Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2014; 20(48): 18458-18465
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18458
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18458
Figure 1 Study flow diagram.
MMC group: Modern medicine control group; “TQD” group: “Tonifying qi and detoxification” group. The group was treated with the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula “tonifying qi and detoxification” (“TQD”) as well as general internal medicine therapy; “TTK” group: “Tonifying the kidney to promote liver regeneration and repair by affecting stem cells and their microenvironment” group. The group was treated with the TCM formula “tonifying the kidney to promote liver regeneration and repair by affecting stem cells and their microenvironment” (“TTK”) as well as general internal medicine treatment.
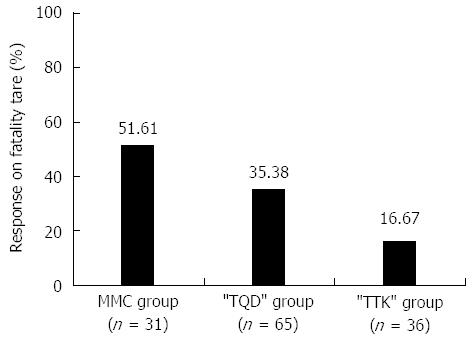
Figure 2 Fatality rates after 8-wk treatment and at 48-wk follow-up%.
The figure showed the fatality rates of three groups: the fatality rate was lowest in the “TTK” group (16.67%); the fatality rate in the “TTK” group was significantly lower than those in the MMC group (16.67% vs 51.61%, P = 0.002) and “TQD” group (16.67% vs 35.38%, P = 0.046).
- Citation: Li HM, Ye ZH, Zhang J, Gao X, Chen YM, Yao X, Gu JX, Zhan L, Ji Y, Xu JL, Zeng YH, Yang F, Xiao L, Sheng GG, Xin W, Long Q, Zhu QJ, Shi ZH, Ruan LG, Yang JY, Li CC, Wu HB, Chen SD, Luo XL. Clinical trial with traditional Chinese medicine intervention ''tonifying the kidney to promote liver regeneration and repair by affecting stem cells and their microenvironment'' for chronic hepatitis B-associated liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(48): 18458-18465
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i48/18458.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18458