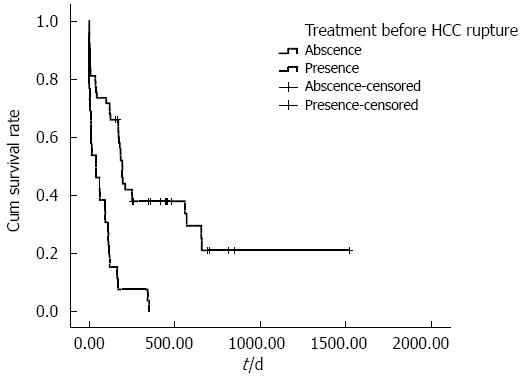
Figure 2 Cumulative survival according to treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma before tumor rupture.
The cumulative survival rate of patients who underwent anti-tumor therapy before HCC rupture was significantly reduced compared with patients who did not undergo therapy before HCC rupture. The mean survival time of patients receiving anti-tumor treatment before HCC rupture was 74.9 d, whereas the mean survival time of patients without therapy before HCC rupture was 492.3 d (P < 0.001). HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
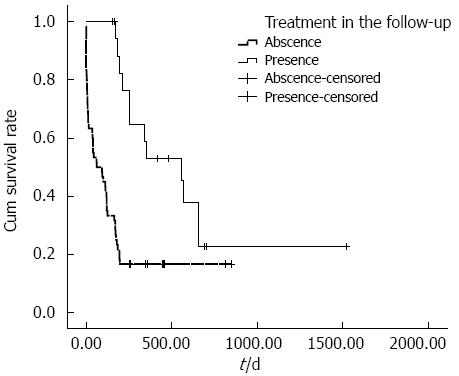
Figure 3 Cumulative survival according to further therapy after hepatocellular carcinoma rupture.
The cumulative survival rate of patients who underwent therapy after HCC rupture was significantly increased compared with patients who did not undergo therapy after HCC rupture. The mean survival time of patients with therapy during the follow-up period was 645.5 d, whereas the mean survival time of patients without therapy was 198.6 d (P < 0.001). HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Han XJ, Su HY, Shao HB, Xu K. Prognostic factors of spontaneously ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(24): 7488-7494
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i24/7488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7488