Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2015; 21(1): 333-341
Published online Jan 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.333
Published online Jan 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.333
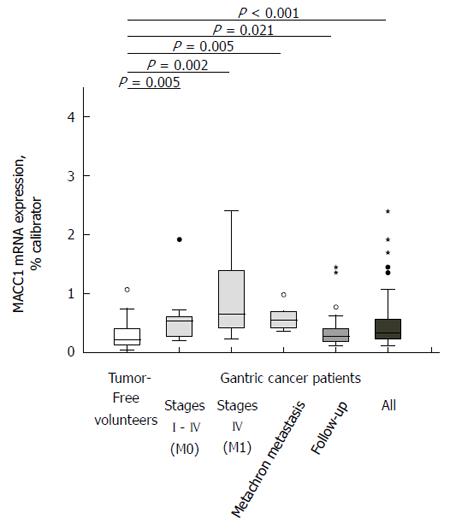
Figure 1 Circulating metastasis associated in colon cancer 1 transcript levels in plasma discriminate gastric cancer patients from tumor-free volunteers.
Levels of circulating metastasis associated in colon cancer 1 (MACC1) transcripts in plasma of all gastric cancer patients (n = 76) were significantly higher than in tumor-free volunteers (n = 54; P < 0.001). All patient subcohorts demonstrated significantly higher levels of circulating MACC1 transcripts when compared to the tumor-free volunteers: patients in stages I to IV (M0) (P = 0.005), patients in stage IV (M1) (P = 0.002), patients with metachronous metastasis (P = 0.005), and patients during follow-up (P = 0.021). Box plot analysis based on quantitative real-time RT-PCR.
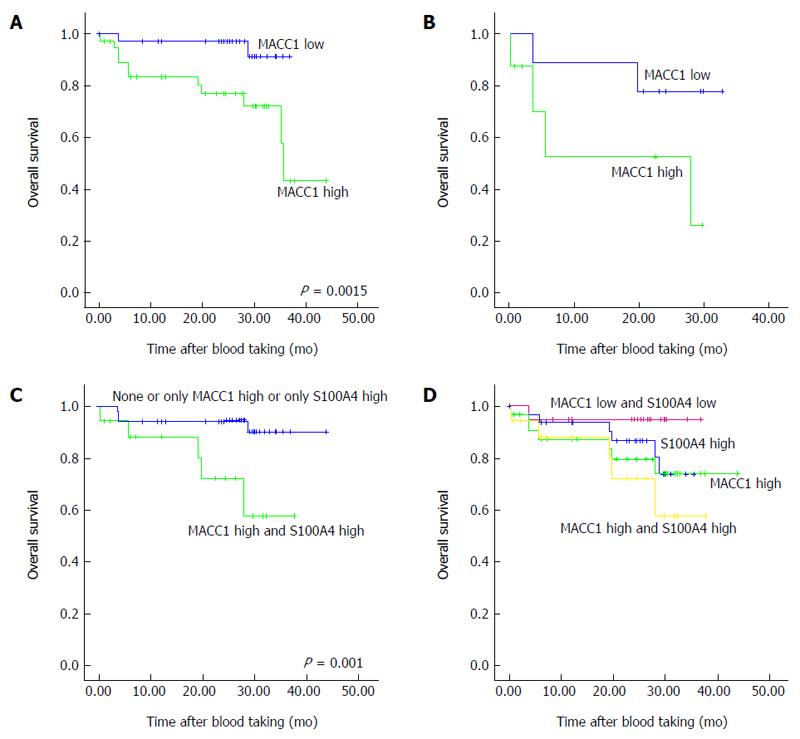
Figure 2 Overall survivals of gastric cancer patients.
A: Overall survival of gastric cancer patients based on circulating transcript levels of metastasis associated in colon cancer 1. Gastric cancer patients with high circulating metastasis associated in colon cancer 1 (MACC1) transcript levels in plasma demonstrated significantly shorter survival when compared with patients demonstrating low MACC1 levels (P = 0.0015). Kaplan-Meier analyses for all gastric cancer patients based on MACC1; B: Overall survival of patients with primary gastric cancer with or without synchronous metastasis based on circulating transcript levels of metastasis associated in colon cancer 1. Newly diagnosed gastric cancer patients with high circulating MACC1 transcript levels in plasma demonstrated shorter survival when compared with patients demonstrating low MACC1 levels. Kaplan-Meier analyses for newly diagnosed gastric cancer patients based on MACC1; C: Overall survival of gastric cancer patients with both markers metastasis associated in colon cancer 1 and S100A4 highly expressed vs none or only one marker highly expressed. Gastric cancer patients with high circulating transcript levels of MACC1 as well as S100A4 in plasma demonstrated significantly shorter survival when compared with patients demonstrating low levels of both biomarkers or with only one biomarker elevated (P = 0.001). Kaplan-Meier analyses for all gastric cancer patients based on MACC1 and S100A4; D: Overall survival of gastric cancer patients with both markers metastasis associated in colon cancer 1 and S100A4 highly expressed, only one or none marker highly expressed. Patients were classified into groups of low expressers of both genes, of patients with high S100A4 levels, of patients with high MACC1 levels, or with high expression of both biomarkers. Gastric cancer patients with high circulating transcript levels of MACC1 as well as S100A4 in plasma demonstrated shorter survival when compared with patients demonstrating low levels of both biomarkers or with only one biomarker elevated. Kaplan-Meier analyses for all gastric cancer patients based on MACC1 and S100A4.
- Citation: Burock S, Herrmann P, Wendler I, Niederstrasser M, Wernecke KD, Stein U. Circulating metastasis associated in colon cancer 1 transcripts in gastric cancer patient plasma as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(1): 333-341
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i1/333.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.333