Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2015; 21(10): 3020-3029
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.3020
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.3020
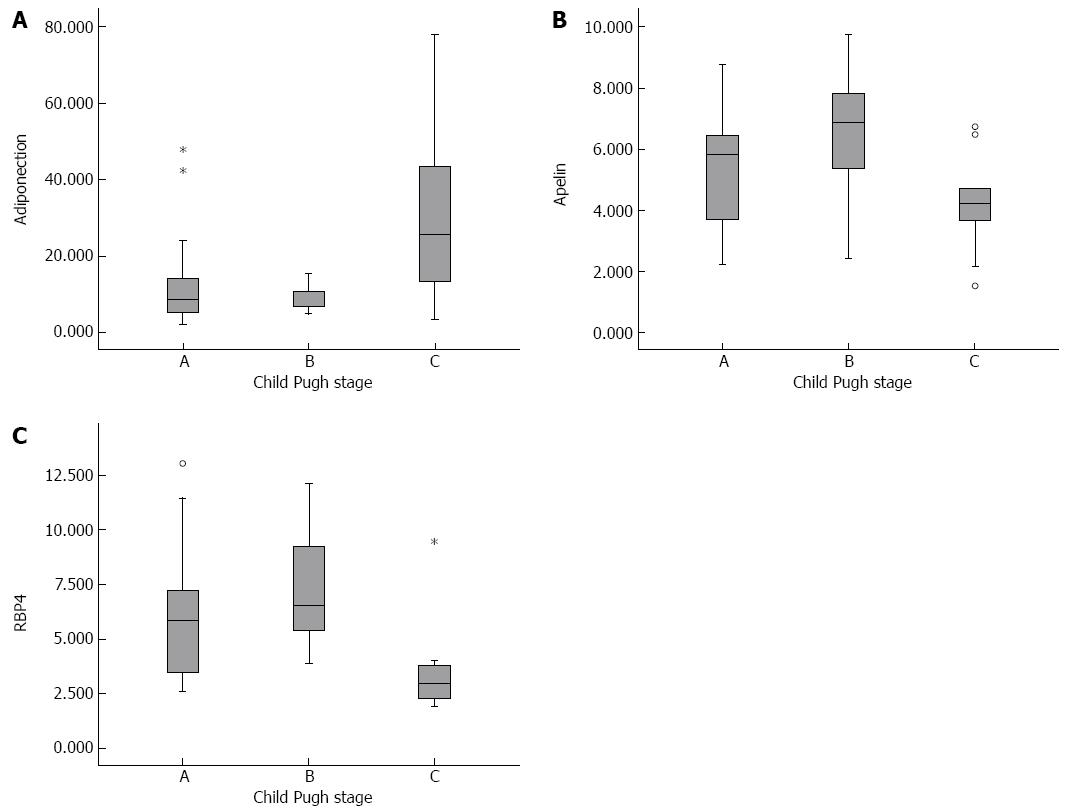
Figure 1 Box plots of adiponectin, apelin and retinol-binding protein 4 levels in relation to Child-Pugh stage in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis.
A: Adiponectin [Child-Pugh (CP) A: 7.99 ± 12.99, CP B: 7.66 ± 21.85, CP C: 25.73 ± 24.6, P = 0.04]; B: Apelin (CP A: 5.83 ± 2.23, CP B: 6.94 ± 2.36, CP C: 3.97 ± 1.78, P = 0.034); C: Retinol-binding protein 4 (CP A: 6.48 ± 3.2, CP B: 6.56 ± 3.37, CP C: 2.89 ± 2.07, P = 0.006).
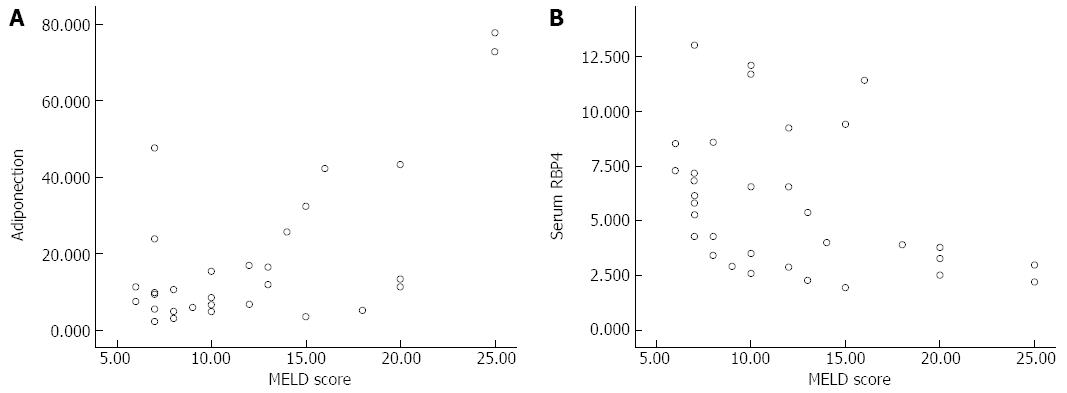
Figure 2 Correlation of serum adiponectin and retinol-binding protein 4 levels with Model for End-stage Liver Disease score in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis.
A: Adiponectin (r = 0.539; P < 0.001); B: Retinol-binding protein 4 (r = - 0.439; P = 0.006).
- Citation: Kalafateli M, Triantos C, Tsochatzis E, Michalaki M, Koutroumpakis E, Thomopoulos K, Kyriazopoulou V, Jelastopulu E, Burroughs A, Lambropoulou-Karatza C, Nikolopoulou V. Adipokines levels are associated with the severity of liver disease in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(10): 3020-3029
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i10/3020.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.3020