Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2015; 21(16): 5023-5031
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.5023
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.5023
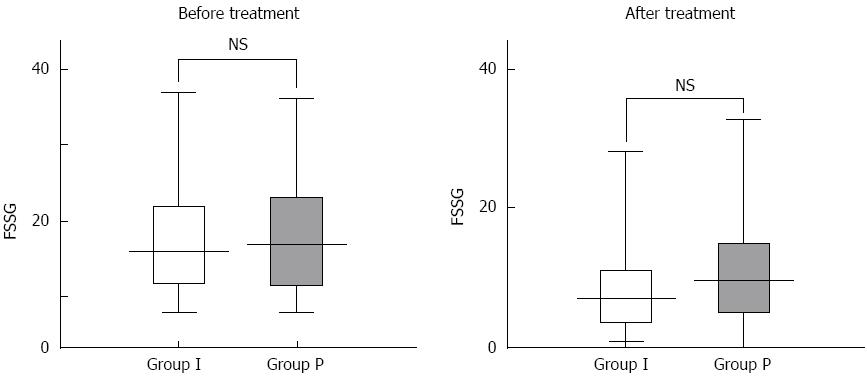
Figure 1 Total Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal reflux disease scores for groups I and P before and after four weeks of treatment.
Values are expressed as the mean ± SD. FSSG: Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal reflux disease; NS: Not significant.
Figure 2 Changes in the Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal reflux disease scores for groups I and P after four weeks of treatment.
Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviations. Significant differences were found between the groups. aP = 0.03 and bP = 0.01. FSSG: Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
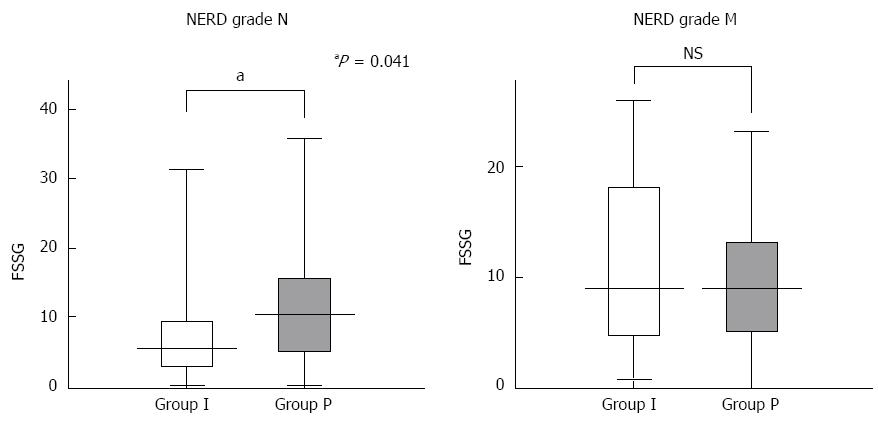
Figure 3 Comparisons of the total Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal reflux disease scores between the study groups in relation to the non-erosive reflux disease grades N and M after four weeks of treatment.
Values are expressed as the mean ± SD. FSSG: Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal reflux disease; NS: Not significant; NERD: Non-erosive reflux disease.
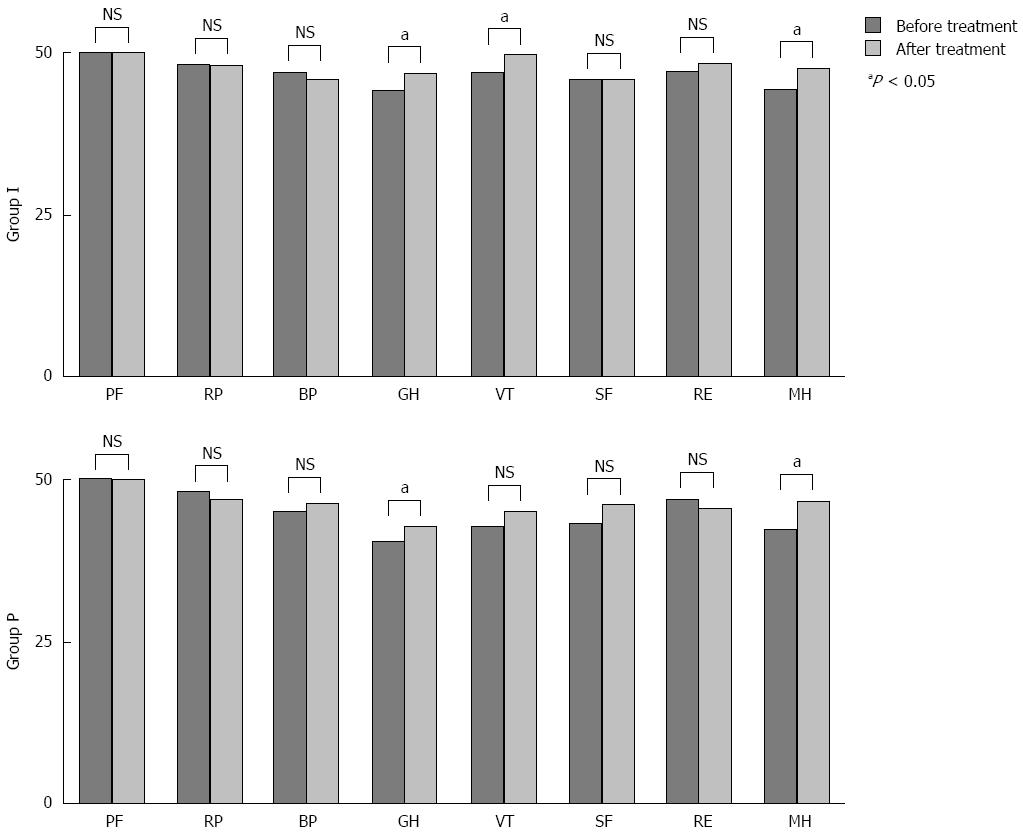
Figure 4 Quality of life assessment of patients in groups I and P before and after treatment using the Short Form-36 questionnaire.
PF: Physical functioning; RP: Role limitation-physical; BP: bodily pain; GH: General health; VT: Vitality; SF: Social functioning; RE: Role limitation-emotional; MH: Mental health; NS: Not significant.
Figure 5 Quality of life assessment of patients in groups I and P before and after treatment using the Short Form-36 questionnaire for non-erosive reflux disease grades N and M.
NERD: Non-erosive reflux disease; PF: Physical functioning; RP: Role limitation-physical; BP: bodily pain; GH: General health; VT: Vitality; SF: Social functioning; RE: Role limitation-emotional; MH: Mental health; NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Suzuki T, Matsushima M, Masui A, Tsuda S, Imai J, Nakamura J, Tsukune Y, Uchida T, Yuhara H, Igarashi M, Koike J, Mine T. Irsogladine maleate and rabeprazole in non-erosive reflux disease: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(16): 5023-5031
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i16/5023.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.5023