Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2014; 20(6): 1614-1622
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1614
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1614
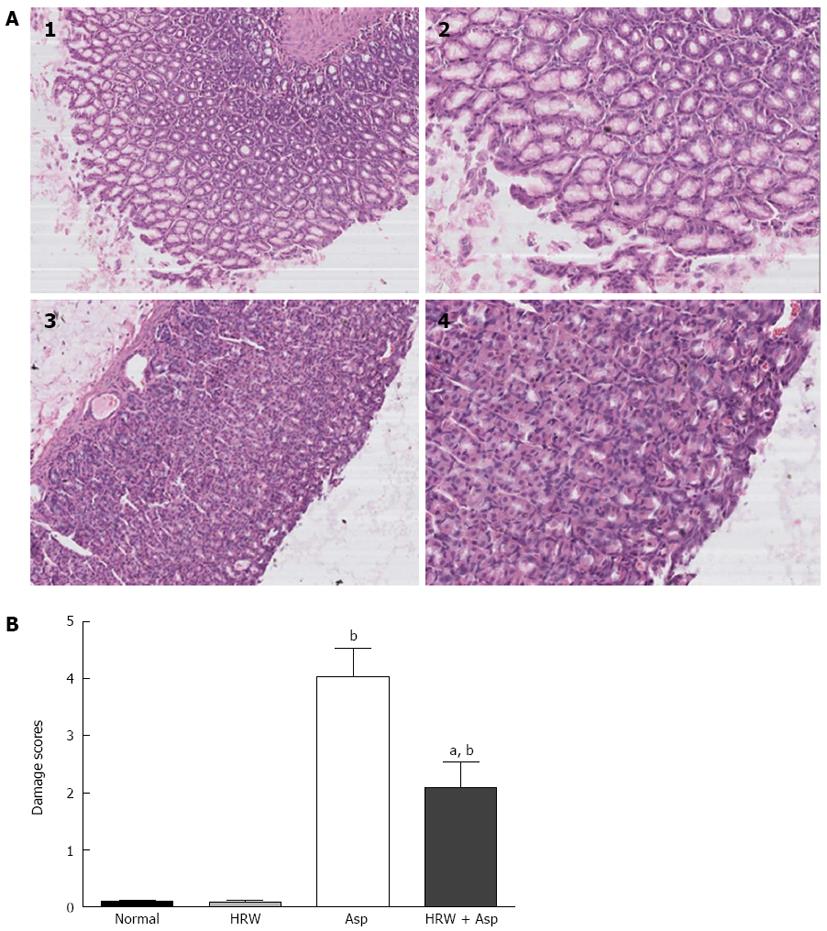
Figure 1 Histopathological examination of stomach sections.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin stained results showed severe degenerative changes in glandular region, epithelial folds and connective septa in aspirin-induced mucosal tissue (1, × 100 and 2, × 200), while hydrogen-rich water (HRW) pretreatment displayed slight changes (3, × 100 and 4, × 200); B: The gastric mucosal damage score in four groups. The mean scores are significantly higher in the aspirin group and HRW plus aspirin group (HRW + Asp) when compared with the normal control group and HRW alone group (bP < 0.01). Pretreatment with HRW could significantly decrease the damage score in HRW + aspirin group (Asp) group when compared with aspirin group (aP < 0.05).
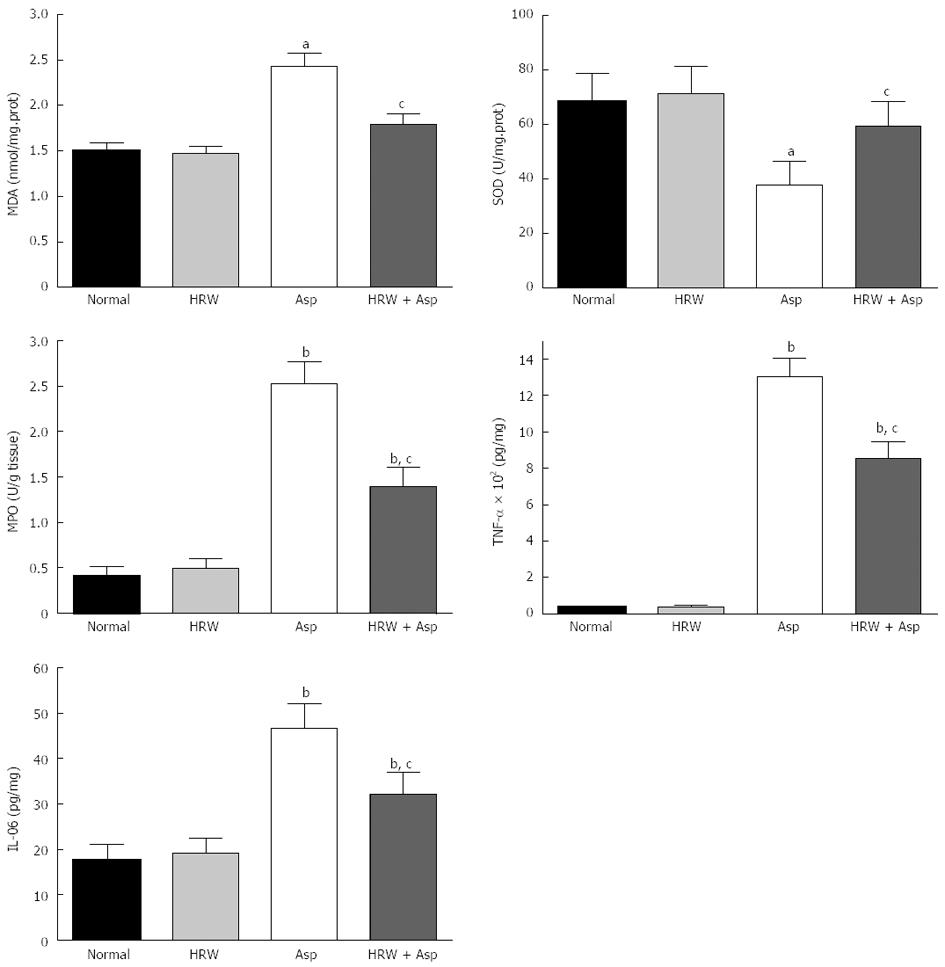
Figure 2 Levels of oxidative stress indicators and cytokines in all groups.
Malonaldehyde (MDA), myeloperoxidase (MPO), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and interleukin (IL)-06 in the gastric mucosal tissues are significantly higher, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels is obviously lower in aspirin group and hydrogen-rich water (HRW) plus aspirin group [HRW + aspirin group (Asp)] when compared with the normal control group and/or HRW alone group (bP < 0.01, aP < 0.05 when compared with the control and HRW groups). Pretreatment with HRW could significantly decrease the MDA, MPO, TNF-α, and IL-06 levels and increase the SOD activity in HRW + Asp group when compared with aspirin group (cP < 0.05).
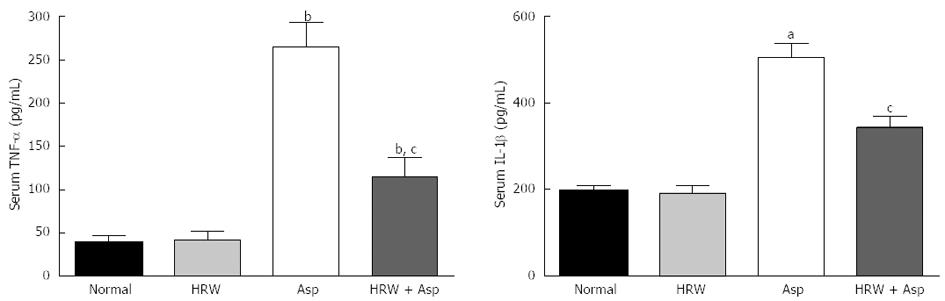
Figure 3 Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-Iβ levels in all groups.
All data are expressed as mean ± SD. The mean tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-Iβ levels are significantly higher in the aspirin group (Asp) and HRW plus aspirin group (HRW + Asp) when compared with the normal control group and/or HRW alone group (bP < 0.01, aP < 0.05 when compared with the control and HRW groups). And pretreatment with HRW could significantly decrease serum TNF-α and IL-Iβ levels in HRW + Asp group when compared with aspirin group (cP < 0.05). HRW: Hydrogen-rich water.
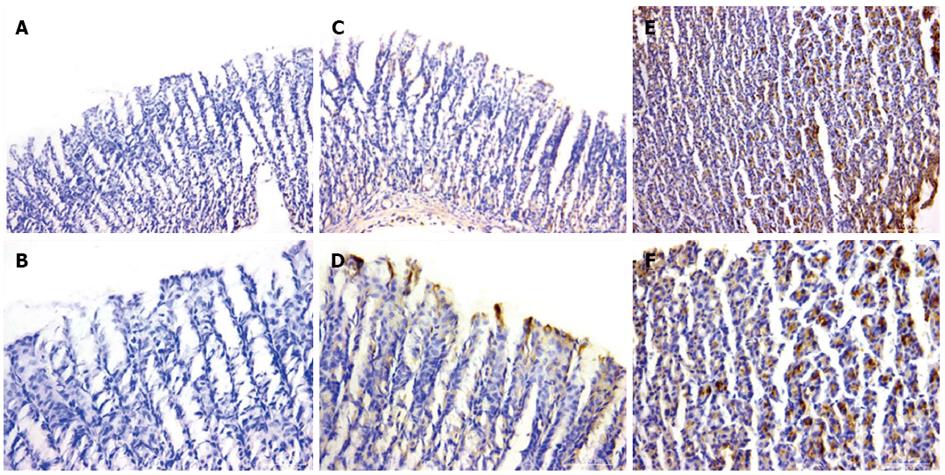
Figure 4 Immunolocalization of cyclooxygenase 2 in gastric tissue.
A, B: The results in the control group; C, D: A scarce cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) immunoreactivity in sub-glandular region of hydrogen plus aspirin-treated rats; E, F: An apparent COX-2 immunoreactivity in the glandular region and epithelial necks of stomach tissues of rats treated with aspirin (A, C, E: × 200 and B, D, F: × 400).
- Citation: Zhang JY, Wu QF, Wan Y, Song SD, Xu J, Xu XS, Chang HL, Tai MH, Dong YF, Liu C. Protective role of hydrogen-rich water on aspirin-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(6): 1614-1622
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i6/1614.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1614