Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2014; 20(6): 1623-1625
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1623
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1623
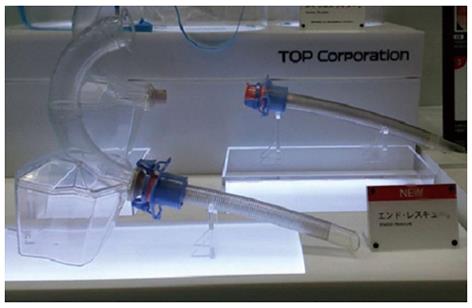
Figure 1 Outer appearance of the inverted overtube (TOP co.
, Tokyo, Japan).
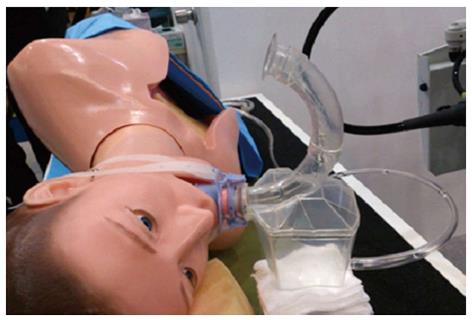
Figure 2 Simulated model in the right lateral position using the inverted overtube.
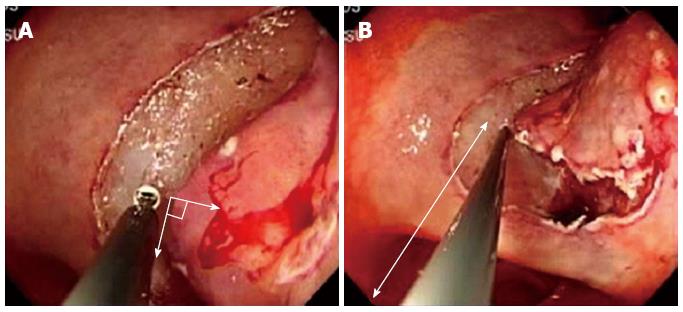
Figure 3 Conventional endoscopic submucosal dissection in left lateral position when pull (A) and push (B) the endoscope.
A: The electric knife is located vertically toward the gastric mucosa of the lower body of the lesser curvature of the anterior wall in the conventional left lateral position; B: The resected line is located farther from the endoscope, making it more difficult to approach.
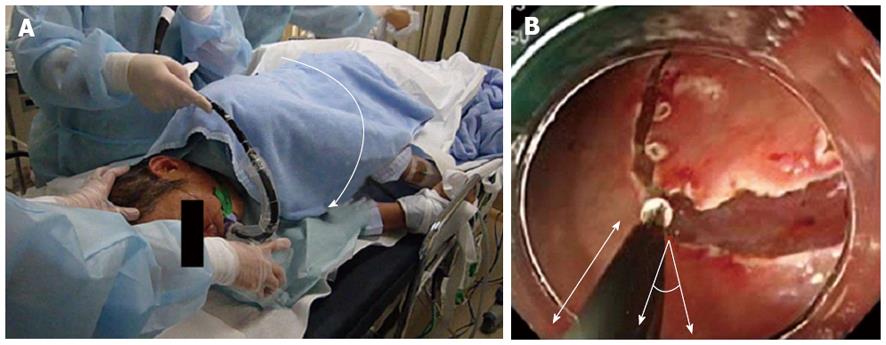
Figure 4 New right lateral position endoscopic submucosal dissection using gravity (A) and location and approach direction of electric knife the during right lateral endoscopic submucosal dissection (B).
A: The rotation of the patients to the right lateral position (curved arrow) allows the inverted overtube to be placed through the mouth; B: As the direction of gravity to the stomach changes, the angle between the electric knife and the gastric mucosa is decreased to approximately 20 degrees, and the mucosa is located closer to the endoscope.
- Citation: Mori H, Rafiq K, Kobara H, Nishiyama N, Fujihara S, Yachida T, Ayagi M, Tani J, Miyoshi H, Masaki T. An effective and safe gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection in the right lateral position using an inverted overtube. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(6): 1623-1625
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i6/1623.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1623