Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2014; 20(48): 18228-18239
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18228
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18228
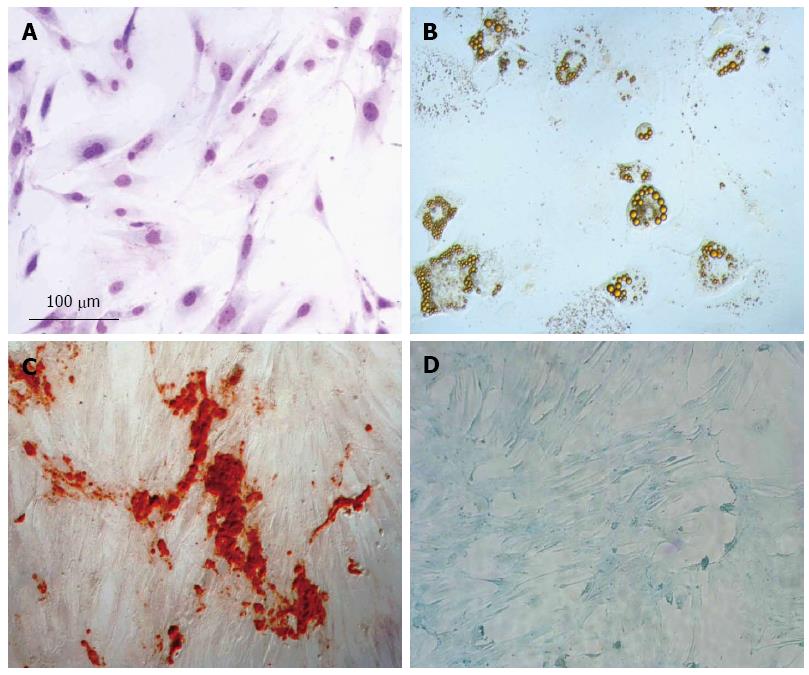
Figure 1 Mesenchymal stem cell characterization.
A: Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) morphology by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining; B: Adipogenic differentiation detected by Oil red, which stains lipid vacuoles; C: Osteogenic differentiation detected by Alizarin Red, which stains deposit of calcium; D: Chondrogenic differentiation, proteoglycans stained by Alcian blue.
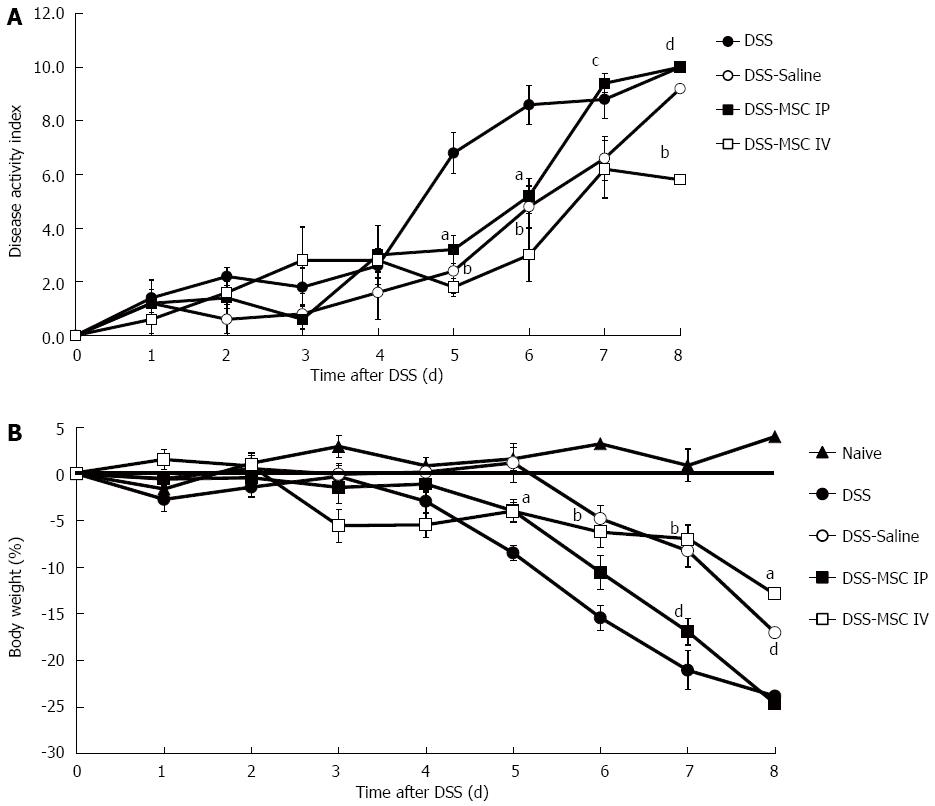
Figure 2 Intravenous mesenchymal stem cells transplantation protects against dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis.
A: Disease activity score. Clinical evolution was monitored by weight change, stool consistency and presence of fecal blood; B: Weight loss. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs DSS group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs DSS-MSC IV group, n = 5 mice/group. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
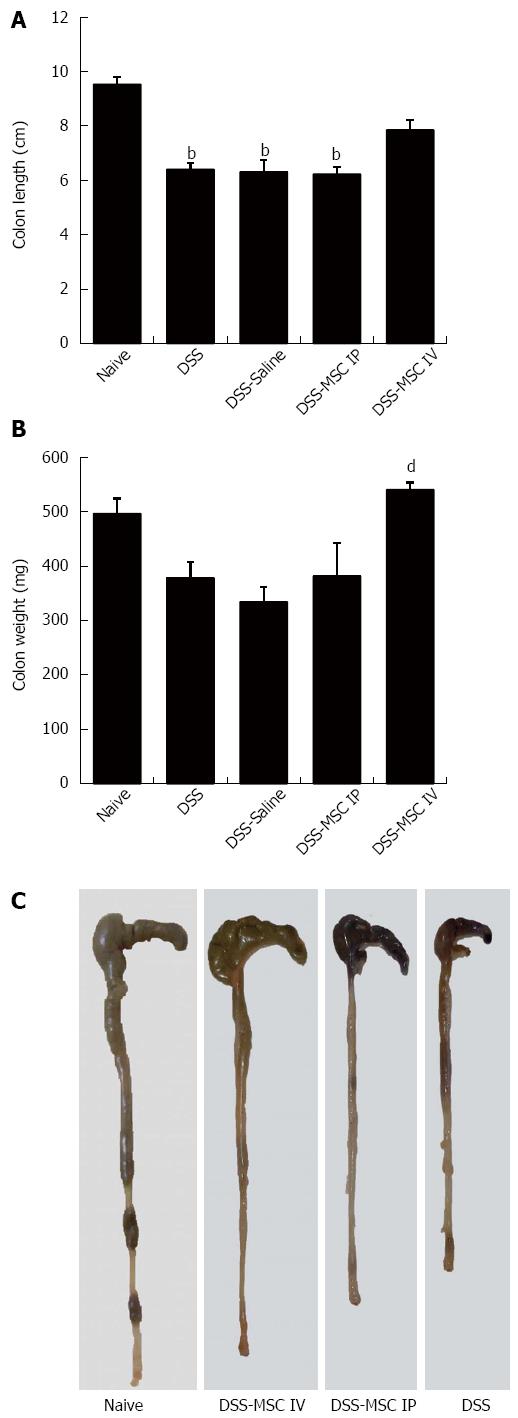
Figure 3 Mice treated with mesenchymal stem cells presented macroscopic colon characteristics similar to healthy animals.
A: Colon length. DSS, DSS-Saline and DSS-MSC IP groups showed a colon length significantly lower than the Naive group; B: Colon weight. DSS-MSC IV group showed significant difference in colon weight compared to DSS group; C: Representative image showing the difference in length between the colons submitted to different treatments. bP < 0.01 vs Naive group; dP < 0.01 vs DSS group, n = 5 mice/group. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
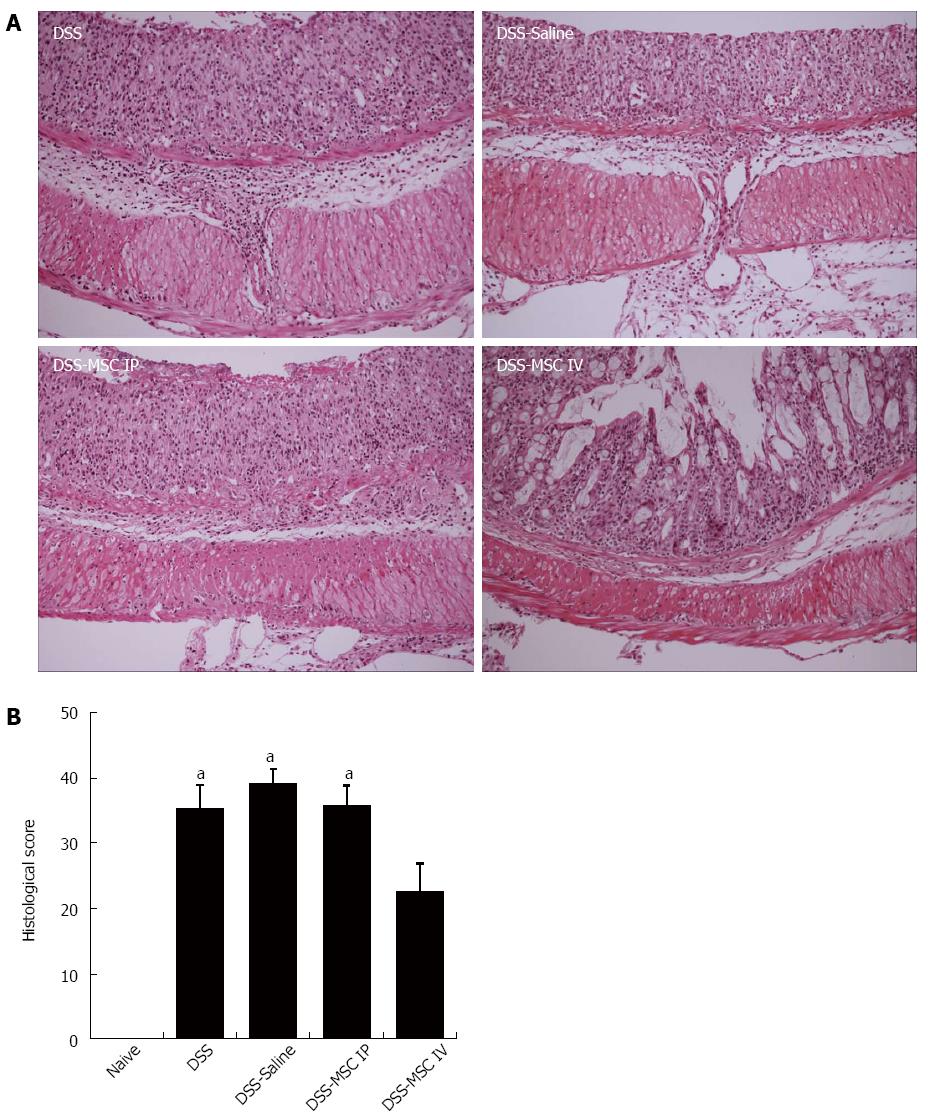
Figure 4 Mesenchymal stem cells administered by intravenous injection promote histological improvement.
Colon histology demonstrated intravenously administered mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) treatment reduced the extent of the inflamed area, crypt damage and infiltration of inflammatory cells. A: Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. Scale bar: 200 μm; B: Histological score of colitis. aP < 0.05 vs Naive group, n = 5 mice/group.
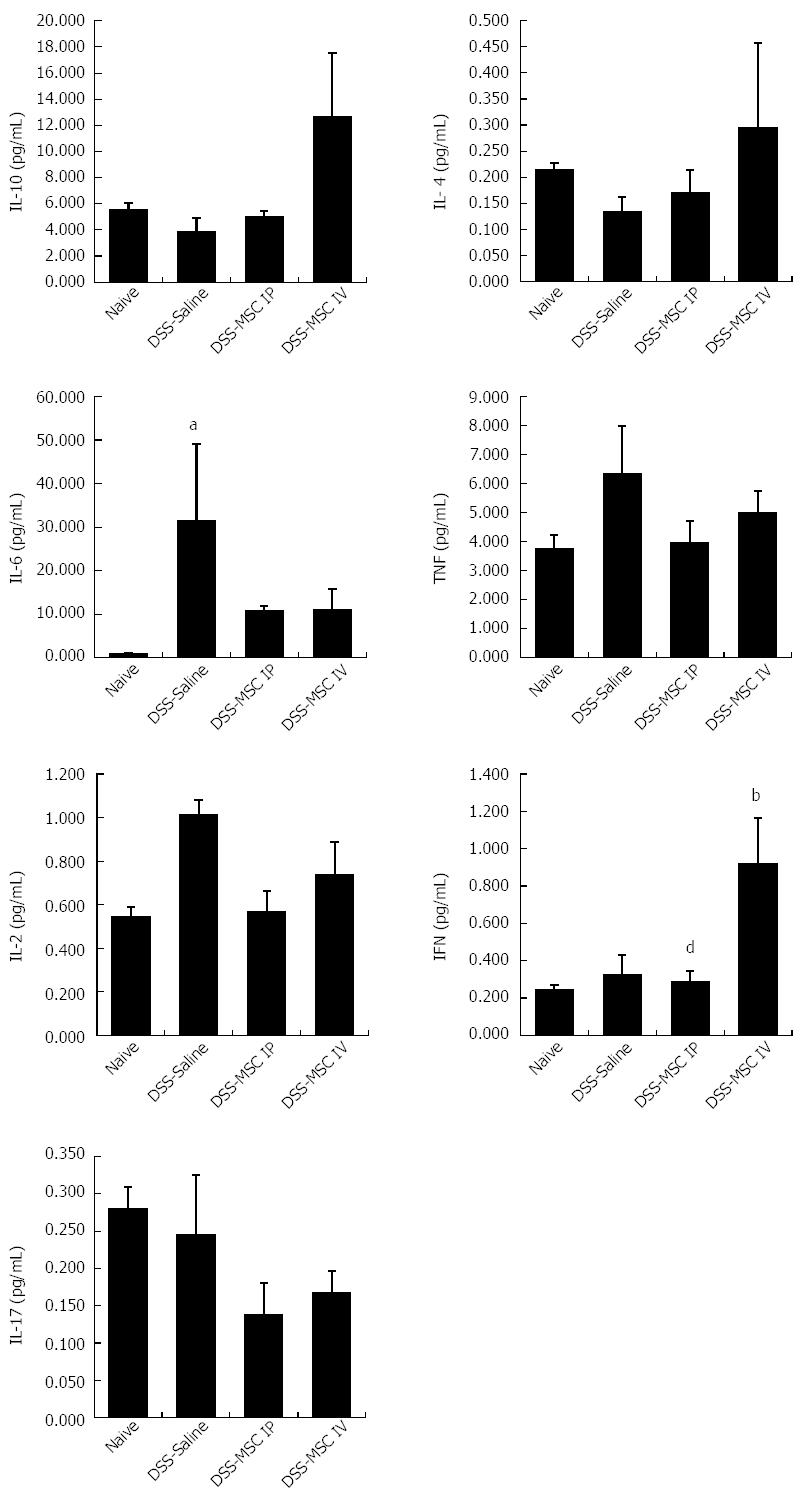
Figure 5 Treatment with mesenchymal stem cells can modulate colonic inflammatory responses in dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis.
There was a tendency for MSC treatment to increase levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-4. Acute DSS colitis demonstrated significantly elevated IL-6 levels, as well as a trend toward higher levels of TNF. Treatment with MSCs appears to decrease the levels of these pro-inflammatory cytokines. IFN levels in the DSS-MSC IV group were significantly higher than in the DSS-MSC IP group. Levels of IL-2 and IL-17 were similar between the groups. bP < 0.01 vs Naive group; dP < 0.01 vs DSS-MSC IV group, n = 5 mice/group. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
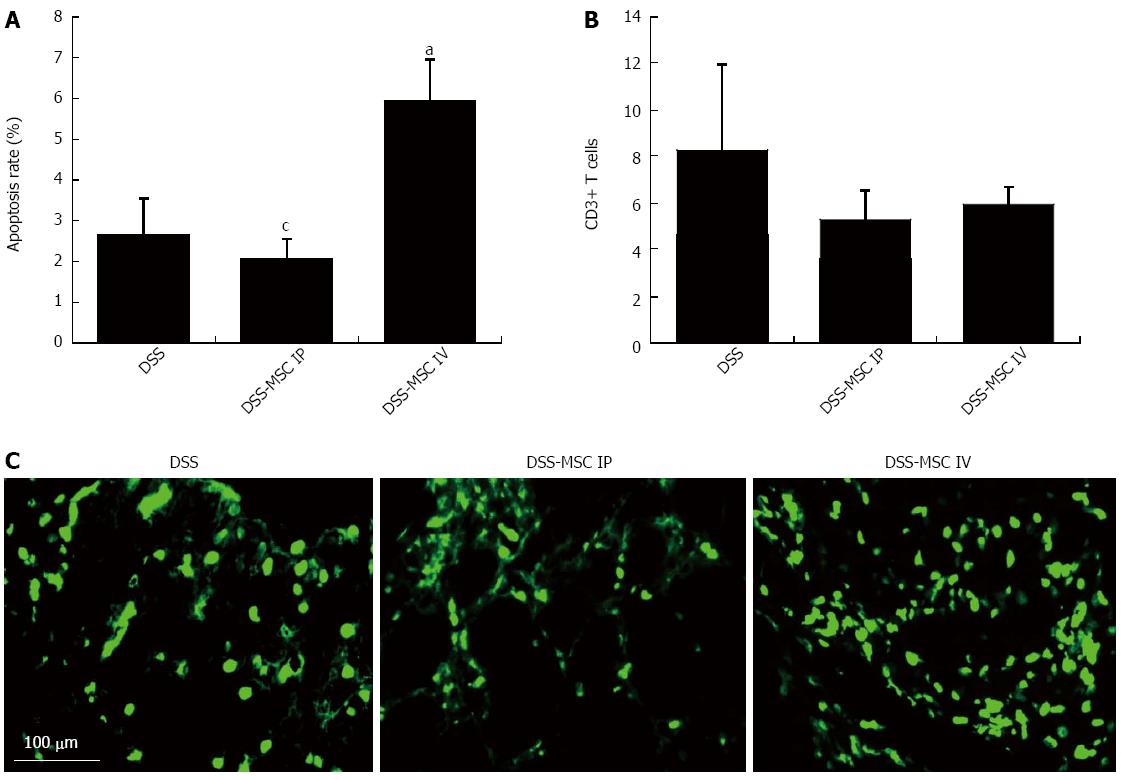
Figure 6 Intravenous administration of mesenchymal stem cells induced T cell apoptosis.
A: Apoptosis rate. TUNEL-positive mononuclear cells were significantly more frequent in the DSS-MSC IV group when compared to the DSS-MSC IP and DSS groups; B: Apoptotic T cells were detected by immunohistochemical staining with anti-CD3 antibody; C: TUNEL assay showing fluorescent apoptotic cells after DSS administration. aP < 0.05 vs DSS group; cP < 0.05 vs DSS-MSC IV, n = 5 mice/group. Scale bar: 100 μm. TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUDP-biotin nick end labeling; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
-
Citation: Gonçalves FDC, Schneider N, Pinto FO, Meyer FS, Visioli F, Pfaffenseller B, Lopez PLDC, Passos EP, Cirne-Lima EO, Meurer L, Paz AH. Intravenous
vs intraperitoneal mesenchymal stem cells administration: What is the best route for treating experimental colitis? World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(48): 18228-18239 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i48/18228.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18228