Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2015; 21(17): 5220-5230
Published online May 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5220
Published online May 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5220
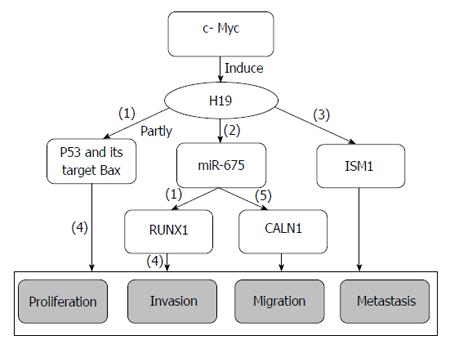
Figure 1 H19 regulating network in gastric cancer.
(1): Inhibitory effects; (2): H19 is treated as the precursor of miR-675; (3): H19 positively regulates its binding protein ISM1; (4): Promoting effects; (5): H19 regulates CALN1 indirectly by miR-675.
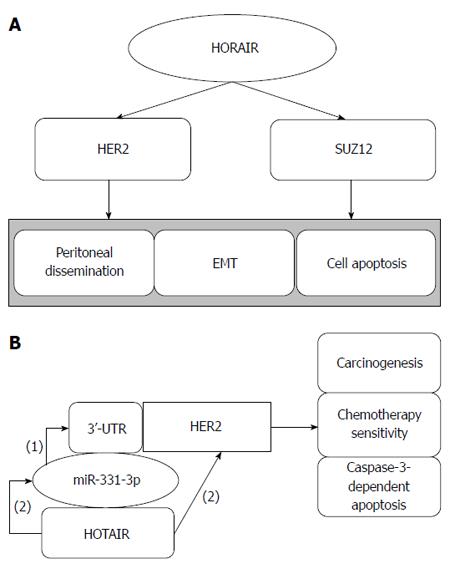
Figure 2 Hox transcript antisense intergenic RNA regulates gastric cancer metastasis and cell apoptosis by human epithelial growth factor receptor 2 and SUZ12 (A), and hox transcript antisense intergenic RNA acts as a ceRNA (B).
(1): miR-331-3p negatively regulates HER2 by binding to its 3’-UTR; (2): HOTAIR indirectly regulates HER2 by competitive binding to miR-331-3p.
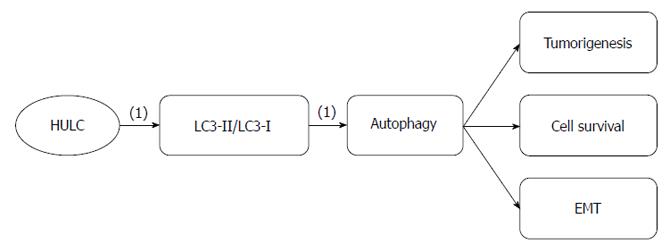
Figure 3 Highly upregulated in liver cancer regulatory roles in gastric cancer.
(1): Promoting effects. HULC: Highly upregulated in liver cancer.
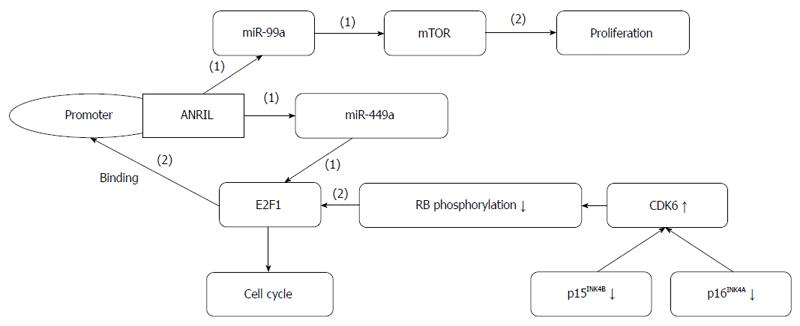
Figure 4 ANRIL forms a positive feedback loop with miR-449a and E2F1, and functions in gastric cancer.
(1): Inhibiting effects; (2): Promoting effects.
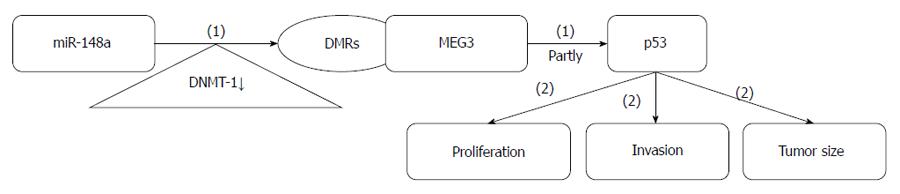
Figure 5 Maternally expressed gene 3 regulatory roles in gastric cancer.
(1) Promoting effects; (2) Inhibiting effects.
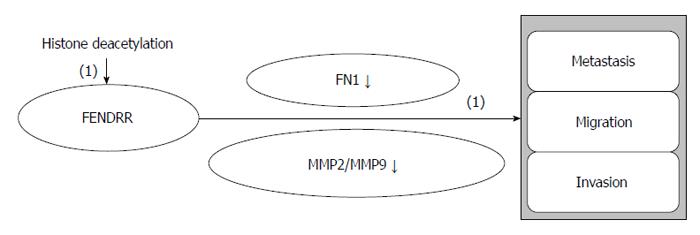
Figure 6 FENDRR regulatory roles in gastric cancer.
(1): Inhibiting effects.
- Citation: Yang ZG, Gao L, Guo XB, Shi YL. Roles of long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer metastasis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(17): 5220-5230
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i17/5220.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5220