Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2014; 20(8): 2071-2078
Published online Feb 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2071
Published online Feb 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2071
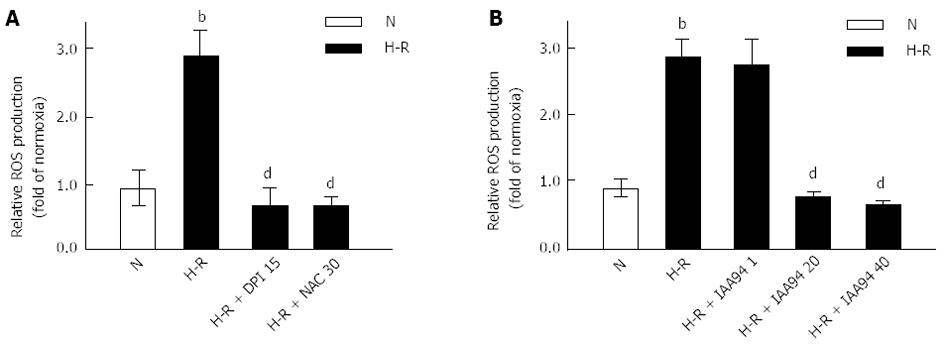
Figure 1 Increased reactive oxygen species production in LOVO cells under hypoxia-reoxygenation conditions.
LOVO cells were cultured in normoxia (N) for 24 h or under hypoxia for 4 h followed by reoxygenation for 20 h (hypoxia-reoxygenation, H-R). DPI (15 μmol/L), NAC (30 mmol/L) (A) and IAA94 at various concentration (1, 20, and 40 μmol/L) (B) decreased the reactive oxygen species production under H-R conditions. Results are expressed as fold of normoxia. Values represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. bP < 0.01 vs N group, dP < 0.01 vs H-R group. ROS: Reactive oxygen species; DPI: Diphenyleneiodonium; NAC: N-acetylcysteine.
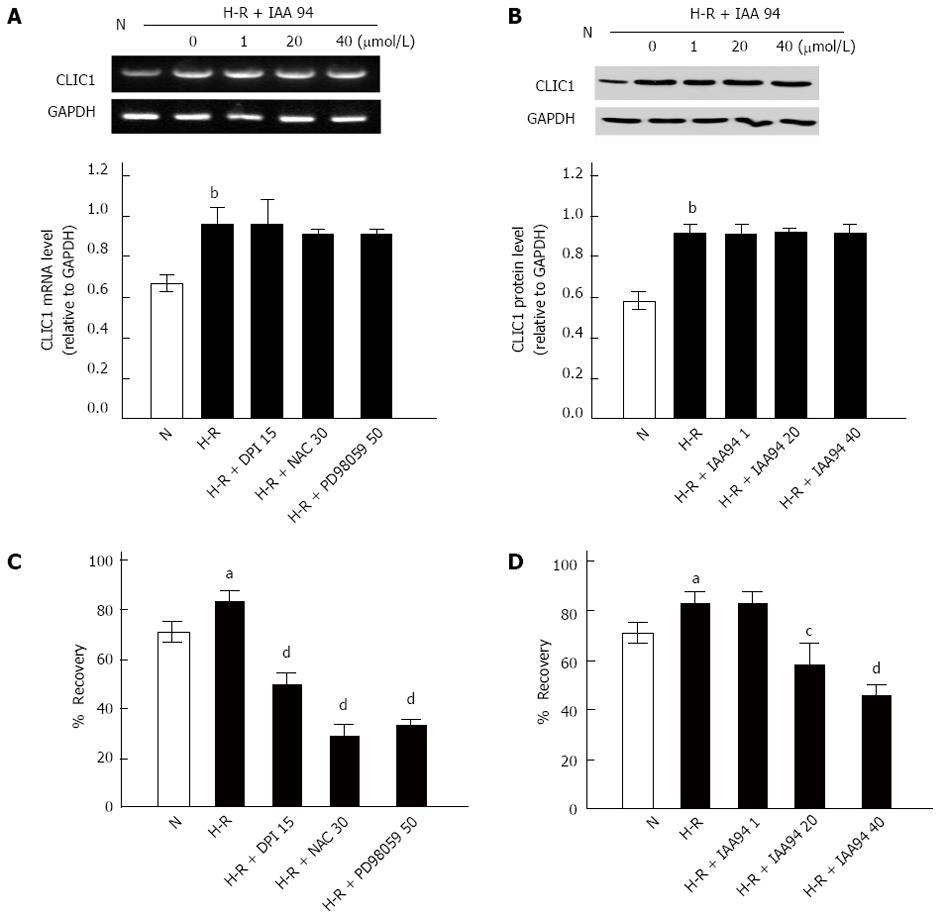
Figure 2 Effect of hypoxia-reoxygenation on the mRNA and protein expression of CLIC1 and wound healing assays in LOVO cells.
A, B: mRNA (A) and protein (B) expression of CLIC1 was significantly increased under hypoxia-reoxygenation (H-R) conditions as revealed by RT-PCR or Western blot analysis, respectively. Results were normalized to GAPDH; C, D: Wound recovery (%) of LOVO cells treated with DPI (15 μmol/L), NAC (30 mmol/L), PD98059 (50 μmol/L) or with IAA94 at various concentrations (1, 20 and 40 μmol/L) for 24 h under H-R conditions, respectively. Values represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs N group, cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs H-R group. DPI: Diphenyleneiodonium; RT-PCR: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
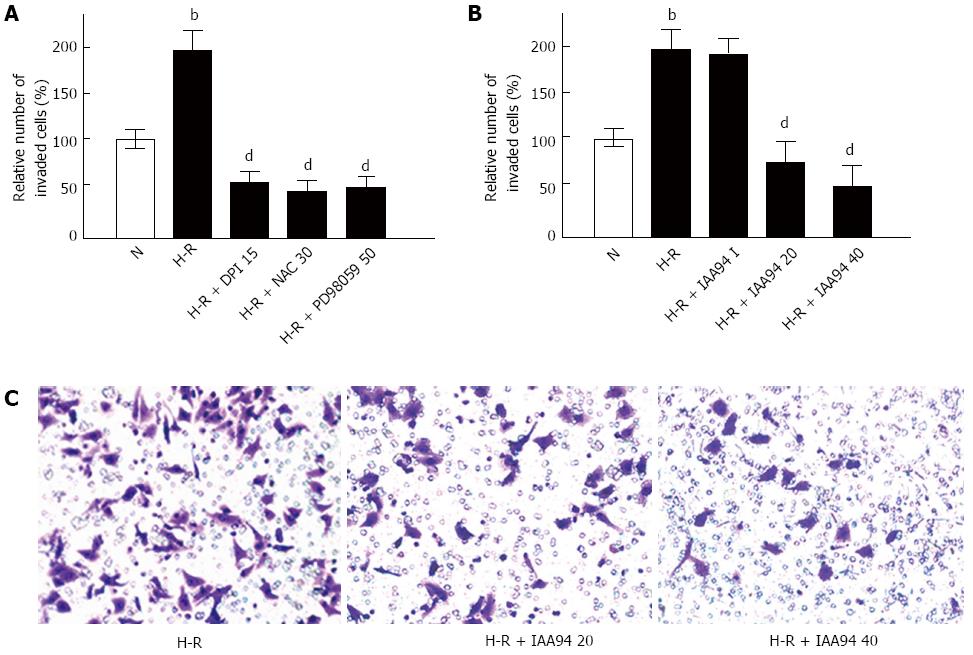
Figure 3 Effect of various treatments for 24 h on LOVO cell invasiveness under hypoxia-reoxygenation conditions.
A, B: Pretreatment with DPI (15 μmol/L), NAC (30 mmol/L), PD98059 (50 μmol/L) or with IAA94 at 20 and 40 μmol/L decreased the invasiveness of LOVO cells compared with H-R group. Results are expressed as fold of normoxia (N); C: LOVO cells incubated with IAA94 for 24 h under hypoxia-reoxygenation (H-R) conditions. The invaded cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet. Values represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. bP < 0.01 vs N group, dP < 0.01 vs H-R group. DPI: Diphenyleneiodonium.
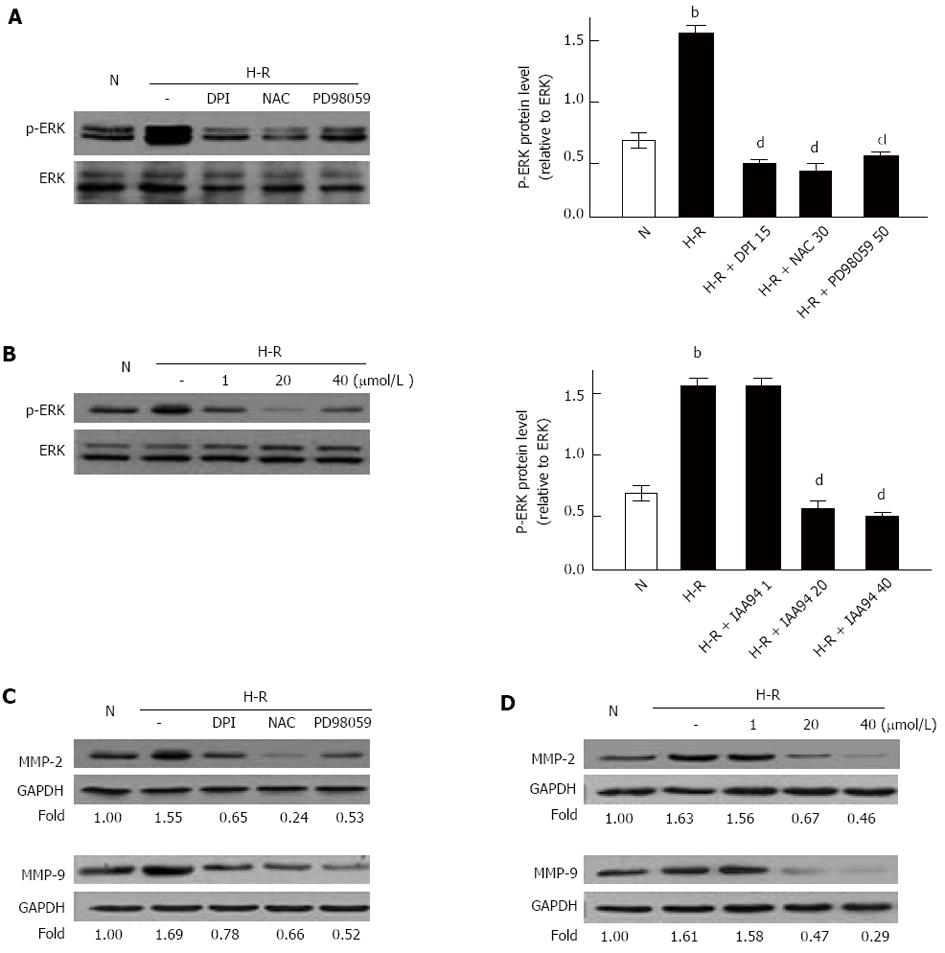
Figure 4 MEK/ERK/MMPs pathway involved in the metastasis of LOVO cells under hypoxia-reoxygenation conditions.
A, C: Treatment with DPI (15 μmol/L), NAC (30 mmol/L) or PD98059 (50 μmol/L) decreased the protein expression of p-ERK or MMP-2 and MMP-9 in LOVO cells compared with H-R group, respectively; B, D: Treatment with 20 and 40 μmol/L IAA94 also decreased the expression of p-ERK or the protein expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in LOVO cells, respectively. Results were normalized to GAPDH. Values represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. bP < 0.01 vs N group, dP < 0.01 vs hypoxia-reoxygenation (H-R) group.
- Citation: Wang P, Zeng Y, Liu T, Zhang C, Yu PW, Hao YX, Luo HX, Liu G. Chloride intracellular channel 1 regulates colon cancer cell migration and invasion through ROS/ERK pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(8): 2071-2078
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i8/2071.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i8.2071