Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2014; 20(7): 1701-1711
Published online Feb 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1701
Published online Feb 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1701
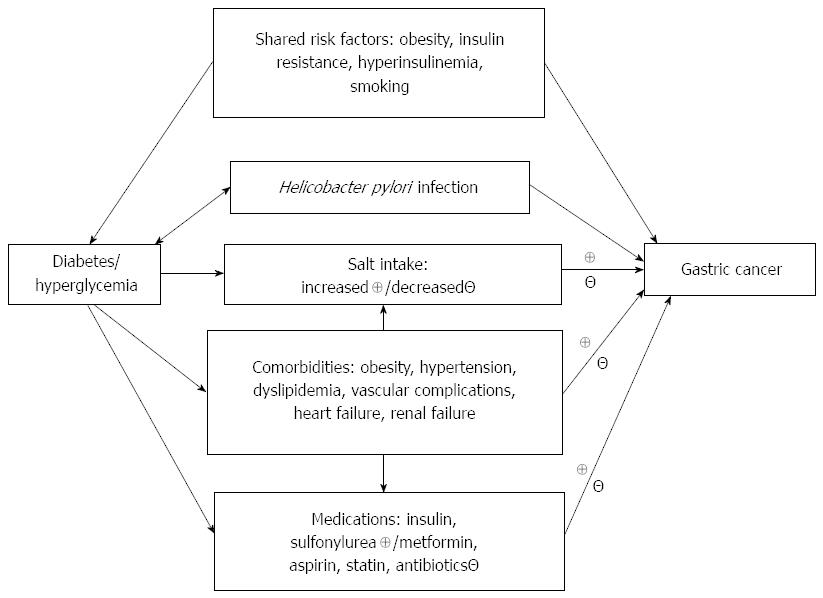
Figure 1 Putative mechanisms linking diabetes and gastric cancer (“⊕’” denotes a positive effect and “Θ“ denotes a negative effect).
A direct effect of hyperglycemia and a synergistic effect between salt intake and Helicobacter pylori infection are both possible but not shown in the dendrogram. Comorbidities may affect the development of gastric cancer, either positively or negatively, through the use of medications and changes in lifestyle, salt intake, dietary components, and the metabolism of drugs. A summary of the explanations on the links can be seen in Table 2.
- Citation: Tseng CH, Tseng FH. Diabetes and gastric cancer: The potential links. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(7): 1701-1711
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i7/1701.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1701