Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2015; 21(22): 6892-6897
Published online Jun 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6892
Published online Jun 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6892
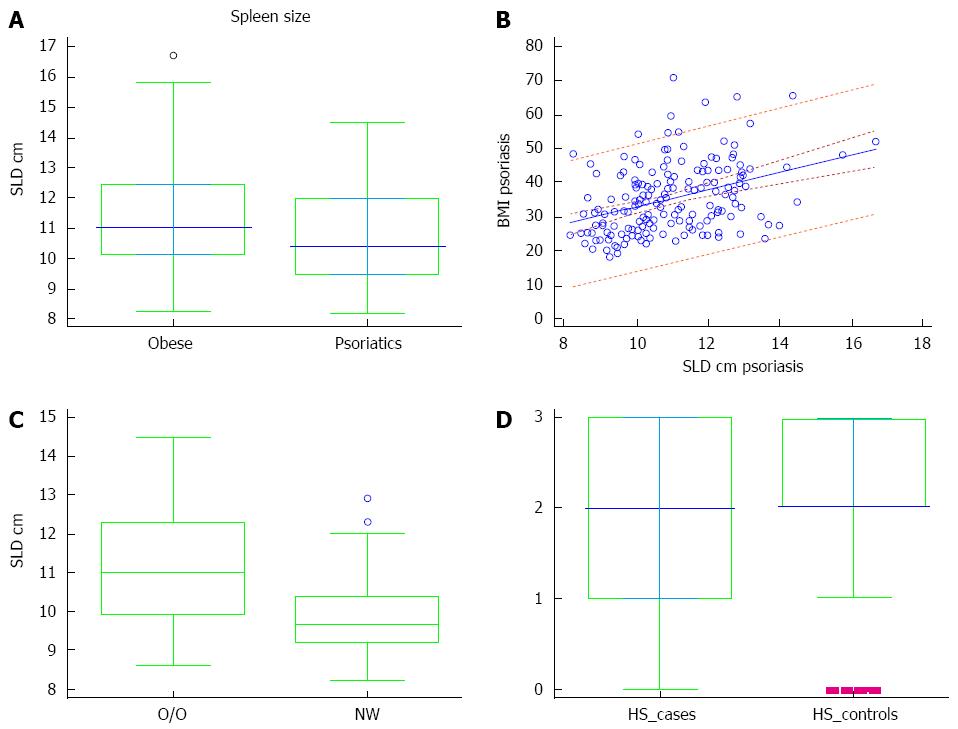
Figure 1 Spleen size, body mass index, and hepatic steatosis.
A: Spleen longitudinal diameter (SLD) in the psoriatic patients and obese controls; B: Prediction of body mass index (BMI) on SLD of patients with psoriasis (dotted lines near the regression line are the 95% confidence curves, the far ones are the 95% prediction curves); C: SLD in overweight/obese psoriatic patients (O/O) and normal weight (NW) psoriatic patients; D: Hepatic steatosis (HS) grade in patients (cases) and controls: grade 0 = absent; 1 = mild; 2 = moderate; 3 = severe. Boxes in A, C and D indicate the interquartile ranges and the transverse lines represent the median.
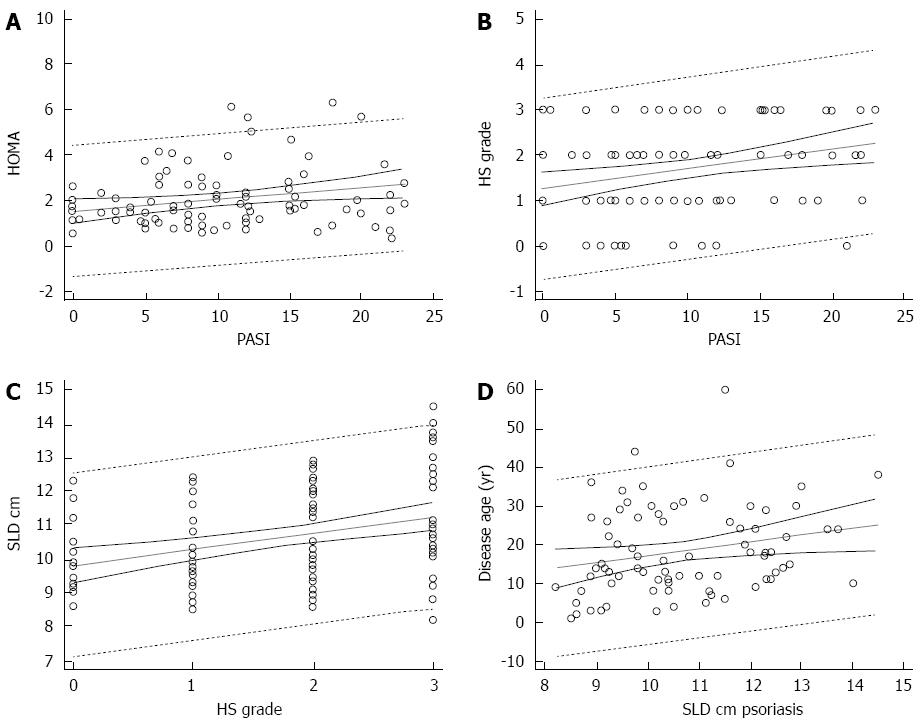
Figure 2 Insulin resistance, hepatic steatosis, spleen size, severity of psoriasis, and disease age of psoriatic patients.
A: Prediction of insulin resistance on severity of psoriasis; B: Prediction of hepatic steatosis (HS) on severity of psoriasis; C: Prediction of SLD on severity of psoriasis; D: Prediction of disease age of psoriatic patients on SLD. Dotted lines near the regression line are the 95% confidence curves, the far ones are the 95% prediction curves. HOMA: Homeostatic metabolic assessment; PASI: Psoriasis area and severity index; SLD: Spleen longitudinal diameter.
- Citation: Balato N, Napolitano M, Ayala F, Patruno C, Megna M, Tarantino G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, spleen and psoriasis: New aspects of low-grade chronic inflammation. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(22): 6892-6897
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i22/6892.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6892