Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2015; 21(24): 7362-7366
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7362
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7362
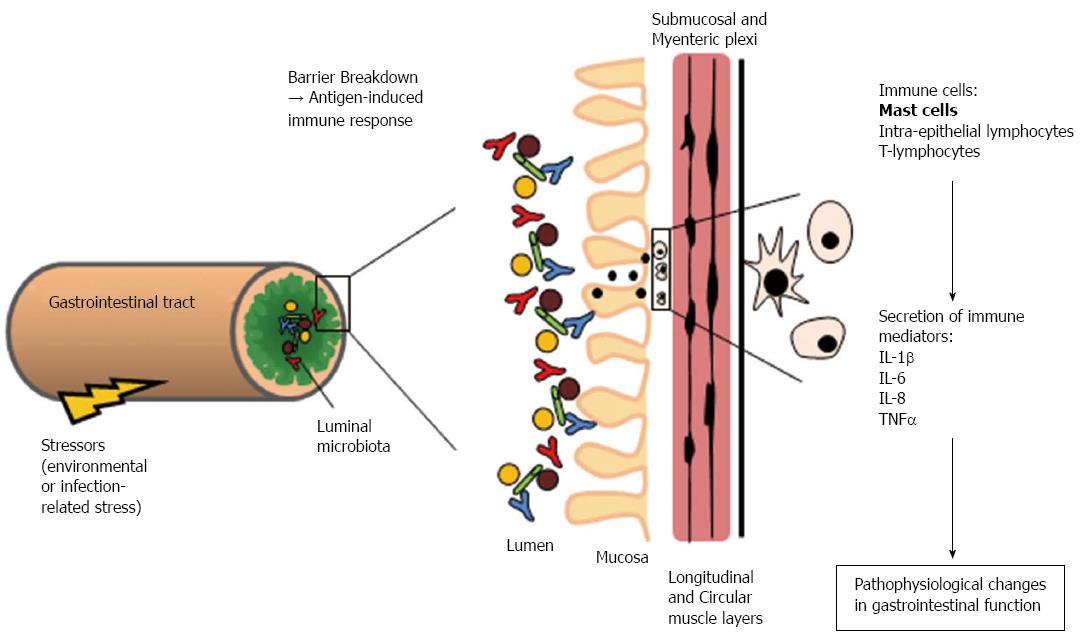
Figure 1 Illustrates a possible mechanism underlying symptom flares in irritable bowel syndrome.
Breach of the mucosal barrier as a result of activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and/or immune activation can stimulate an antigen-induced immune response. The primed gut has increased numbers of immune cells present which release cytokines that are associated with exacerbation of IBS symptoms. IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Citation: O’Malley D. Immunomodulation of enteric neural function in irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(24): 7362-7366
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i24/7362.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7362